Abstract
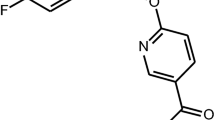
Clozapine is the gold-standard agent for treatment resistant schizophrenia but its mechanism of action remains unclear. There is emerging evidence of the potential role of the GABAB receptor in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. It has been hypothesised that clozapine can mediate its actions via the GABAB receptor. Baclofen is currently recognised as the prototype GABAB receptor agonist. There are some potential clinical similarities between clozapine and baclofen. Indeed, baclofen has been previously proposed for use as an antipsychotic agent. Our analysis of the X-ray crystal structure of GABAB receptor along with molecular docking calculations, suggests that clozapine could directly bind to the GABAB receptor similar to that of baclofen. This finding could lead to a better understanding of the pharmacological uniqueness of clozapine, potential development of a biomarker for treatment resistant schizophrenia and the development of more targeted treatments leading to personalisation of treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Insel TR. Rethinking schizophrenia. Nature. 2010;468:187–93.
Van Os J, Kapur S. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2009;374:635–45.
McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J. Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiol Rev. 2008;30:67–76.
Marwaha S, Johnson S, Bebbington P, Stafford M, Angermeyer MC, Brugha T, et al. Rates and correlates of employment in people with schizophrenia in the UK, France and Germany. Br J Psychiatry. 2007;191:30–37.
Siskind D, Siskind V, Kisely S. Clozapine response rates among people with treatment-resistant schizophrenia data from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Psychiatry. 2017;62:772–7.
Taylor DM. Clozapine for treatment-resistant schizophrenia: still the gold standard? CNS Drugs. 2017;31:177–80.
Siskind D, McCartney L, Goldschlager R, Kisely S. Clozapine versus first and second generation antipsychotics in treatment refractory schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psych. 2016;209:385–92.
Faden J. Treatment resistant schizophrenia: a brief overview of treatment options. J Clin Psych. 2019;80:18ac12394.
Hippius H. A historical perspective of clozapine. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60:22–23.
Idanpaan-Heikkila J, Alhava E, Olkimora M. Clozapine and agranulocytosis. Lancet. 1975;2:611.
Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988;45:789–96.
Tiihonen J, Lonnquist J, Wahlbeck K, Klaukka T, Niskanen L, Tanskanen A, et al. 11year follow-up of mortality in patients with schizophrenia: a population based cohort study (FIN11 study). Lancet. 2009;374:620–7.
Howes OD, Kapur S. The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: version III—the final common pathway. Schizophr Bull. 2009;35:549–62.
Wolkin A, Barouche F, Wolf AP, Rotrosen J, Fowler JS, Shiue CY, et al. Dopamine blockade and clinical response: evidence for two biological subgroups of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1989;146:905–8.
Yilmaz Z, Zai CC, Hwang R, Mann S, Arenovich T, Remington G, et al. Antipsychotics, dopamine D2 receptor occupancy and clinical improvement in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Res. 2012;140:214–20.
O’Connor WT, O’Shea SD. Clozapine and GABA transmission in schizophrenia disease models: establishing principles to guide treatments. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;50:47–80.
Meltzer HY. Mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs. In: Charney D, Coyle JT, Nemeroff C, editors. Neuropsychopharmacology: the fifth generation of progress. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2002. pp. 819–831.
Kapur S, Seeman P. Does fast dissociation from the dopamine d(2) receptor explain the action of atypical antipsychotics? A new hypothesis. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:360–9.
Daskalakis ZJ, George TP. Clozapine, GABA(B), and the treatment of resistant schizophrenia. Clinical Pharmacol Ther. 2009;86:442–6.
Orhan F, Fatouros-Bergman H, Goiny M, Malmqvist A, Piehl F, Karolinska Schizophrenia Project (KaSP) Consortium. et al. CSF GABA is reduced in first-episode psychosis and associates to symptom severity. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1244–50.
Bowery N. GABA B receptor: a site of therapeutic benefit. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6:37–43.
Bendtsen L, Zakrzewska J, Abbott J, Braschinsky M, Di Stefano G, Donnet A, et al. European academy of neurology guideline on trigeminal neuralgia. Eur J Neurol. 2019;26:831–49.
Rose AK, Jones A. Baclofen: its effectiveness in reducing harmful drinking, craving and negative mood. A meta-analysis. Addiction. 2018;113:1396–406.
Fredericksen P. Baclofen in the treatment of schizophrenia. Lancet. 1975;1:702.
Schöpf J, Hucker H. Baclofen in the treatment of schizophrenia: a pilot study. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol. 1977;10:89–91.
Beckmann H, Frische M, Rüther E, Zimmer R. Baclofen (para-chlorphenyl-GABA) in schizophrenia. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol. 1977;10:26–31.
Davis KL, Hollister LE, Berger PA. Baclofen in schizophrenia. Lancet. 1976;1:1245.
Simpson GM, Branchey MH, Shrivastava RK. Baclofen in schizophrenia. Lancet. 1976;1:966–7.
Gulmann NC, Bahr B, Andersen B, Eliassen HM. A double-blind trial of baclofen against placebo in the treatment of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1976;54:287–93.
Bigelow LB, Nasrallah H, Carman J, Gillin JC, Wyatt RJ. Baclofen treatment in chronic schizophrenia: a clinical trial. Am J Psychiatry. 1977;134:318–20.
Micoulaud-Franchi JA, Aramaki M, Geoffroy PA, Richieri R, Cermolacce M, Faget C, et al. Effect of clozapine on perceptual abnormalities and sensory gating. A preliminary cross-sectional study in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;35:184–7.
Bortolato M, Frau R, Orrù M, Piras AP, Fà M, Tuveri A, et al. Activation of GABA (B) recptors reverses spontaneous gating deficits in juvenile DBA/2J mice. Psychopharmacology. 2007;194:361–9.
Beas BS, Setlow B, Bizon JL. Effect of acute administration of the GABA B receptor agonist on behavioural flexibility in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2016;233:2787–97.
Ilg AK, Enkel T, Bartsch D, Bähner F. Behavioral effects of acute systemic low-dose clozapine in wild-type rats: Implications for the use of DREADDS in behavioural neuroscience. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018;12:173.
Moncrieff J. Does antipsychotic withdrawal provoke psychosis? Review of the literature on rapid onset psychosis (supersensitivity psychosis) and withdrawal–related relapse. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006;114:3–13.
Miller R. Mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs of different classes, refractoriness to therapeutic effects of classical neuroleptics and individual variation in sensitivity to their actions: PART 11. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7:315–30.
Leandre F, Ginory A. A case of baclofen withdrawal induced psychosis treated with lorazepam. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2019;53:174.
Kirubakaran V, Mayfield D, Rengachary S. Dyskinesia and psychosis in a patient following baclofen withdrawal. Am J Psychiatry. 1984;141:692–3.
Arnold ES, Rudd SM, Kirshner H. Manic psychosis following rapid withdrawal from baclofen. Am J Psychiatry. 1980;137:1466–7.
Khokhar JY, Dwiel LL, Henricks AM, Doucette WT, Green AI. The link between schizophrenia and substance use disorder: a unifying hypothesis. Schizophr Res. 2018;194:78–85.
George TP, Sernyak MJ, Ziedonis DM, Woods SW. Effects of clozapine on smoking in chronic schizophrenia outpatients. J Clin Psychiatry. 1995;56:344–6.
Siskind DJ, Harris M, Phillipou A, Morgan VA, Waterreus A, Galletly C, et al. Clozapine users in Australia: their characteristics and experience of care based on data from the 2010 National Survey of High Impact Psychosis. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2017;26:325–37.
Benes FM, McSparren J, Bird ED, SanGiovanni JP, Vincent SL. Deficits in small interneurons in prefrontal and cingulate cortices of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1991;48:996–1001.
Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hagman JO, Tafazzoli A, Bunney WE Jr, et al. Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52:258–66.
Olsen RW, Homanics GE. Function of GABAA receptors: insights from mutant and knockout mice. In: Martin DL, Olsen RW, editors. In GABA in the nervous system: the view at 50 years. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2000. pp. 81–96
Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Mosbacher J, Gassmann M. Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABA(B) receptors. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:835–67.
Bowery NG, Bettler B, Froestl W, Gallagher JP, Marshall F, Raiteri M, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors: structure and function. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:247–64.
Bortolato M, Frau R, Orrù M, Piras AP, Fà M, Tuveri A, et al. Activation of GABA(B) receptors reverses spontaneous gating deficits in juvenile DBA/2J mice. Psychopharmacology. 2007;194:361–9.
Mizukami K, Sasaki M, Ishikawa M, Iwakiri M, Hidaka S, Shiraishi H, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptor in the hippocampus of subjects with schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett. 2000;283:101–4.
Ishikawa M, Mizukami K, Iwakiri M, Asada T. Immunohistochemical and immunoblot analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neurosci Lett. 2005;383:272–7.
Mizukami K, Sasaki M, Ishikawa M, Iwakiri M, Hidaka S, Shiraishi H, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of the gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptor in the hippocampus of subjects with schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2000;283:101–4.
Freedman R, Adams CE, Adler LE, Bickford PC, Gault J, Harris JG, et al. Inhibitory neurophysiological deficit as a phenotype for genetic investigation of schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet. 2000;97:58–64.
Adler LE, Olincy A, Cawthra EM, McRae KA, Harris JG, Nagamoto HT, et al. Varied effects of atypical neuroleptics on P50 auditory gating in schizophrenia patients. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:1822–8.
Liu SK, Fitzgerald PB, Daigle M, Chen R, Daskalakis ZJ. The relationship between cortical inhibition, antipsychotic treatment, and the symptoms of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:503–9.
Kaster TS, de Jesus D, Radhu N, Farzan F, Blumberger DM, Rajji TK, et al. Clozapine potentiation of GABA mediated cortical inhibition in treatment resistant schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2015;165:157–62.
Daskalakis ZJ, Christensen BK, Fitzgerald PB, Moller B, Fountain SI, Chen R. Increased cortical inhibition in persons with schizophrenia treated with clozapine. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22:203–9.
Geng Y, Bush M, Mosyak L, Wang F, Fan QR. Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human GABA(B) receptor. Nature. 2013;504:254–9.
Frangaj A, Fan QR. Structural biology of GABAB receptor. Neuropharmacology. 2018;136:68–79.
Kaupmann K, Huggel K, Heid J, Flor PJ, Bischoff S, Mickel SJ, et al. Expression cloning of GABA(B) receptors uncovers similarity to metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature. 1997;386:239–46.
Malitschek B, Schweizer C, Keir M, Heid J, Froestl W, Mosbacher J, et al. The N-terminal domain of gamma-aminobutyric Acid(B) receptors is sufficient to specify agonist and antagonist binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56:448–54.
Froestl W. Chemistry and pharmacology of GABAB receptor ligands. Adv Pharmacol. 2010;58:19–62.
Wu Y, Blichowski M, Daskalakis ZJ, Wu Z, Liu CC, Cortez MA, et al. Evidence that clozapine directly interacts on the GABAB receptor. Neuroreport. 2011;22:637–41.
Lee J, Takeuchi H, Fervaha G, Sin GL, Foussias G, Agid O, et al. Subtyping schizophrenia by treatment response: antipsychotic development and the central role of positive symptoms. Can J Psychiatry. 2015;60:515–22.
Siskind D, Siskind V, Kisely S. Clozapine response rates among people with treatment resistant schizophrenia: data from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Psychiatry. 2017;62:772–77.
Okhuijsen-Pfeifer C, Huijsman EAH, Hasan A, Sommer IEC, Leucht S, Kahn RS, et al. Clozapine as first- or second-line treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2018;138:281–8.
Jain AN. Surflex: fully automatic flexible molecular docking using a molecular similarity-based search engine. J Med Chem. 2003;46:499–511.
Gasteiger J, Marsili M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron. 1980;36:3219–28.
Powell MJD. Restart procedures for the conjugate gradient method. Math Program. 1977;12:241–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, P.C., McKinnon, R.A., Miners, J.O. et al. Binding of clozapine to the GABAB receptor: clinical and structural insights. Mol Psychiatry 25, 1910–1919 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0709-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0709-5
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review of neuroimaging studies of clozapine-resistant schizophrenia
Schizophrenia (2023)
-
Opposing effects of clozapine and brexpiprazole on β-aminoisobutyric acid: Pathophysiology of antipsychotics-induced weight gain
Schizophrenia (2023)
-
Binding of SEP-363856 within TAAR1 and the 5HT1A receptor: implications for the design of novel antipsychotic drugs
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
A preliminary genetic association study of GAD1 and GABAB receptor genes in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)
-
Pharmacological Targets and Mechanisms of Action of Antipsychotic Substances in the Context of the Neurochemical Theory of the Pathogenesis of Schizophrenia
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2022)