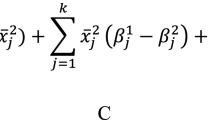Abstract
A robust estimator is proposed for the parameters that characterize the linear regression problem. It is based on the notion of shrinkages, often used in Finance and previously studied for outlier detection in multivariate data. A thorough simulation study is conducted to investigate: the efficiency with Normal and heavy-tailed errors, the robustness under contamination, the computational time, the affine equivariance and breakdown value of the regression estimator. Two classical data-sets often used in the literature and a real socioeconomic data-set about the Living Environment Deprivation of areas in Liverpool (UK), are studied. The results from the simulations and the real data examples show the advantages of the proposed robust estimator in regression.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agulló J, Croux C, Van Aelst S (2008) The multivariate least-trimmed squares estimator. J Multivar Anal 99(3):311–338
Arribas-Bel D, Patino JE, Duque JC (2017) Remote sensing-based measurement of Living Environment Deprivation: improving classical approaches with machine learning. PLOS ONE 12(5):e0176684
Cabana E, Lillo R E, Laniado H (Nov 2019) Multivariate outlier detection based on a robust mahalanobis distance with shrinkage estimators. Stat Pap. ISSN 1613-9798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-019-01148-1
Croux C, Rousseeuw PJ, Hössjer O (1994) Generalized S-estimators. J Am Stat Assoc 89(428):1271
Croux C, Van Aelst S, Dehon C (2003) Bounded influence regression using high breakdown scatter matrices. Ann Inst Stat Math 55(2):265–285
D’Alimonte D, Cornford D (2008) Outlier detection with partial information: application to emergency mapping. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 22(5):613–620
De Grève JP, Vanbeveren D (1980) Close binary systems before and after mass transfer: a comparison of observations and theory. Astrophy Space Sci 68(2):433–457
DeMiguel V, Martin-Utrera A, Nogales FJ (2013) Size matters: optimal calibration of shrinkage estimators for portfolio selection. J Bank Finance 37(8):3018–3034
Donoho DL, Huber PJ (1983) The notion of breakdown point. In: Bickel PJ, Doksum K, Hodges JL (eds) A festschrift for Erich L. Lehmann, vol 157184. CRC Press, Wadsworth
Edgeworth FY (1887) On observations relating to several quantities. Hermathena 6:279–285
Falk M (1997) On mad and comedians. Ann Inst Stat Math 49(4):615–644
Gervini D, Yohai VJ (2002) A class of robust and fully efficient regression estimators. Ann Stat 30(2):583–616
Hawkins DM, Olive DJ (2002) Inconsistency of resampling algorithms for high-breakdown regression estimators and a new algorithm. J Am Stat Assoc 97(457):136–148
Hawkins DM, Bradu D, Kass GV (1984) Location of several outliers in multiple-regression data using elemental sets. Technometrics 26(3):197
Huber PJ (1964) Robust estimation of a location parameter. Ann Math Stat 35(1):73–101
Huber PJ (1973) Robust regression: asymptotics, conjectures and monte Carlo. Ann Stat 1(5):799–821
Huber P J (1981) Robust statistics. Wiley, New York
Humphreys R M (1978) Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. I. Supergiants and O stars in the Milky Way. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 38:309
James W, Stein C (1992) Estimation with quadratic loss. In: Kotz S, Johnson NL (eds) Breakthroughs in Statistics. Springer Series in Statistics (Perspectives in Statistics). Springer, New York, NY, pp 443–460
Jeong D, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda T, Gachon P (2012) Comparison of transfer functions in statistical downscaling models for daily temperature and precipitation over canada. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 26(5):633–653
Jolliffe I (2011) Principal component analysis. In: Lovric M (eds) International encyclopedia of statistical science. Springer, Berlin, pp 1094–1096
Ledoit O, Wolf M (2003a) Improved estimation of the covariance matrix of stock returns with an application to portfolio selection. J Empir Finance 10(5):603–621
Ledoit O, Wolf M N (2003b) Honey, I shrunk the sample covariance matrix. UPF Economics and Business Working Paper No. 691
Ledoit O, Wolf M (2004) A well-conditioned estimator for large-dimensional covariance matrices. J Multivar Anal 88(2):365–411
Leroy AM, Rousseeuw PJ (1987) Robust regression and outlier detection. John wiley & sons, New York
Lopuhaa HP, Rousseeuw PJ (1991) Breakdown points of affine equivariant estimators of multivariate location and covariance matrices. Ann Stat 19(1):229–248
Maronna R, Morgenthaler S (1986) Robust regression through robust covariances. Commun Stat—Theory Methods 15(4):1347–1365
Maronna RA, Zamar RH (2002) Robust estimates of location and dispersion for high-dimensional datasets. Technometrics 44(4):307–317
Maronna RA, Martin RD, Yohai VJ (2006) Robust statistics : theory and methods. Wiley, New York
Mourino H, Barao MI (2010) A comparison between the linear regression model with autocorrelated errors and the partial adjustment model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 24(4):499–511
Oja H (2010) Multivariate nonparametric methods with R: an approach based on spatial signs and ranks. Springer, Berlin
Pan Z, Liu P, Gao S, Feng M, Zhang Y (2018) Evaluation of flood season segmentation using seasonal exceedance probability measurement after outlier identification in the three gorges reservoir. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32(6):1573–1586
Riani M, Perrotta D, Torti F (2012) FSDA: a MATLAB toolbox for robust analysis and interactive data exploration. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 116:17–32
Rousseeuw PJ (1983) Multivariate estimation with high breakdown point. Math Stat Appl 8:287–297
Rousseeuw PJ (1984) Least median of squares regression. J Am Stat Assoc 79(388):871–880
Rousseeuw PJ, Croux C (1993) Alternatives to the median absolute deviation. J Am Stat Assoc 88(424):1273
Rousseeuw P, Yohai V (1984) Robust regression by means of S-estimators. Springer, New York, pp 256–272
Rousseeuw PJ, Aelst SV, Van Driessen K, Agulló J (2004) Robust multivariate regression. Technometrics 46(3):293–305
Ruppert D (1992) Computing S estimators for regression and multivariate location/dispersion. J Comput Graph Stat 1(3):253
Sajesh TA, Srinivasan MR (2012) Outlier detection for high dimensional data using the Comedian approach. J Stat Comput Simul 82(5):745–757
Sguera C, Galeano P, Lillo RE (2016) Functional outlier detection by a local depth with application to no x levels. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30(4):1115–1130
Siegel AF (1982) Robust regression using repeated medians. Biometrika 69(1):242
Stromberg AJ, Hössjer O, Hawkins DM (2000) The least trimmed differences regression estimator and alternatives. J Am Stat Assoc 95(451):853–864
Tung Y, Yeh K, Yang J (1997) Regionalization of unit hydrograph parameters: 1. Comp Regres Anal Tech 11:17
Vardi Y, Zhang CH (2000) The multivariate L1-median and associated data depth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S Am 97(4):1423–6
Verboven S, Hubert M (2005) LIBRA: a MATLAB library for robust analysis. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 75(2):127–136
Xiong S, Joseph VR (2013) Regression with outlier shrinkage. J Stat Plan Inference 143(11):1988–2001
Yohai VJ (1987) High breakdown-point and high efficiency robust estimates for regression. Ann Stat 15(2):642–656
Yu C, Yao W (2017) Robust linear regression: a review and comparison. Commun Stat—Simul Comput 46(8):6261–6282
Zou H, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2006) Sparse principal component analysis. J Comput Graph Stat 15(2):265–286
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editor and the referee for the constructive and valuable comments. This research was partially supported by MINISTERIO DE ECONOMIA, INDUSTRIA Y COMPETITIVIDAD, Award Number: ECO2015-66593-P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research was partially supported by MINISTERIO DE ECONOMIA, INDUSTRIA Y COMPETITIVIDAD, Award Number: ECO2015-66593-P.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabana, E., Lillo, R.E. & Laniado, H. Robust regression based on shrinkage with application to Living Environment Deprivation. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 34, 293–310 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01774-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01774-4