Abstract
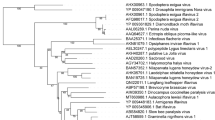
This work identified a novel rhabdo-like virus in a Chinese black cutworm (Agrotis ipsilon), which we tentatively named “Agrotis ipsilon virus” (AIpsV). The complete genome of AIpsV is 15,454 nucleotides in length and contains seven open reading frames, collectively encoding more than 160 amino acids. The AIpsV genome is predicted to encode three structural proteins, nucleoprotein (N), glycoprotein (G), and large polymerase protein (L), and four unknown proteins. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the AIpsV clusters with Wuhan ant virus and Hubei rhabdo-like virus 1 within the rhabdo-like virus clade. The level of expression of AIpsV genes was found to be higher in the pupal and adult stages than in the egg and larval stages.

Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Walker PJ, Blasdell KR, Calisher CH, Dietzgen RG, Kondo H, Kurath G, Longdon B, Stone DM, Tesh RB, Tordo N, Vasilakis N, Whitfield AE (2018) ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Rhabdoviridae. J Gen Virol 99(4):447–448
International Committee Taxonomy of Viruses. Virus Taxonomy: (2018b) Release. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/taxonomy/. Accessed 25 May 2019
Li CX, Shi M, Tian JH, Lin XD, Kang YJ, Chen LJ, Qin XC, Xu J, Holmes EC, Zhang YZ (2015) Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. eLife 4:e05378
Shi M, Lin XD, Tian JH, Chen LJ, Chen X, Li CX, Qin XC, Li J, Cao JP, Eden JS, Buchmann J, Wang W, Xu J, Holmes EC, Zhang YZ (2016) Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 540:539–543
Xie Y, Wu G, Tang J, Luo R, Patterson J, Liu S, Huang W, He G, Gu S, Li S, Zhou X, Lam TW, Li Y, Xu X, Wong GK, Wang J (2014) SOAPdenovo-Trans: de novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 30:1660–1666
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Capella-Gutierrez S, Silla-Martinez JM, Gabaldon T (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25:1972–1973
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32:268–274
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14:587
Funding
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB755703), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31702057 and 31601897), and Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars from Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Grant no. 2020JQ05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Ethical approval
An ethics statement is not required for experiments that involve insect only.
Additional information
Handling Editor: T. K. Frey.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
705_2020_4559_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. S1 Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of members of the order Mononegavirales and chuviruses, based on RdRp protein sequences. The clade corresponding to the family Rhabdoviridae is highlighted. Numbers near nodes indicate ultrafast bootstrap values. The bar indicates the estimated number of substitutions per site
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Li, H., Yuan, G. et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel rhabdo-like virus from the Chinese black cutworm Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Arch Virol 165, 989–991 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04559-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04559-w