Abstract
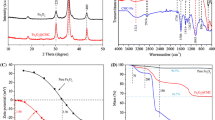
In this study, magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) were produced by a green method, using aqueous extract of spent-tea waste as the reducing agent, which was subsequently used to prepare the magnetic and biodegradable Fe3O4/cellulose nanocomposite. The nanostructures were compared using advanced techniques such as UV–Vis spectrophotometry, Fourier transform infrared, X-ray spectroscopy, imaging by electron microscopy, thermal analysis, and vibrating-sample magnetometery. The data from the analyses showed that the synthesized nanocomposite had a spherical shape with an average particle size of 15.5 nm, which is smaller than the mean (28 nm) of the pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles. These results also showed that the prepared nanocomposite had a higher thermal resistance (450–800 °C) compared to pure cellulose. Another important feature of the nanoscale was the magnetic property (25 emu/g), which was smaller than that obtained in pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles (45 emu/g). In addition, the swelling capacity was studied as one of the functional capabilities of the nanocomposite, which was 139.3 g/g, more than the swell capacity obtained for pure cellulose (66.8 g/g). According to the results, the prepared Fe3O4/cellulose nanocomposite is suggested to be applied in metronidazole drug delivery system regarding its suitable and acceptable properties, such as high absorption capacity, controlled magnetic transferability and biodegradability as well as non-toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Donaldson, L. Tran, L.A. Jimenez, R. Duffin, D.E. Newby, N. Mills, W. MacNee, V. Stone, Combustion-derived nanoparticles: a review of their toxicology following inhalation exposure. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2(10), 1–14 (2005)
E.J. Guidelli, A.P. Ramos, M.E.D. Zaniquelli, O. Baffa, Green synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles using natural rubber latex extracted from Hevea brasiliensis. Spectrochim. Acta A. 82(1), 140–145 (2011)
Y. Li, T.-Y. Wu, S.-M. Chen, M.A. Ali, F.M.A. AlHemaid, Green synthesis and electrochemical characterizations of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Magnolia kobus. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7(12), 12742–12751 (2012)
V.K. Sharma, R.A. Yngard, Y. Lin, Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 145(1–2), 83–96 (2009)
T. Varadavenkatesan, R. Vinayagam, R. Selvaraj, Structural characterization of silver nanoparticles phyto-mediated by a plant waste, seed hull of Vigna mungo and their biological applications. J. Mol. Struct. 1147(5), 629–635 (2017)
S. Iravani, Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 13(10), 2638–2650 (2011)
V.V. Makarov, A.J. Love, O.V. Sinitsyna, S.S. Makarova, I.V. Yaminsky, M.E. Taliansky, N.O. Kalinina, Green nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat 6(1), 35–44 (2014)
N. Kumar, S. Kumbhat, Essentials in nanoscience and nanotechnology (Wiley, Hoboken, 2016)
F.M. Kievit, M. Zhang, Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 44(10), 853–862 (2011)
J. Nam, N. Won, J. Bang, H. Jin, J. Park, S. Jung, S. Jung, Y. Park, S. Kim, Surface engineering of inorganic nanoparticles for imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 65(5), 622–648 (2013)
S. Ahmed, M. Ahmad, B.L. Swami, S. Ikram, A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 7(1), 17–28 (2016)
S. Ahmed, S.A. Chaudhry, S. Ikram, A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: a prospect towards green chemistry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 166, 272–284 (2017)
S. Senapati, Biosynthesis and immobilization of nanopaticles and their applications, Ph.D. thesis, University of Pune, Mumbai, (2005)
I. Hussain, N.B. Singh, A. Singh, H. Singh, S.C. Singh, Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 38(4), 545–560 (2016)
S. Baker, B.P. Harini, D. Rakshith, S. Satish, Marine microbes: invisible nanofactories. J. Pharm. Res. 6(3), 383–388 (2013)
K. Parveen, V. Banse, L. Ledwani, Green synthesis of nanoparticles: their advantages and disadvantages. AIP Conf. Proc. 1724(1), 020048 (2016)
M. Shah, D. Fawcett, S. Sharma, S. Tripathy, G. Poinern, Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials 8(11), 7278–7308 (2015)
D. Ledwith, A. Whelan, J. Kelly, A rapid, straight-forward method for controlling the morphology of stable silver nanoparticles. J. Mate. Chem. 17(23), 2459–2464 (2007)
S.S. Shankar, A. Rai, A. Ahmad, M. Sastry, Controlling the optical properties of lemongrass extract synthesized gold nanotriangles and potential application in infrared-absorbing optical coatings. Chem. Mater. 17(3), 566–572 (2005)
M. Sorbiun, E. Shayegan Mehr, A. Ramazani, A. Mashhadi Malekzadeh, Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts and evaluation of their antibacterial properties. Nanochem. Res. 3(1), 1–16 (2018)
A. Bahadur, S. Iqbal, A. Saeed, M.I. Bashir, M. Shoaib, M. Waqas, G. Shabir, A. Jabbar, Green synthesis of ultrafine super-paramagnetic magnetite nano-fluid: a magnetic and dielectric study. Chem. Pap. 71(8), 1445–1451 (2017)
Y. Cai, Y. Shen, A. Xie, S. Li, X. Wang, A Green synthesis of soya bean sprouts- mediated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(19), 2938–2943 (2010)
N. Latha, M. Gowri, Green synthesis of Cr2O3 nanoparticles using Tridax procumbens leaf extract and its antibacterial. Synthesis 3(47), 1551–1556 (2014)
V.V. Makarov, S.S. Makarova, A.J. Love, O.V. Sinitsyna, A.O. Dudnik, I.V. Yaminsky, M.E. Taliansky, N.O. Kalinina, Biosynthesis of stable iron oxide nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Hordeum vulgare, and Rumex acetosa Plants. Langmuir 30(20), 5982–5988 (2014)
S. Venkateswarlu, B.N. Kumar, B. Prathima, K. Anitha, N.V.V. Jyothi, A novel green synthesis of Fe3O4–Ag core shell recyclable nanoparticles using Vitis vinifera stem extract and its enhanced antibacterial performance. Phys B 457, 30–35 (2015)
C. Prasad, S. Gangadhara, P. Venkateswarlu, Bio-inspired green synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using watermelon rinds and their catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 6(6), 797–802 (2015)
V. Niraimathee, V. Subha, R.E. Ravindran, S. Renganathan, Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles from Mimosa pudica root extract. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Develop. 15(3), 227–240 (2016)
R. López-García, J.L. Herrero, M.E. Barriada, S. de Vicente, Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Development of magnetic hybrid materials for efficient As(V) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 301, 83–91 (2016)
W.H. Li, N. Yang, Green and facile synthesis of Ag–Fe3O4 nanocomposites using the aqueous extract of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves and their antibacterial performance. Mater. Lett. 162, 157–160 (2016)
R.R. Koli, M.R. Phadatare, B.B. Sinha, D.M. Sakate, A.V. Ghule, G.S. Ghodake, N.G. Deshpande, V.J. Fulari, Gram bean extract-mediated synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for tuning the magneto-structural properties that influence the hyperthermia performance. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. 95, 357–365 (2019)
R. Rahmani, M. Gharanfoli, M. Gholamin, M. Darroudi, J. Chamani, K. Sadri, Green synthesis of 99mTc-labeled-Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Quince seeds extract and evaluation of their cytotoxicity and biodistribution in rats. J. Mol. Struct. 1196, 394–402 (2019)
Á. Ruíz-Baltazar, S. Reyes-López, M. Mondragón-Sánchez, A. Robles-Cortés, R. Pérez, Eco-friendly synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles: evaluation of their catalytic activity in methylene blue degradation by kinetic adsorption models. Results Phys. 12, 989–995 (2019)
K.D. Sirdeshpande, A. Sridhar, K.M. Cholkar, R. Selvaraj, Structural characterization of mesoporous magnetite nanoparticles synthesized using the leaf extract of Calliandra haematocephala and their photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye. Appl. Nanosci. 8(4), 675–683 (2018)
Z. Izadiyan, K. Shameli, M. Miyake, H. Hara, S. Eva, B. Mohamad, K. Kalantar, S. Husna, M. Taib, E. Rasouli, Cytotoxicity assay of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Juglans regia green husk extract. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 2011–2023 (2018)
G. Xia, K.O. Reddy, C.U. Maheswari, J. Jayaramudu, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, V. Rajulu, Preparation and properties of biodegradable spent tea leaf powder/poly (propylene carbonate) composite films. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 20(4), 377–387 (2015)
D. Lin, B. Pan, L. Zhu, B. Xing, Characterization and phenanthrene sorption of tea leaf powdersJ. Agric. Food Chem. 55(14), 5718–5724 (2007)
S. Wan, Z. Ma, Y. Xue, M. Ma, S. Xu, L. Qian, Q. Zhang, Sorption of lead(II), cadmium(II), and copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions using tea waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(9), 3629–3635 (2014)
A. Rostami-Vartooni, A. Moradi-Saadatmand, M. Bagherzadeh, M. Mahdavi, Green synthesis of Ag/Fe3O4/ZrO2 nanocomposite using aqueous Centaurea cyanus flower extract and its catalytic application for reduction of organic pollutants Iran. J. Catal. 9(1), 27–35 (2019)
R. Heydari, M. Foroutan Koudehi, S.M. Pourmortazavi, Antibacterial activity of Fe3O4/Cu nanocomposite: Green synthesis using Carum carvi L seeds aqueous extrac. Chem. Select. 4(2), 531–535 (2019)
S.H. Adyani, E. Soleimani, Green synthesis of Ag/Fe3O4/RGO nanocomposites by Punica granatum peel extract: Catalytic activity for reduction of organic pollutants. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44(5), 2711–2730 (2019)
M.K. Satheeshkumar, E. Ranjith Kumar, Ch Srinivas, N. Suriyanarayanan, M. Deepty, C.L. Prajapat, T.V. Chandrasekhar Rao, D.L. Sastry, Study of structural, morphological and magnetic properties Ag substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey assisted combustion method and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469, 691–697 (2019)
S. Mallakpour, M. Hatami, An effective, low-cost and recyclable bio-adsorbent having amino acid intercalated LDH@Fe3O4/PVA magnetic nanocomposites for removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. App. Clay Sci. 174, 127–137 (2019)
Y. Jiao, C. Wan, W. Bao, H. Gao, D. Liang, J. Li, Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@cellulose aerogel nanocomposite and its application in Fenton-like degradation of Rhodamine B. Carbohydr. Polym 189, 371–378 (2018)
Q. Lu, Y. Zhang, H. Hu, W. Wang, Z. Huang, D. Chen, M. Yang, J. Liang, In situ synthesis of a stable Fe3O4@Cellulose nanocomposite for efficient catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Nanomaterials 9(2), 275 (2019)
L.E. Low, B.T. Tey, B.H. Ong, S.Y. Tang, A facile and rapid sonochemical synthesis of monodispersed Fe3O4@cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites without inert gas protection. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng 13(4), e2209 (2018)
D. Shen, J. Liu, L. Gan, N. Huang, M. Long, Green synthesis of Fe3O4/cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol hybride aerogel and its application for dye removal. J. Polym. Environ. 26(6), 2234–2242 (2018)
V. Sadanand, N. Rajini, B. Satyanarayana, A. VaradaRajulu, Polymer/metal nanocomposites by in situ and ex situ generation. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 21, 408–416 (2016)
J. Duan, K. Obi Reddy, A.V. Rajulu, Effects of spent tea leaf powder on the properties and functions of cellulose green composite films. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4(1), 440–448 (2016)
M.M. Khodaei, A. Alizadeh, M. Haghipour, Cellulose/Fe3O4/Co3O4 nanocomposite as a highly efficient and reusable catalyst for the synthesis of 1-((Benzo[d]thiazol-2-ylamino)(aryl)-methyl) naphthalen-2-ol Derivatives. Org. Chem. Res. 4(2), 159–173 (2018)
M. Yadav, Study on thermal and mechanical properties of cellulose/iron oxide bionanocomposites film. Compos. Commun. 10, 1–5 (2018)
L.E. Low, B.T. Tey, B.H. Ong, Unravelling pH-responsive behaviour of Fe3O4@ CNCs-stabilized pickering emulsions under the influence of magnetic field. Carbohydr. Polym 155, 391–399 (2017)
H.Y. Zhu, Y.Q. Fu, R. Jiang, J.H. Jiang, L. Xiao, G.M. Zeng, S.L. Zhao, Y. Wang, Adsorption removal of congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 173(2), 494–502 (2011)
M. Yadollahi, S. Farhoudian, S. Barkhordari, I. Gholamali, H. Farhadnejad, H. Motasadizade, Facile synthesis of chitosan/ZnO bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 82, 273–278 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Our real debt of gratitude goes to Arak University for financial support of this work (Grant No. 98/109 dated 22/7/2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizi, A. Green Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Its Application in Preparation of Fe3O4/Cellulose Magnetic Nanocomposite: A Suitable Proposal for Drug Delivery Systems. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 3552–3561 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01500-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01500-1