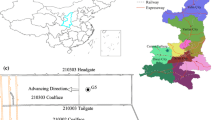
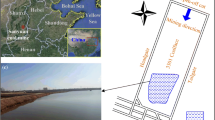
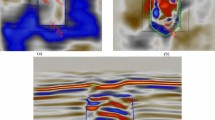
Abstract
A method to calculate the height of a water-conducting fractured zone (HWCFZ) was developed based on the plate and shell theory, and the development of the HWCFZ in bedrock and Q2l loess strata is discussed in detail. First, the subsidence-deflection curve equation of the overlying stratum is theoretically derived, and then the ultimate deflection and free space height of rock strata are calculated. Moreover, the strata tensile strain is calculated by using integral calculus. In addition, the failure state of the rock is analyzed by comparing the theoretically calculated tensile strain with the experimentally measured yield tensile strain, allowing one to attain the maximum value of HWCFZ. This approach was tested at the Jinjitan coal mine; the theoretically predicted, experimentally measured, and numerically computed maximum HWCFZ values were 189.5, 187.3, and 188.5 m, respectively, demonstrating the accuracy of the proposed method. These results are highly significant for safe and environment-friendly coal mining in northwest Shaanxi, China.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde eine Methode zur Berechnung der Höhe einer Bergbau-induzierten, wasserführenden Störungszone (HWCFZ) entwickelt, basierend auf der Plate-Shell-Theorie. Außerdem wird die Entwicklung der HWCFZ im Muttergestein und in Q2l-Löss-Schichten detailliert diskutiert. Zunächst wurde die Gleichung für die Absenkungs-Auslenkungskurve der Deckschichten theoretisch abgeleitet. Anschließend wurden die finale Auslenkung und die Höhe der Hohlräume im Fels berechnet. Durch Integration wurde außerdem die Zugdehnung der Schichten berechnet. Ferner wurde durch Vergleich der theoretisch berechneten Zugdehnung mit der experimentell gemessenen Zugdehnung der Bruchzustand des Gesteins analysiert. Das erlaubt die Ermittlung des Maximums der HWCFZ. Dieser Ansatz wurde für das Jinjitan Kohlebergwerg getestet. Die Werte für theoretisch vorhergesagte, experimentell ermittelte und numerisch berechnete maximale HWCFZ betrugen 189.5, 187.3 bzw. 188.5 m. Das zeigt die Genauigkeit der vorgeschlagenen Methode. Diese Ergebnisse sind für den sicheren und umweltfreundlichen Kohleabbau in Nordwest-Shaanxi (China) sehr wichtig.
Resumen
Se desarrolló un método para calcular la altura de una zona fracturada conductora de agua (HWCFZ) basado en la teoría de las placas y las láminas; se discute en detalle, el desarrollo de la HWCFZ en el lecho rocoso y los estratos de loess Q2l. En primer lugar, la ecuación de la curva de subsidencia-deflexión del estrato suprayacente se derivó teóricamente y luego se calculó la deflexión final y la altura del espacio libre de los estratos de roca. Además, mediante el cálculo integral, se calculó la deformación por tracción de los estratos. Se analizó el estado de falla de la roca comparando la tensión de tensión calculada teóricamente con la tensión de tensión de rendimiento medida experimentalmente, lo que permite alcanzar el valor máximo de HWCFZ. Este enfoque fue probado en la mina de carbón Jinjitan; los valores máximos de HWCFZ teóricamente predichos, medidos experimentalmente y calculados numéricamente fueron 189,5, 187,3 y 188,5 m, respectivamente, lo que demuestra la precisión del método propuesto. Estos resultados son altamente significativos para la minería del carbón segura y cuidadosa del medio ambiente en el noroeste de Shaanxi, China.
抽象
在板壳理论基础上,提出一种导水裂隙带高度(HWCFZ)计算方法,讨论了导水裂隙带在基岩和Q2l黄土中的发展。首先,从理论上推导出上覆岩层的沉降-挠度曲线方程;然后,计算岩层的极限挠度和自由空间高度。用积分法计算岩层的拉应变。此外,通过拉伸应变的理论计算值与拉伸屈服应变的实测值对比,分析岩层破断状态,得到最大导水裂隙带高度(HWCFZ)。该方法被应用于金鸡滩煤矿,导水裂隙带高度的理论预测值、实测值和数值计算结果分别为189.5 m、187.3 m和188.5 m,验证了该预测方法的准确性。研究对实现陕北地区安全、环境友好型煤炭开采具有重要意义。








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam PJ, Paul LY (2000) Broadening the scope of mine water environmental impact assessment: a UK perspective. Environ Impact Assess Rev 20:85–96
Adhikary DP, Guo H (2014) Measurement of longwall mining induced strata permeability. Geotech Geol Eng 32(3):617–626
Andreas K, Nikola R (2011) Sustainable development of energy, water and environment systems. Water Resour Manag 25:2917–2918
Che XY, Hou EK, Xie XS, Chen T, Feng J (2016) Analysis on development height of water flowing fractured zone in coal seam mining. China Sci Pap 11(3):270–273 (in Chinese)
Cheng L, Wang T, Qi P, Li YH (2017) Investigation of waterproof pillar design under aquifer in Cu-Pb-Zn mining of Xinzhuang. Eng J Wuhan Univ 50(3):368–374 (in Chinese)
Comprehensive Group on Consultation and Research in the Field of Energy (2015) Strategic research on clean, efficient, sustainable exploitation and utilization of coal in China. Strat Study CAE 17(9):001–005 (in Chinese)
Fan GW, Zhang DS (2015) Mechanisms of aquifer protection in underground coal mining. Mine Water Environ 34(1):95–104
Gao YF, Huang WP, Liu GL, Zhang SF, Zhu QM, Den ZY (2012) The relationship between permeable fractured zone and rock stratum tensile deformation. J Min Saf Eng 29(3):301–306 (in Chinese)
Hu XJ, Li WP, Cao DT, Liu MC (2012) Index of multiple factors and expected height of fully mechanized water flowing fractured zone. J China Coal Soc. 37(4):613–620 (in Chinese)
Hu YB, Li WP, Wang QQ, Liu SL, Wang ZK (2019) Evolution of floor water inrush from a structural fractured zone with confined water. Mine Water Environ 38(2):252–260
Huang KZ (1987) Theory of plates and shells. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Liu TQ (1995) Influence of mining activities on mine rock mass and control engineering. J China Coal Soc 20(1):1–5 (in Chinese)
Liu Y (2018) Dynamic evolution and application of water conducting fractured zone during extraction of Jurassic coal seams in northern Shaanxi. Diss, China Univ of Mining and Technology
Liu B, He L, Luo L (2009) Numerical modeling on fluid-solid coupling for the waterproof coal pillar design. J Min Saf Eng 26(4):445-449,454 (Chinese)
Liu XS, Tan YL, Ning JG, Tian CL, Wang J (2015) The height of water-conducting fractured zones in longwall mining of shallow coal seams. Geotech Geol Eng 33(3):693–700
Liu SL, Li WP, Wang QQ (2018) Height of the water-flowing fractured zone of the Jurassic coal seam in northwestern China. Mine Water Environ 37:312–321
Liu Y, Liu QM, Li WP, Li T, He JH (2019) Height of water-conducting fractured zone in coal mining in the soil–rock composite structure overburdens. Environ Earth Sci 78(7):242
Lv GL, Yang L, Tian GJ, Zhang Y, Lv PT, Chen YB (2016) Detection and analysis of height of water flowing fractured zone in roof of fully mechanized caving face in deep and extra thick seam. China Coal 42(11):53–57 (in Chinese)
Majdi A, Hassani FP, Nasiri MY (2012) Prediction of the height of destressed zone above the mined panel roof in longwall coal mining. Int J Coal Geol 98:62–72
Miao XX, Cui XM, Wang JA, Xu JL (2011) The height of fractured water-conducting zone in undermined rock strata. Eng Geol 120:32–39
Palchik V (2003) Formation of fractured zones in overburden due to longwall mining. Environ Geol 44(1):28–38
Qian MG (2003) Key strata theory of strata control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Qian MG, Shi PW (2003) Mine pressure and strata control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Shao HQ, Wang JW, Xu SH, Gu SC (2014) The study of draining water drilling design method of Jurassic coalfield roof. Min Eng 12(6):59–61 (in Chinese)
Sui WH, Hang Y, Ma L, Wu Z, Zhou Y, Long G (2015) Interactions of overburden failure zones due to multiple-seam mining using longwall caving. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74(3):1019–1035
Tie MXK, Wo NSJ (1977) Theory of plates and shells. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Tongji University (2014) Advanced mathematics. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Tu M, Yu ZL (2004) Analysis of overburden movement and failure in mining under extremely thick loose and strong aquifer. J Min Saf Eng 21(2):1–3 (in Chinese)
Wang SM, Hang QX (2010) Coal mining and ecological water level protection in ecologically fragile areas. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang SR, Wang JA, Dai Y (2005) Discrete element analysis of top coal movement and failure mechanism in fully mechanized caving mining in heavy inclined thick Seam. J Univ Sci Technol B 27(1):5–8 (in Chinese)
Wang LG, Wang ZS, Hang JH, Zhou DL (2012) Prediction on the height of water-flowing fractured zone for shallow seam covered with thin bedrock and thick windblown sands. J Min Saf Eng 29(5):607–612 (in Chinese)
Xu ZL (2006) Elastic mechanics. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Yi MS (2008) Study and application of key strata theory in shallow seam of Shendong mining area. Diss, China Univ of Mining and Technology
Zhang DS, Fan GW, Ma LQ, Wang A, Liu YD (2009) Harmony of large-scale underground mining and surface ecological environment protection in desert district—a case study in Shendong mining area, northwest of China. Proc Earth Planet 1:1114–1120
Zhang JM, Zhang K, Cao ZG, Zhang Y (2017) Mining-bursting simulation and height calculation method for conducting-water fractured zone. J China Coal Soc 42(6):1557–1564 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Cao SG, Guo S, Wan T, Wang JJ (2018) Study on the height of fractured water-conducting zone under aquifer for short wall blocking mining. J Min Saf Eng 35(1):106–111 (in Chinese)
Zhao DK, Wu Q (2018) An approach to predict the height of fractured water-conducting zone of coal roof strata using random forest regression. Sci Rep 8:10986
Zhou Z, Zhao WS, Zhu CQ, Zhang KZ, Duan Y (2018) Prediction of water flowing fracture zone height based on the plastic hinge theory. Chin J Undergr Space Eng 14(5):1305–1312 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The study was jointly supported by the State Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 41430643) and the National Basic Research 973 Program of China (Grant 2015CB251601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Li, W., Wang, Q. et al. Study on the Height of the Mining-Induced Water-Conducting Fracture Zone Under the Q2l Loess Cover of the Jurassic Coal Seam in Northern Shaanxi, China. Mine Water Environ 39, 57–67 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00656-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00656-z