Abstract
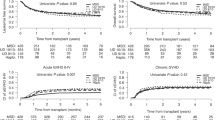
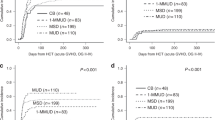
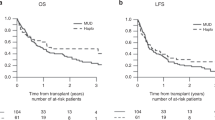
Relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) remains a major therapeutic challenge. Despite the consensus for proceeding to allogeneic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in relapsing patients with ALL who achieve second complete remission (CR2) with salvage therapy, most patients lack a suitable matched-related histocompatible donor. The present multicenter retrospective study compared, for ALL patients in CR2, the HSCT outcome from all four possible alternative hematopoietic stem cell sources, namely matched unrelated 10/10 (n = 281), mismatched unrelated 9/10 (n = 125), haploidentical (n = 105), and cord blood (n = 104) donors. The 2-year outcomes were not statistically different between the four donor sources with respect to overall survival (38.3–47.2%), leukemia-free survival (30.5–39.6%), relapse incidence (32.6–37.6%), nonrelapse mortality (27.5–34.6%), and graft-versus-host disease-free relapse survival (21.4–33.1%). Donor choices for ALL patients achieving CR2 post first relapse are broad, ensuring that most patient in need secures a graft. Therefore, in practice, the donor choice should depend on timely availability and policy center.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huguet F, Chevret S, Leguay T, Thomas X, Boissel N, Escoffre-Barbe M, et al. Intensified therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: report of the randomized GRAALL-2005 clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2514–23.
Jabbour E, O’Brien S, Konopleva M, Kantarjian H. New insights into the pathophysiology and therapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer. 2015;121:2517–28.
Fielding AK, Richards SM, Chopra R, Lazarus HM, Litzow MR, Buck G, et al. Outcome of 609 adults after relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); an MRC UKALL12/ECOG 2993 study. Blood. 2007;109:944–50.
Forman SJ, Rowe JM. The myth of the second remission of acute leukemia in the adult. Blood. 2013;121:1077–82.
Maffini E, Lanza F, Saraceni F. Treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Hematol Int. 2019;1:85–93.
Desjonqueres A, Chevallier P, Thomas X, Huguet F, Leguay T, Bernard M, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapsing after first-line pediatric-inspired therapy: a retrospective GRAALL study. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6:e504.
Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Ciceri F, Mohty M, Nagler A. Definition of GvHD-free, relapse-free survival for registry-based studies: an ALWP-EBMT analysis on patients with AML in remission. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:610–1.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME. Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:215–33.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation. 1974;18:295–304.
Terwey TH, Vega-Ruiz A, Hemmati PG, Martus P, Dietz E, le Coutre P, et al. NIH-defined graft-versus-host disease after reduced intensity or myeloablative conditioning in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26:536–42.
Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH, et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116:354–65.
Marks DI, Aversa F, Lazarus HM. Alternative donor transplants for adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a comparison of the three major options. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006;38:467–75.
Terakura S, Atsuta Y, Tsukada N, Kobayashi T, Tanaka M, Kanda J, et al. Comparison of outcomes of 8/8 and 7/8 allele-matched unrelated bone marrow transplantation and single-unit cord blood transplantation in adults with acute leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22:330–8.
Han LJ, Wang Y, Fan ZP, Huang F, Zhou J, Fu YW, et al. Haploidentical transplantation compared with matched sibling and unrelated donor transplantation for adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in first complete remission. Br J Haematol. 2017;179:120–30.
Srour SA, Milton DR, Bashey A, Karduss-Urueta A, Al Malki MM, Romee R, et al. Haploidentical transplantation with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide for high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23:318–24.
Santoro N, Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Bacigalupo A, Ciceri F, Gulbas Z, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical stem cell transplantation in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a study on behalf of the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:113.
Gokbuget N, Kneba M, Raff T, Trautmann H, Bartram CR, Arnold R, et al. Adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and molecular failure display a poor prognosis and are candidates for stem cell transplantation and targeted therapies. Blood. 2012;120:1868–76.
Gokbuget N, Dombret H, Ribera JM, Fielding AK, Advani A, Bassan R, et al. International reference analysis of outcomes in adults with B-precursor Ph-negative relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2016;101:1524–33.
Simon R, Makuch RW. A non-parametric graphical representation of the relationship between survival and the occurrence of an event: application to responder versus non-responder bias. Stat Med. 1984;3:35–44.
Pavlu J, Labopin M, Zoellner AK, Sakellari I, Stelljes M, Finke J, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for primary refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Cancer. 2017;123:1965–70.
Davies SM, Ramsay NK, Klein JP, Weisdorf DJ, Bolwell B, Cahn JY, et al. Comparison of preparative regimens in transplants for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:340–7.
Eroglu C, Pala C, Kaynar L, Yaray K, Aksozen MT, Bankir M, et al. Comparison of total body irradiation plus cyclophosphamide with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimens in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:2474–9.
Cahu X, Labopin M, Giebel S, Aljurf M, Kyrcz-Krzemien S, Socie G, et al. Impact of conditioning with TBI in adult patients with T-cell ALL who receive a myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a report from the acute leukemia working party of EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:351–7.
Giebel S, Labopin M, Socie G, Beelen D, Browne P, Volin L, et al. Improving results of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission: an analysis from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica. 2017;102:139–49.
Zhang H, Chen J, Que W. A meta-analysis of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood transplantation versus unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation in acute leukemia patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:1164–73.
Rocha V, Labopin M, Sanz G, Arcese W, Schwerdtfeger R, Bosi A, et al. Transplants of umbilical-cord blood or bone marrow from unrelated donors in adults with acute leukemia. N. Engl J Med. 2004;351:2276–85.
Eapen M, Rocha V, Sanz G, Scaradavou A, Zhang MJ, Arcese W, et al. Effect of graft source on unrelated donor haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in adults with acute leukaemia: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:653–60.
Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Bader P, Bonini C, Duarte RF, Dufour C, et al. Use of haploidentical stem cell transplantation continues to increase: the 2015 European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant activity survey report. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52:811–7.
Gokbuget N, Stanze D, Beck J, Diedrich H, Horst HA, Huttmann A, et al. Outcome of relapsed adult lymphoblastic leukemia depends on response to salvage chemotherapy, prognostic factors, and performance of stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120:2032–41.
O’Brien S, Thomas D, Ravandi F, Faderl S, Cortes J, Borthakur G, et al. Outcome of adults with acute lymphocytic leukemia after second salvage therapy. Cancer. 2008;113:3186–91.
Oriol A, Vives S, Hernandez-Rivas JM, Tormo M, Heras I, Rivas C, et al. Outcome after relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adult patients included in four consecutive risk-adapted trials by the PETHEMA Study Group. Haematologica. 2010;95:589–96.
Kantarjian HM, Thomas D, Ravandi F, Faderl S, Jabbour E, Garcia-Manero G, et al. Defining the course and prognosis of adults with acute lymphocytic leukemia in first salvage after induction failure or short first remission duration. Cancer. 2010;116:5568–74.
Thomas DA, Kantarjian H, Smith TL, Koller C, Cortes J, O’Brien S, et al. Primary refractory and relapsed adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: characteristics, treatment results, and prognosis with salvage therapy. Cancer. 1999;86:1216–30.
Mullighan CG. The molecular genetic makeup of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:389–96.
Mullighan CG. Molecular genetics of B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Investig. 2012;122:3407–15.
Choi S, Henderson MJ, Kwan E, Beesley AH, Sutton R, Bahar AY, et al. Relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia involving selection of a preexisting drug-resistant subclone. Blood. 2007;110:632–9.
Kanakry CG, Fuchs EJ, Luznik L. Modern approaches to HLA-haploidentical blood or marrow transplantation. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13:132.
Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M, Martinelli G, Liedtke M, Stock W, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:740–53.
Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gokbuget N, Fielding AK, Schuh AC, Ribera JM, et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl J Med. 2017;376:836–47.
Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M, Liedtke M, Stock W, Gokbuget N, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard of care in relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: final report and long-term survival follow-up from the randomized, phase 3 INO-VATE study. Cancer. 2019;125:2474–87.
Marks DI, Kebriaei P, Stelljes M, Gokbuget N, Kantarjian H, Advani AS, et al. Outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplantation after inotuzumab ozogamicin treatment for relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:1720–9.
Yeshurun M, Weisdorf D, Rowe JM, Tallman MS, Zhang MJ, Wang HL, et al. The impact of the graft-versus-leukemia effect on survival in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019;3:670–80.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participating centers of the EBMT and national registries for providing patients for the study, and data managers for their valuable contribution (Additional file 1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EB, ML, SG, MM, and AN designed the study and/or analyzed the data. DR, SM, CS, BG, RR, ZNO, JP, JH, DB, JA provided important clinical data. All authors contributed to the writing of the report and approved the final version of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brissot, E., Labopin, M., Russo, D. et al. Alternative donors provide comparable results to matched unrelated donors in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in second complete remission: a report from the EBMT Acute Leukemia Working Party. Bone Marrow Transplant 55, 1763–1772 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0849-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0849-x
This article is cited by
-
Second haploidentical stem cell transplantation (HAPLO-SCT2) after relapse from a first HAPLO-SCT in acute leukaemia—a study on behalf of the Acute Leukaemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT)
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Indications for haematopoietic cell transplantation for haematological diseases, solid tumours and immune disorders: current practice in Europe, 2022
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide containing regimens after matched sibling, matched unrelated and haploidentical donor transplants in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission, a comparative study of the ALWP of the EBMT
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Evolving therapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: state-of-the-art treatment and future directions
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2020)