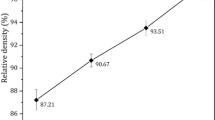
Abstract
In this work, two copper metal matrix composites (MMCs) reinforced with 20 wt.% of Ti(C,N) or Ti2AlN particles were studied. The reinforcement particles were synthesized by flash sintering under 2 bar nitrogen atmosphere causing an SHS reaction ignited by electrical current. This reaction led to produce TiC0.7N0.3 solid solution for the MMC1 reinforcement and Ti2AlN, TiN, and Ti3Al titanium aluminide for the MMC2 reinforcement. Both MMCs were densified by liquid phase sintering. The structural characterization was performed by XRD analysis while the morphology and chemical element distribution of both MMCs were analyzed by SEM and EDS. The structure of the two MMCs was relatively dense and showed good wettability. The mechanical and tribological behavior of MMCs evaluated by nanoindentation and wear testing reveals that the addition of 20 wt.% of reinforcement considerably improves the properties of copper matrix. Indeed, the MMC1 proved to be 3 times harder and 10 times more wear-resistant than the MMC2 composite.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.B. Miracle, Metal Matrix Composites—From Science to Technological Significance, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2005, 65, p 2526–2540
F.J. Lino Alves, A.M. Baptista, and A.T. Marques, Metal Matrix Composites in Aerospace Engineering, Advanced Composite Materials for Aerospace Engineering, S. Rana and R. Fangueiro, Ed., Woodhead Publishing, Elsevier Ltd., 2016, p 59–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100037-3.00003-1
R. M’Saoubi, D. Axinte, S.L. Soo, C. Nobel, H. Attia, G. Kappmeyer, S. Engin, and W.M. Sim, High Performance Cutting of Advanced Aerospace Alloys and Composite Materials, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol., 2015, 64(2), p 557–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2015.05.002
G.S. Hanumanth and G.A. Irons, Solidification of Particle-Reinforced Metal-Matrix Composites, Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci., 1996, 27(4), p 663–671
K.M. Sree Manu, L. Ajay Raag, T.P.D. Rajan, M. Gupta, and B.C. Pai, Liquid Metal Infiltration Processing of Metallic Composites: A Critical Review, Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci., 2016, 47(5), p 2799–2819
S.B. Venkata Siva, K.L. Sahoo, R.I. Ganguly, R.R. Dash, S.K. Singh, B.K. Satpathy, and G. Srinivasarao, Preparation of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite with Novel in Situ Ceramic Composite Particulates, Developed from Waste Colliery Shale Material, Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci., 2013, 44(4), p 800–808
S. Azem, M. Nechiche, and K. Taibi, Development of Copper Matrix Composite Reinforced with FeAl Particles Produced by Combustion Synthesis, Powder Technol., 2011, 208(2), p 515–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2010.08.052
R. Hadian, M. Emamy, and J. Campbell, Modification of Cast Al-Mg2Si Metal Matrix Composite by Li, Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci., 2009, 40(6), p 822–832
A. Mortensen and J. Llorca, Metal Matrix Composites, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2010, 40(1), p 243–270. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-070909-104511
C.M. Ward-Close, R. Minor, and P.J. Doorbar, Intermetallic-Matrix Composites—A Review, Intermetallics, 1996, 9795(95), p 217–229
Y. Liu, Y. Li, F. Li, H. Cui, L. Zhang, and S. Guo, Synthesis and Microstructure of Ti2AlN Ceramic by Thermal Explosion, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43(16), p 13618–13621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.071
T.W.B. Riyadi, T. Zhang, D. Marchant, and X. Zhu, NiAl–TiC–Al2O3 Composite Formed by Self-Propagation High-Temperature Synthesis Process: Combustion Behaviour, Microstructure, and Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 805, p 104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.349
H.C. Yi, Review (Combustion) Synthesis (SHS) of Powder-Compacted Materials, J. Mater. Sci., 1990, 25(2), p 1159–1168
A.G. Merzhanov, History and Recent Developments in SHS, Ceram. Int., 1995, 21(5), p 371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-8842(95)96211-7
M.P. Behera, T. Dougherty, and S. Singamneni, Conventional and Additive Manufacturing with Metal Matrix Composites: A Perspective, Procedia Manuf., 2019, 30, p 159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.02.023
P.K. Deshpande and R.Y. Lin, Wear Resistance of WC Particle Reinforced Copper Matrix Composites and the Effect of Porosity, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 418(1–2), p 137–145
R.N. Caron and A. Sharif, Copper Alloys: Properties and Applications, Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng., Ref, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-803581-8.02562-5
L. Zhou, J. Xiong, Z. Guo, J. Ye, and J. Liu, Tribological Performances of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets with Different Graphite Contents in Dry Sliding Condition, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2017, 68, p 113–120
K. Qi, M. Yang, S. Li, J. Liu, T. Li, and J. Ye, Microstructure and Oxidation Behavior of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets with in Situ Synthesized Ni3Al Phase, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2018, 73, p 157–161
S. Kang, Stability of N in Ti(CN) Solid Solutions for Cermet Applications, Powder Metall., 1997, 40(2), p 139–142. https://doi.org/10.1179/pom.1997.40.2.139
I.J. Jung, S. Kang, S.H. Jhi, and J. Ihm, Study of the Formation of Ti(CN) Solid Solutions, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(11), p 3241–3245
Q. Xu, X. Ai, J. Zhao, W. Qin, Y. Wang, and F. Gong, Comparison of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets Processed by Hot-Pressing Sintering and Conventional Pressureless Sintering, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 619, p 538–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.261
M. Dios, Z. Gonzalez, P. Alvaredo, R. Bermejo, E. Gordo, and B. Ferrari, Novel Colloidal Approach for the Microstructural Improvement in Ti(C, N)/FeNi Cermets, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 724, p 327–338
H. Hu, Y. Cheng, Z. Yin, Y. Zhang, and T. Lu, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Ti(C, N) Based Cermet Cutting Tool Materials Fabricated by Microwave Sintering, Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(10), p 15017–15023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.053
M.W. Barsoum, The MN+1AXN Phases: A New Class of Solids: Thermodynamically Stable Nanolaminates, Prog. Solid State Chem., 2000, 28(1–4), p 201–281
M.W. Barsoum, T. El-Raghy, and A. Procopio, Synthesis of Ti4AIN3 and Phase Equilibria in the Ti-AI-N System, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. A, 2000, 31, p 373–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-0273-1
V.D. Jovic, B.M. Jovic, S. Gupta, T. El-Raghy, and M.W. Barsoum, Corrosion Behavior of Select MAX Phases in NaOH, HCl and H2SO4, Corros. Sci., 2006, 48(12), p 4274–4282
E.S. Choi, J. Sung, Q.M. Wang, K.H. Kim, A. Busnaina, and M.C. Kang, Material Properties and Machining Performance of Hybrid Ti2AlN Bulk Material for Micro Electrical Discharge Machining, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2012, 22(SUPPL.3), p s781–s786. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(12)61804-4
Z.M. Sun, Progress in Research and Development on MAX Phases: A Family of Layered Ternary Compounds, Int. Mater. Rev., 2011, 56(3), p 143–166. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280410Y.0000000001
Y. Liu, L. Zhang, W. Xiao, L. Zhang, Y. Pu, and S. Guo, Rapid Synthesis of Ti2AlN Ceramic via Thermal Explosion, Mater. Lett., 2015, 149, p 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.02.105
Y. Liu, Y. Li, F. Li, H. Cui, Y. Pu, S. Guo, and Z. Shi, Highly Textured Ti2AlN Ceramic Prepared via Thermal Explosion Followed by Edge-Free Spark Plasma Sintering, Scr. Mater., 2017, 136, p 55–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.04.013
F. Lang and Z. Yu, The Corrosion Resistance and Wear Resistance of Thick TiN Coatings Deposited by Arc Ion Plating, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2001, 145(1–3), p 80–87
Z. Yan, D. Jiang, X. Gao, M. Hu, D. Wang, Y. Fu, J. Sun, D. Feng, and L. Weng, Friction and Wear Behavior of TiN Films against Ceramic and Steel Balls, Tribol. Int., 2018, 124, p 61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.03.031
Z.J. Zhan, D.D. Zhang, C.H. Guo, and W. Chai, Tribological Properties of Ti3SnC2/Cu Composite, Key Eng. Mater., 2014, 602–603, p 519–522. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.602-603.519
J. Zhang, J.Y. Wang, and Y.C. Zhou, Structure Stability of Ti3AlC2 in Cu and Microstructure Evolution of Cu-Ti3AlC2 composites, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(13), p 4381–4390
D.D. Zhang, Z.J. Zhan, C.H. Guo, and G.M. Tang, Preparation and Properties of Cu Matrix Reinforced with Ti2AlN Ceramic Particles, Key Eng. Mater., 2014, 602–603, p 523–526. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.602-603.523
ISO 14577, Metallic Materials—Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters—Part 1: Test Method, Int. Organ. Stand., 2002
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7(6), p 1564–1583
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology, J. Mater. Res., 2004, 19(1), p 3–20. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2004.19.1.3
J. Hay, Introduction to Instrumented Indentation Testing, Exp. Tech., 2009, 33(6), p 66–72
G. Constantinides, K.S. Ravi Chandran, F.J. Ulm, and K.J. Van Vliet, Grid Indentation Analysis of Composite Microstructure and Mechanics: Principles and Validation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 430(1–2), p 189–202
J.W. Leggoe, Determination of the Elastic Modulus of Microscale Ceramic Particles via Nanoindentation, J. Mater. Res., 2004, 19(8), p 2437–2447
F.J. Ulm, M. Vandamme, C. Bobko, J. Alberto Ortega, K. Tai, and C. Ortiz, Statistical Indentation Techniques for Hydrated Nanocomposites: Concrete, Bone, and Shale, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(9), p 2677–2692
L. Hultman, Thermal Stability of Nitride Thin Films, Vacuum, 2000, 57(1), p 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-207X(00)00143-3
I.M. Low, W.K. Pang, S.J. Kennedy, and R.I. Smith, High-Temperature Thermal Stability of Ti2AlN and Ti4AlN3: A Comparative Diffraction Study, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 31(1–2), p 159–166
Y. Liu, Z. Shi, J. Wang, G. Qiao, Z. Jin, and Z. Shen, Reactive Consolidation of Layered-Ternary Ti2AlN Ceramics by Spark Plasma Sintering of a Ti/AlN Powder Mixture, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 31(5), p 863–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.11.018
X. Wang, Y. Feng, G. Qian, J. Zhang, Q. Zhang, and F. Ding, A New Core-Shell Ti3AlC2/Cu Composite Powder Prepared by Electroless Plating Method, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 240, p 261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.12.039
O. Dezellus, B. Gardiola, J. Andrieux, and S. Lay, Experimental Evidence of Copper Insertion in a Crystallographic Structure of Ti3SiC2 MAX Phase, Scr. Mater., 2015, 104, p 17–20
M. Nechiche, V. Gauthier-Brunet, V. Mauchamp, A. Joulain, T. Cabioc’h, X. Milhet, P. Chartier, and S. Dubois, Synthesis and Characterization of a New (Ti1-ε, Cuε)3(Al, Cu)C2 MAX Phase Solid Solution, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 37(2), p 459–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.09.028
M.W. Barsoum and M. Radovic, Elastic and Mechanical Properties of the MAX Phases, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2011, 41(1), p 195–227. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-062910-100448
M. Naguib, V.N. Mochalin, M.W. Barsoum, and Y. Gogotsi, 25th Anniversary Article: MXenes: A New Family of Two-Dimensional Materials, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(7), p 992–1005
M. Schloffer, F. Iqbal, H. Gabrisch, E. Schwaighofer, F.P. Schimansky, S. Mayer, A. Stark, T. Lippmann, M. Göken, F. Pyczak, and H. Clemens, Microstructure Development and Hardness of a Powder Metallurgical Multi Phase γ-TiAl Based Alloy, Intermetallics, 2012, 22, p 231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2011.11.015
Y. Liu and Z. Jin, Electric Current Assisted Sintering of Continuous Functionally Graded Ti2AlN/TiN Material, Ceram. Int., 2012, 38(1), p 217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.06.053
S.F. Moustafa, S.A. El-Badry, A.M. Sanad, and B. Kieback, Friction and Wear of Copper-Graphite Composites Made with Cu-Coated and Uncoated Graphite Powders, Wear, 2002, 253(7–8), p 699–710
Acknowledgments
This present research was supported by the MESRS Algerian Ministry and Directorate General for Scientific Research and Technological Development (Algeria). The authors are grateful to the ICD-LASMIS and LaMé laboratories for their characterization support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dehlouz, S., Alhussein, A., Lacroix, F. et al. Self-combustion of Ti-C and Ti-Al Powder Mixture in a Nitrogen Atmosphere: Product Application as Reinforcement in Metal Matrix Composites. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 1984–1994 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04709-w
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04709-w