Abstract
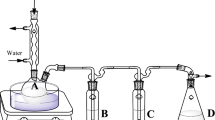
Environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFR) are emerging contaminants of health concern. Their levels in the environment are not well known because few studies have optimized EPFR extraction. Therefore, here we studied the extraction and decay of EPFR that are formed on the surfaces of Cu(II)-montmorillonite clay contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) including benzo[a]pyrene and anthracene. EPFR were analyzed by electron paramagnetic resonance. Results show that acetone or dichloromethane/acetone effectively extract benzo[a]pyrene-EPFR. By contrast, CCl4, acetonitrile or methanol do not extract benzo[a]pyrene-EPFR, but extract residual benzo[a]pyrene at 62.2% for CCl4, 77.8% for acetonitrile and 59.1% for methanol. EPFR concentration decreases with ultrasonic intensity and time, from 60 s at 16 kHz to 1200 s at 40 kHz. The decay of PAH–EPFR in acetone displays two steps, a fast decay from 0 to about 5 h, then a slower decay from 5 to 50 h. The 1/e lifetime during the slow decay period was about 168 h for benzo[a]pyrene-EPFR and 180 h for anthracene-EPFR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas I, Badran G, Verdin A, Ledoux F, Roumié M, Courcot D, Garçon G (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives in airborne particulate matter: sources, analysis and toxicity. Environ Chem Lett 16:439–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0697-0
Chen Q, Sun H, Wang M, Mu Z, Wang Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Z (2018a) Dominant fraction of EPFRs from nonsolvent-extractable organic matter in fine particulates over Xi'an, China. Environ Sci Technol 52:9646–9655. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01980
Chen QC, Wang M, Wang Y, Zhang L, Xue J, Sun H, Mu Z (2018b) Rapid determination of environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) in atmospheric particles with a quartz sheet-based approach using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. Atmos Environ 184:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.04.046
Chen QC, Sun H, Wang M, Wang Y, Zhang L, Han Y (2019) Environmentally persistent free radical (EPFR) formation by visible-light illumination of the organic matter in atmospheric particles. Environ Sci Technol 53:10053–10061. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02327
Gao P, Yao D, Qian Y, Zhong S, Zhang L, Xue G, Jia HZ (2018) Factors controlling the formation of persistent free radicals in hydrochar during hydrothermal conversion of rice straw. Environ Chem Lett 16:1463–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0757-0
Gong X, Shen Z, Zhang Q, Zeng Y, Sun J, Ho SSH, Lei Y, Zhang T, Xu H, Cui S, Huang Y, Cao J (2019) Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) source profiles in urban PM2.5 fugitive dust: a large-scale study for 20 Chinese cites. Sci Total Environ 687:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.099
Jia HZ, Zhao J, Fan XY, Dilimulati K, Wang CY (2012) Photodegradation of phenanthrene on cation-modified clays under visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 123–124:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.017
Jia HZ, Chen H, Nulaji G, Li X, Wang C (2015a) Effect of low-molecular-weight organic acids on photo-degradation of phenanthrene catalyzed by Fe(III)-smectite under visible light. Chemosphere 138:266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.076
Jia HZ, Li L, Chen H, Zhao Y, Li X, Wang C (2015b) Exchangeable cations-mediated photodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on smectite surface under visible light. J Hazard Mater 287:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.040
Jia HZ, Nulaji G, Gao H, Wang F, Zhu Y, Wang CY (2016) Formation and stabilization of environmentally persistent free radicals induced by the interaction of anthracene with Fe(III)-modified clays. Environ Sci Technol 50:6310–6319. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00527
Jia HZ, Zhao S, Shi Y, Zhu L, Wang C, Sharma VK (2018) Transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and formation of environmentally persistent free radicals on modified montmorillonite: the role of surface metal ions and iolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecular properties. Environ Sci Technol 52:5725–5733. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00425
Jia HZ, Zhao S, Shi YF, Zhu KC, Gao P, Zhu L (2019) Mechanisms for light-driven evolution of environmentally persistent free radicals and photolytic degradation of PAHs on Fe(III)-montmorillonite surface. J Hazard Mater 362:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.019
Kiruri LW, Khachatryan L, Dellinger B, Lomnicki S (2014) Effect of copper oxide concentration on the formation and persistency of environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) in particulates. Environ Sci Technol 48:2212–2217. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404013g
Kosnar Z, Mercl F, Perna I, Tlustos P (2016) Investigation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content in fly ash and bottom ash of biomass incineration plants in relation to the operating temperature and unburned carbon content. Sci Total Environ 563–564:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.059
Liu Y, Lee ML (1997) Solid-phase microextraction of PAHs from aqueous samples using fibers coated with HPLC chemically bonded silica stationary phases. Anal Chem 69:5001–5005
Llewellyn C, Doerr S, Douglas P (2004) Soxhlet extraction of organic compounds associated with soil water repellency. Environ Chem Lett 2:41–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-004-0069-4
Lomnicki S, Truong H, Dellinger B (2008) Copper oxide-based model of persistent free radical formation on combustion-derived particulate matter. Environ Sci Technol 42:4982–4988
Miranda AJR, Khan S, Pedrozo MJ, Alexandre KCB, Maciel RM, Escalfoni R, Tristão MLB, Aucelio RQ (2019) Combination of ultrasonic extraction in a surfactant-rich medium and distillation for mercury speciation in offshore petroleum produced waters by gas chromatography cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta 158:105641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2019.105641
Mortland MM, Pinnavaia TJ (1971) Formation of Coupper(II) arene complexes on the interlamellar surfaces of montmorillonite. Nat Phy Sci 229:75–77
Northcott G (2001) Partitioning, extractability, and formation of nonextractable PAH residues in soil. 1. Compound differences in aging and sequestration. Environ Sci Technol 35:1103–1110
Silva SNR (2018) Multiresidue cetermination of carbamate, organophosphate, neonicotinoid and triazole pesticides in roasted coffee using ultrasonic solvent extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Aoac Int 18:324. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.18-0294
Srogi K (2007) Monitoring of environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review. Environ Chem Lett 5:169–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-007-0095-0
Truong H, Lomnicki S, Dellinger B (2010) Potential for misidentification of environmentally persistent free radicals as molecular pollutants in particulate matter. Environ Sci Technol 44:1933–1939
Vejerano E, Lomnicki A, Dellinger B (2011) Formation and stabilization of combustion-generated environmentally persistent free radicals on an Fe(III)2O3/silica surface. Environ Sci Technol 45:589–594
Velali E, Papachristou E, Pantazaki A, Besis A, Samara C, Labrianidis C, Lialiaris T (2018) In vitro cellular toxicity induced by extractable organic fractions of particles exhausted from urban combustion sources—role of PAHs. Environ Pollut 243:1166–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.075
Zhan C, Wan D, Han Y, Zhang J (2019) Historical variation of black carbon and PAHs over the last ~200 years in central North China: evidence from lake sediment records. Sci Total Environ 690:891–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.008
Zhang W, Zheng J, Zheng P, Tsang DCW, Qiu R (2015) The roles of humic substances in the interactions of phenanthrene and heavy metals on the bentonite surface. J Soil Sediment 15:1463–1472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1112-8
Zhang Y, Yang C, Li Y, Huang Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Li Q (2019) Ultrasonic extraction and oxidation characteristics of functional groups during coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel 242:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.01.043
Zhao S, Gao P, Miao D, Wu L, Qian Y, Chen S, Sharma VK, Jia HZ (2019a) Formation and evolution of solvent-extracted and nonextractable environmentally persistent free radicals in aly ash of sunicipal solid waste incinerators. Environ Sci Technol 53:10120–10130. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03453
Zhao S, Miao D, Zhu K, Tao K, Wang C, Sharma VK, Jia HZ (2019b) Interaction of benzo[a]pyrene with Cu(II)-montmorillonite: generation and toxicity of environmentally persistent free radicals and reactive oxygen species. Environ Int 129:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.037
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 41571446 & 41877126), the “Open Project” of the State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse (PCRRF17020), and the “One Hundred Talents” program of Shaanxi Province (SXBR9171) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Zhang, C., Ni, Z. et al. Optimized extraction of environmentally persistent free radicals from clays contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Chem Lett 18, 949–955 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00982-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00982-2