Abstract
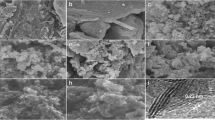
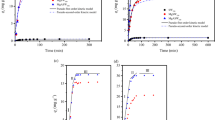
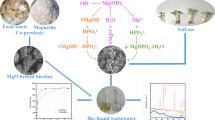
The g-MoS2 coated biochar (g-MoS2-BC) composites were synthesized by coating original biochar with g-MoS2 nanosheets at 300°C(BC300)/700°C (BC700). The adsorption properties of the g-MoS2-BC composites for ciprofloxacin (CIP) were investigated with an aim to exploit its high efficiency toward soil amendment. The specific surface area and the pore structures of biochar coated g-MoS2 nanosheets were significantly increased. The g-MoS2-BC composites provided more it electrons, which was favorable in enhancing the it-it electron donor-acceptor (EDA) interactions between CIP and biochar. As a result, the g-MoS2-BC composites showed faster adsorption rate and greater adsorption capacity for CIP than the original biochar. The coated g-MoS2 nanosheets contributed more to CIP adsorption on the g-MoS2-BC composites due to their greater CIP adsorption capacity than the original biochar. Moreover, the synergistic effect was observed for CIP adsorption on g-MoS2-BC700, and suppression effect on g-MoS2-BC300. In addition, the adsorption of CIP onto g-MoS2-BC composites also exhibited strong dependence on the solution pH, since it can affect both the adsorbent surface charge and the speciation of contaminants. It was reasonably suggested that the mechanisms of CIP adsorption on g-MoS2-BC composites involved pore-filling effects, it-it EDA interaction, electrostatic interaction, and ion exchange interaction. These results are useful for the modification of biochar in exploiting the novel amendment for contaminated soils.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrafioti E, Kalderis D, Diamadopoulos E (2014). Arsenic and chromium removal from water using biochars derived from rice husk, organic solid wastes and sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Management, 133: 309–314
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha A U, Lim J E, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee S S, Ok Y S (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99: 19–33
Cao X D, Ma L N, Gao B, Harris W (2009). Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(9): 3285–3291
Chao Y, Yang L, Ji H, Zhu W, Pang J, Han C, Li H (2017). Graphene-analogue molybdenum disulfide for adsorptive removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 36(3): 815–821
Chen C P, Zhou W J, Yang Q, Zhu L F, Zhu L Z (2014). Sorption characteristics of nitrosodiphenylamine (NDPhA) and diphenyla-mine (DPhA) onto organo bentonite from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 240: 487–493
Guo X T, Dong H, Yang C, Zhang Q, Liao C J, Zha F G, Gao L M (2016). Application of goethite modified biochar for tylosin removal from aqueous solution. Colloid surface A, 502: 81–88
Han L, Ro K S, Sun K, Sun H, Wang Z, Libra J A, Xing B. (2016). New evidence for high sorption capacity of hydrochar for hydrophobic organic pollutants. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(24): 13274–13282
Han S, Liu K, Hu L F, Teng F, Yu P P, Zhu Y F (2017). Superior adsorption and regenerable dye adsorbent based on flower-like molybdenum disulfide nanostructure. Scientific Reports, 7(10): 43599
Huang Q, Song S, Chen Z, Hu B, Chen J, Wang X (2019). Biochar-based materials and their applications in removal of organic contaminants from wastewater: State-of-the-art review. Biochar, 1(1): 45–73
Karimnezhad L, Haghighi M, FatehifarE(2014). Adsorption of benzene and toluene from waste gas using activated carbon activated by ZnCl2- Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 8(6): 835–844
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Alvarez P J J (2011). Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(5): 1827–1833
Shang J G, Kong X R, He L L, Li W H, Liao Q J H (2016). Low-cost biochar derived from herbal residue: Characterization and application for ciprofloxacin adsorption. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(10): 2449–2458
Sun K, Ran Y, Yang Y, Xing B S, Mao J (2013). Interaction mechanism of benzene and phenanthrene in condensed organic matter: Importance of adsorption (nanopore-filling). Geoderma, 204-205: 68–74
Tan X, Liu S, Liu Y, Gu Y, Zeng G, Cai X, Yan Z, Yang C, Hu X, Chen B (2016). One pot synthesis of carbon supported calcined-Mg/Al layered double hydroxides for antibiotic removal by slow pyrolysis of biomass waste. Scientific Reports, 6(12): 39691
Tang L, Yu J F, Pang Y, Zeng G M, Deng Y C, Wang J J, Ren X Y, Ye S J, Peng B, Feng H P (2018). Sustainable efficient adsorbent: Alkali-acid modified magnetic biochar derived from sewage sludge for aqueous organic contaminant removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 336: 160–169
Thiele-Bruhn S, SÊren T B (2003). Pharmaceutical antibiotic compounds in soil: A review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 166(2): 145–167
Wang H, Wen F, Chen Y, Sun T, Meng Y, Zhang Y (2016). Electrocatalytic determination of nitrite based on straw cellulose/ molybdenum sulfide nanocomposite. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 85: 692–697
Wang J, Wang C, Huang Q, Ding F, He X (2015). Adsorption of PAHs on the sediments from the yellow river delta as a function of particle size and salinity. Soil & Sediment Contaminant, 24(2): 103–115
Wang R, Cai X, Shen F (2014). TiO2 hollow microspheres with mesoporous surface: Superior adsorption performance for dye removal. Applied Surface Science, 305: 352–358
Xie J F, Zhang J J, Li S, Grote F B, Zhang X D, Zhang H R, Wang X, Lei Y, Pan B C, Xie Y (2013). Controllable disorder engineering in oxygen-incorporated M0S2 ultrathin nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(47): 17881–17888
Xing B, Pignatello J J (1997). Dual-mode sorption of low-polarity compounds in glassy poly (Vinyl Chloride) and soil organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(3): 792–799
Yang W, Lu Y, Zheng F, Xue X, Li N, Liu D (2012). Adsorption behavior and mechanisms of norfloxacin onto porous resins and carbon nanotube. Chemical Engineering Journal, 179: 112–118
Zhang M, Gao B, Yao Y, Xue Y, Inyang M (2012). Synthesis, characterization, and environmental implications of graphene-coated biochar. Science of the Total Environment, 435-436: 567–572
Zhao N, Zhao C F, Lv Y Z, Zhang W F, Du Y G, Hao Z P, Zhang J (2017). Adsorption and coadsorption mechanisms of Cr(VI) and organic contaminants on H3PO4 treated biochar. Chemosphere, 186: 422–429
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1800704) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21577124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• The g-MoS2 coated composites (g-MoS2-BC) were synthesized.
• The coated g-MoS2 greatly increased the adsorption ability of biochar.
• The synergistic effect was observed for CIP adsorption on g-MoS2-RC700.
• The adsorption mechanisms of CIP on g-MoS2-BC were proposed.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Xing, R., Zhou, W. et al. Adsorption characteristics of ciprofloxacin onto g-MoS2 coated biochar nanocomposites. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 14, 41 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-019-1218-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-019-1218-0