Abstract
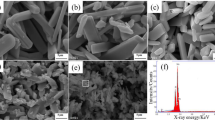
The agglomeration behaviour of Mo powder, especially fine Mo powder, has been a major concern. The degree of powder agglomeration is directly related to the uniformity of Mo and its alloy powder mixtures and related target materials. This study mainly focuses on how to efficiently reduce the soft agglomerates behaviour of Mo powder. Analysis of the micromorphology and median particle size (D50) of modified Mo powder showed that the soft agglomerates behaviour of Mo powder can be divided into three stages: drawing, gathering, and sticking. Modification of the Mo powder surface by the polymer surfactant PVP-K30 can effectively prevent the agglomeration of the Mo powder. Additionally, the surface hydroxyl groups of the Mo powder disappeared, the agglomerate factor decreased from 13.02 to 5.04, and the flowability of the Mo powder was significantly improved. This is important for improving the grain uniformity and application performance of Mo target materials synthesized from Mo powder.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Jha, Extractive Metallurgy of Molybdenum (Wiley, New Jersey, 2013)
J.H. Perepezko, The hotter the engine, the better. Science 326, 1068–1069 (2009)
A.B. Li, L.J. Huang, Q.Y. Meng, Hot working of Ti–6Al–3Mo–2Zr–0.3Si alloy with lamellar α + β starting structure using processing map. Mater. Des. 30, 1625–1631 (2009)
B. Gorr, M. Azim, H.J. Christ, Microstructure evolution in a new refractory high-entropy alloy W-Mo–Cr–Ti–Al. Matell. Mater. Trans. 47A, 961–970 (2016)
R. Xu, B. Liu, Z. Yan, F. Chen, Low-cost and high-strength powder metallurgy Ti–Al–Mo–Fe alloy and its application. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 12049–12060 (2019)
X.Q. Yang, H. Tan, N. Lin, Z. Li, Y. He, Effects of the lanthanum content on the microstructure and properties of the molybdenum alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 61, 179–184 (2016)
B.M. Trost, M. Lautens, Molybdenum catalysts for allylic alkylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104, 5543–5545 (1982)
L. Dong, J. Wang, L. Wei, C. Li, Z. Jie, Fabrication and thermionic emission properties of lanthanum carbide doped tungsten cathodes. Mater. Lett. 146, 47–50 (2015)
B.S.L. Prasad, A.R. Annamalai, Tungsten heavy alloys with molybdenum, Y2O3 and lanthanum. A review. J. Superhard. Mater. 41, 1–16 (2019)
J. Lisboa, J. Marin, M. Barrera, Engineering of fuel plates on uranium–molybdenum monolithic. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 5, 274–286 (2015)
R.B. Péréz-Sáez, V. Recarte, Advanced shape memory alloys processed by powder metallurgy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2, 49–53 (2000)
C.T. Lin, W.R. Peng, P.C. Peng, Simultaneous generation of baseband and radio signals using only one single-electrode Mach–Zehnder modulator with enhanced linearity. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 18, 2481–2483 (2006)
G. Kostorz, Phase Transformations in Materials (Wiley-VCH, Berlin, 2001)
Z.L. Yin, X.H. Li, Q.Y. Chen, Study on the kinetics of the thermal decompositions of ammonium molybdates. Thermochim. Acta 352, 107–110 (2000)
Z.L. Yin, X.H. Li, Study on the thermal decomposition of a commercial polyphase ammonium tetramolybdate. Thermochim. Acta 244, 283–289 (1994)
J.R. Harris, Negative staining and cryoelectron microscopy. Microsc. Today 5, 18–18 (1997)
R.K. Enneti, T.A. Wolfe, Effect of ammonium dimolybdate (ADM) on the reduction of molybdenum trioxide. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 31, 253–257 (2012)
Y. Sun, X. Hui, J. Sun, Influence of ammonium molybdate precursor on Mo powder preparation and working properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 483, 168–171 (2008)
R.M. German, Sintering: From Empirical Observations to Scientific Principles || Geometric Trajectories During Sintering, Vol. 124 (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2014), pp. 141–181
R.K. Enneti, T.A. Wolfe, Agglomeration during reduction of MoO3. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 31, 47–50 (2012)
T. Ressler, R.E. Jentoft, J. Wienold, In situ XAS and XRD studies on the formation of Mo suboxides during reduction of MoO3. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6360–6370 (2000)
G.B. Basim, B.M. Moudgil, Effect of soft agglomerates on CMP slurry performance. J. Colloids Interface Sci. 256, 137–142 (2002)
Z.Y. Deng, Y. Zhou, Y. Inagaki, M. Ando, T. Ohji, Role of Zr(OH)4 hard agglomerates in fabricating porous ZrO2 ceramics and the reinforcing mechanisms. Acta Mater. 51, 731–739 (2003)
R.N. Grass, S. Tsantilis, S.E. Pratsinis, Design of high-temperature, gas-phase synthesis of hard or soft TiO2 agglomerates. AIChE J. 52, 1318–1325 (2010)
D.D. Hu, J.B. Zhuang, M.L. Ding, A review of studies on the granular agglomeration mechanisms and anti-agglomeration methods. Key Eng. Mater. 501, 5 (2012)
C.K. Li, P.A. Xiao, X.H. Zhang, Stirring mill of TiH2/SiC powders and sintering of titanium alloy with ultrafine grains. Mater. Sci. Eng. Met. 20, 266–272 (2015)
I. Farahbakhsh, A. Zakeri, P. Manikandan, Evaluation of nanostructured coating layers formed on Ni balls during mechanical alloying of Cu powder. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2830–2837 (2011)
Q.L. Hou, J.W. Wang, H.T. Duan, Influence of SHMP on ZrO2 coated on the surface of the rutile titanium dioxide. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. 46, 07096–07099 (2015)
W.J. Tseng, D.M. Liu, C.K. Hsu, Influence of stearic acid on suspension structure and green microstructure of injection-molded zirconia ceramics. Ceram. Int. 25, 191–195 (1999)
A.M. Semiletov, A.A. Chirkunov, Y.I. Kuznetsov, Protection of aluminum alloy AD31 from corrosion by adsorption layers of trialkoxysilanes and stearic acid. Mater. Corros. 71, 77–85 (2020)
X.B. Cao, C. Li, Y. Li, F. Fang, X. Cui, Y. Yao, J. Wei, Enhanced performance of perovskite solar cells by modulating the Lewis acid–base reaction. Nanoscale 10, 1039 (2016)
K. Li, L. Shuai, Z. Jing, Z. Feng, C. Li, Preparation and stabilization of γ-Bi2O3 photocatalyst by adding surfactant and its photocatalytic performance. Mater. Res. Express 4, 6 (2017)
K. Seo, K. Sinha, E. Novitskaya, O.A. Graeve, Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) effects on iron oxide nanoparticle formation. Mater. Lett. 215, 203–206 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support received from the Start-up Research Fund of Zhengzhou University (No. 32211157) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M652569).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Li, Q., Guo, M. et al. Study of the Agglomeration Behaviour of Surface-Modified Molybdenum Powder. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 4487–4497 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00651-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00651-7