Abstract
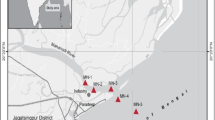
Daya Bay is facing the influence of human activities and nature changes, which result in phytoplankton adjusting to the changing environment. The data about environmental changes and phytoplankton were obtained from four seasonal cruises in 2013 in the bay. It is helpful to explore seasonal succession of phytoplankton driven by the determining environmental factors in this bay. Temperature is a significant indicator of season change. The limiting factor of phytoplankton growth totally changed from P (PO4-P) limiting during the southwest monsoon to Si (SiO3-Si) limiting during northeast monsoon. The order of diatoms and dinoflagellates was the dominant phytoplankton groups in Daya Bay. The dominant species included chain-forming diatoms (Skeletonema, Pseudo-nitzschia, Thalassionema, Chaetoceros and Rhizosolenia) were found all the year round and filamentous cyanobacteria (Trichodesmium) in spring and autumn. Partial least square regression (PLS) found that salinity, temperature and nutrients were important driving force for phytoplankton seasonal succession.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achary MS, Panigrahi S, Satpathy KK, Sahu G, Mohanty AK, Selvanayagam M, Panigrahy RC (2014) Nutrient dynamics and seasonal variation of phytoplankton assemblages in the coastal waters of southwest Bay of Bengal. Environ Monit Assess 186:5681–5695
Carrascal LM, Galvan I, Gordo O (2009) Partial least squares regression as an alternative to current regression methods used in ecology. OIKOS 118:681–690
Chu TV, Torreton JP, Mari X, Nguyen HMT, Pham KT, Pham TT, Bouvier T, Bettarel Y, Pringault O, Bouvier C et al. (2014) Nutrient ratios and the complex structure of phytoplankton communities in a highly turbid estuary of Southeast Asia. Environ Monit Assess 186:8555–8572
Dong JD, Zhang YY, Wang YS, Zhang S, Wang HK (2008) Spatial and seasonal variations of Cyanobacteria and their nitrogen fixation rates in Sanya Bay, South China Sea. Sci Mar 72:239–251
Dong JD, Zhang YY, Zhang S, Wang YS, Yang ZH, Wu ML (2010) Identification of temporal and spatial variations of water quality in Sanya Bay, China by three-way principal component analysis. Environ Earth Sci 60:1673–1682
Dupuis AP, Hann BJ (2009) Warm spring and summer water temperatures in small eutrophic lakes of the Canadian prairies: potential implications for phytoplankton and zooplankton. J Plankton Res 31:489–502
Fu C, Gaichas S, Link JS, Bundy A, Boldt JL, Cook AM, Gamble R, Utne KR, Liu H, Friedland KD (2012) Relative importance of fisheries, trophodynamic and environmental drivers in a series of marine ecosystems. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 459:169
Hassen MB, Drira Z, Hamaza A, Ayadi H, Akrout F, Messaoudi S, Issaoui H, Aleya L, Bouain A (2009) Phytoplankton dynamics related to water mass properties in the Gulf of Gabes: ecological implications. J Mar Syst 75:216–226
Huang LM, Jian WJ, Song XY, Huang XP, Liu S, Qian PY, Yin KD, Wu M (2004) Species diversity and distribution for phytoplankton of the Pearl River estuary during rainy and dry seasons. Mar Pollut Bull 49:588–596
Jickells TD (1998) Nutrient biogeochemistry of the coastal zone. Science 281:217–222
Ling J, Wu ML, Chen YF, Zhang YY, Dong JD (2014) Identification of spatial and temporal patterns of coastal waters in Sanya Bay, South China Sea by chemometrics. J Environ Inf 23:37–43
Pielou EC (1966) Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. J Theor Biol 10:370–383
Qiu YW, Wang ZD, Zhu LS (2005) Variation trend of nutrient and chlorophyll contents and their effects on ecological environment in Daya Bay. J Oceanogr Taiwan Strait 24:131–139
Redfield AC, Ketchum BH, Richards FA (1963) The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In The Sea, MN Hill, ed. John Wiley, New York, p 26–77
Rocha C, Galvao H, Barbosa A (2002) Role of transient silicon limitation in the development of cyanobacteria blooms in the Guadiana estuary, south-western Iberia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 228:35–45
Roelofsen HD, van Bodegom PM, Kooistra L, Witte J-PM (2014) Predicting leaf traits of herbaceous species from their spectral characteristics. Ecol Evol 4:706–719
Seu-Anoi NM, Ouattara A, Kone YJM, Gourene G (2011) Seasonal distribution of phytoplankton in the Aby lagoon system, Ivory Coast, West Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 36:321–330
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:379–423
Song XY, Huang LM, Zhang JL, Huang XP, Zhang JB, Yin JQ, Tan YH, Liu S (2004) Variation of phytoplankton biomass and primary production in Daya Bay during spring and summer. Marine Pollution Bulletin 49:1036–1044
Sun C-C, Wang Y-S, Sun S, Zhang F-Q (2006a) Analysis dynamics of phytoplankton community characteristics in Daya Bay. Acta Ecol Sin 26:3948–3958
Sun CC, Wang YS, Sun S, Zhang FQ (2006b) Dynamic analysis of phytoplankton community characteristics in Daya Bay, China. Acta Ecol Sin 26:3948–3958
Sun J, Liu D, Bai J, Gao H, Han X (2004) Phytoplankton community of the Bohai Sea in winter 2001. J Ocean Univ China 34:413–422
Wang HH, Song SH, Qi YZ (2014) A comparative study of phytoneuston and the phytoplankton community structure in Daya Bay, South China Sea. J Sea Res 85:474–482
Wang YS, Lou ZP, Sun CC, Wu ML, Han SH (2006a) Multivariate statistical analysis of water quality and phytoplankton characteristics in Daya Bay, China, from 1999 to 2002. Oceanologia 48:193–211
Wang YS, Lou ZP, Sun CC, Sun S (2008) Ecological environment changes in Daya Bay, China, from 1982 to 2004. Mar Pollut Bull 56(11):1871–1879
Wang ZH, Qi YZ, Chen JF, Xu N, Yang YF (2006b) Phytoplankton abundance, community structure and nutrients in cultural areas of Daya Bay, South China Sea. J Mar Syst 62:85–94
Webster IT, Rea N, Padovan AV, Dostine P, Townsend SA, Cook S (2005) An analysis of primary production in the Daly River, a relatively unimpacted tropical river in northern Australia. Mar Freshw Res 56:303–316
Wold S, Sjostrom M, Eriksson L (2001) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 58:109–130
Wu ML, Wang YS (2007) Using chemometrics to evaluate anthropogenic effects in Daya Bay, China. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 72:732–742
Wu ML, Wang YS, Sun CC, Sun FL, Cheng H, Wang YT, Dong JD, Wu JF (2012) Monsoon-driven dynamics of water quality by multivariate statistical methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud 41:66–76
Wu ML, Wang YS, Sun CC, Wang HL, Dong JD, Han SH (2009a) Identification of anthropogenic effects and seasonality on water quality in Daya Bay, South China Sea. J Environ Manag 90:3082–3090
Wu ML, Wang YS, Sun CC, Wang HL, Dong JD, Yin JP, Han SH (2010) Identification of coastal water quality by statistical analysis methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 60:852–860
Wu ML, Wang YS, Sun CC, Wang HL, Lou ZP, Dong JD (2009b) Using chemometrics to identify water quality in Daya Bay, China. Oceanologia 51:217–232
Wu ML, Wang YS, Wang YT, Sun FL, Sun CC, Jiang ZY, Cheng H (2014) Influence of environmental changes on phytoplankton pattern in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía 49:323–337
Xu, GZ (1989) Environments and resources of Daya Bay. Anhui Science Publishing House, HeFei
Zhou WH, Li T, Cai CH, Huang LM, Wang HK, Xu JR, Dong JD, Zhang S (2009) Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton and bacterioplankton biomass in Sanya Bay, northern South China Sea. J Environ Sci China 21:595–603
Zhu ZY, Ng WM, Liu SM, Zhang J, Chen JC, Wu Y (2009) Estuarine phytoplankton dynamics and shift of limiting factors: a study in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary and adjacent area. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 84:393–401
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31971480, No. 41876126, No. U1901211, and No. 41430966), Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (No. GML2019ZD0305) and Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. ISEE2019ZR02 and No. ISEE2018ZD02), the National Key Research and Development Program “Biological Habitat Repair Project” (No. 2016YFC1403003) and International Scientific & Technological Cooperation Project of Department of Education of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2015KGJHZ017). The authors thank all the staff of Daya Bay Marine Biology Research Station of Chinese Academy of Sciences for providing support and help, and the information system of China Ecosystem Research Network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the related authors confirmed there were no conflict of ethical approval.
Informed consent
All the related authors have known the informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ML., Wang, YT., Cheng, H. et al. Phytoplankton community, structure and succession delineated by partial least square regression in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Ecotoxicology 29, 751–761 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02188-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02188-2