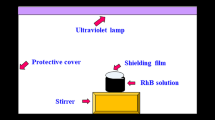
Abstract
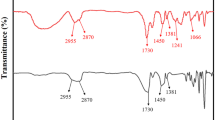
In order to protect the articles in buildings from ultraviolet radiation and save air-conditioning energy, polyvinyl butyral laminated glass are employed and produced in large quantities. Several inorganic particles with blocking effect have been doped into PVB, such as TiO2, ZnO, and ATO. T-ZnOw is a widely used functional structural material with excellent absorption properties. Herein, T-ZnOw was lipophilic modified with silane coupling agent KH-570, and T-ZnOw/PVB composite films were prepared via subsequent solution blending. As per the FTIR spectrum, a characteristic peak of Si–O–Zn at 1165 cm−1 was observed, indicating that T-ZnOw was successfully modified by KH-570. T-ZnOw before and after modification was separately mixed with the St/H2O mixed solution. The modified T-ZnOw could be dispersed in styrene instead of water, displaying a certain lipophilicity. On the other hand, from a microscopic perspective, the SEM images suggest that filling the filler in the form of a suspension can disperse the modified T-ZnOw in PVB in an independent four-needle form, which contributes toward improvement of the agglomeration of T-ZnOw in the PVB matrix. The UV–Vis–NIR spectrum shows that the addition of T-ZnOw reduced the UV transmittance of T-ZnOw/PVB composite films from 50.84 to 25.77%, resulting in a decrease in near-infrared transmittance from 82.14 to 43.22%. The ultraviolet and near-infrared light barrier properties of composite films were more than twice that of the ordinary PVB films. Moreover, the modified T-ZnOw endowed composite films with stronger ultraviolet light and near-infrared light-blocking properties, or better visible light transmittance. And the falling ball impact test proved that there was no clear relationship between the thickness of the film and the adhesion. This work proposes a new solution and preparation method for the production of energy-saving glass. Therefore, it is expected that using composite films instead of traditional PVB films to make laminated glass can greatly contribute toward energy conservation and environmental protection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.S. Luo, J.P. Yang, X.J. Dai et al., Preparation and optical properties of novel transparent Al-doped-ZnO/epoxy nanocomposites. China Ceram. Ind. 113(21), 9406–9411 (2004)
Q.B. Ma, Z.Z. Ye, H.P. He et al., Influence of annealing temperature on the properties of transparent conductive and near-infrared reflective ZnO:Ga films. Scr. Mater. 58(1), 21–24 (2008)
C.G. Granqvist, I. Hamberg, J.S.E.M. Svensson, Window coatings with selective radiative properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 24(1), 93–95 (1985)
S. Schelm, G.B. Smith, P.D. Garrett et al., Tuning the surface-plasmon resonance in nanoparticles for glazing applications. J. Appl. Phys. 97(12), 353-43 (2005)
J. Belis, J. Depauw, D. Callewaert et al., Failure mechanisms and residual capacity of annealed glass/SGP laminated beams at room temperature. Eng. Fail. Anal. 16(6), 1866–1875 (2009)
I.M.D. Rosa, A. Dinescu, F. Sarasini et al., Effect of short carbon fibers and MWCNTs on microwave absorbing properties of polyester composites containing nickel-coated carbon fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(1), 102–109 (2010)
Y. Feng, B. Qiu et al., Absorbing properties and structural design of microwave absorbers based on carbonyl iron and barium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 318(1), 8–13 (2007)
C.H. Peng, C.C. Hwang, J. Wan et al., Microwave-absorbing characteristics for the composites of thermal-plastic polyurethane (TPU)-bonded NiZn-ferrites prepared by combustion synthesis method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 117(1), 27–36 (2005)
A.K. Dhaliwal, J.N. Hay, The characterization of polyvinyl butyral by thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta 391(1–2), 245–255 (2002)
M.A. El-Sherbiny, N.S.A. El-Rehim, Spectroscopic and dielectric behavior of pure and nickel-doped polyvinyl butyral films. Polym. Test. 20(4), 371–378 (2001)
K. Nakane, T. Kurita, T. Ogihara et al., Properties of poly(vinyl butyral)/TiO2 nanocomposites formed by sol–gel process. Compos. Part B (Eng.) 35(3), 219–222 (2004)
M. Alexandre, P. Dubois, Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: preparation, properties and uses of a new class of materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 28(1–2), 1–63 (2000)
A.C. Balazs, T. Emrick, T.P. Russell, Nanoparticle polymer composites: where two small worlds meet. Science 314(5802), 1107–1110 (2006)
P. Wait Kumar, N. Khan, D. Kumar, Polyvinyl butryl (PVB), versatile template for designing nanocomposite/composite materials: a review. Green Chem. Technol. Lett. 2(4), 185–194 (2016)
W. Wang, Y. Yuan, L. Zhang et al., Annealing effects on properties of LaB6/ATO thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 38(5), 4313–4318 (2012)
F. Jiang, Y.K. Leong, M. Saunders et al., Uniform dispersion of lanthanum hexaboride nanoparticles in a silica thin film: synthesis and optical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(11), 5833–5838 (2012)
K. Adachi, M. Miratsu, T. Asahi, Absorption and scattering of near-infrared light by dispersed lanthanum hexaboride nanoparticles for solar control filters. J. Mater. Res. 25(03), 510–521 (2010)
S. Schelm, G.B. Smith, Dilute LaB6 nanoparticles in polymer as optimized clear solar control glazing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82(24), 4346–4348 (2003)
L. Feng, C. Cheng, B.D. Yao et al., Photoluminescence study of single ZnO nanostructures: size effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(5), 323 (2009)
L.C. Chao, S.H. Yang, Growth and Auger electron spectroscopy characterization of donut-shaped ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(17), 7162–7165 (2007)
E.K. Shokr, M.M. Wakkad, H.A.A. El-Ghanny et al., Sb-doping effects on optical and electrical parameters of SnO2 films. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 61(1), 75–85 (2000)
E. Elangovan, K. Ramamurthi, Studies on optical properties of polycrystalline SnO2:Sb thin films prepared using SnCl2 precursor. Cryst. Res. Technol. 38(9), 779–784 (2010)
M.J. Alam, D.C. Cameron, Characterization of transparent conductive ITO thin films deposited on titanium dioxide film by a sol–gel process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 142(01), 776–780 (2001)
N. Al-Dahoudi, M.A. Aegerter, Wet coating deposition of ITO coatings on plastic substrates. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 26(1–3), 693–697 (2003)
H.R. Fallah, M. Ghasemi, A. Hassanzadeh et al., The effect of annealing on structural, electrical and optical properties of nanostructured ITO films prepared by e-beam evaporation. Mater. Res. Bull. 42(3), 487–496 (2007)
D. Wu, J. Liu, Y. Wang, Enhancing indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film adhesiveness using the coupling agent silane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(9), 2934–2938 (2010)
H. Liu, X. Zeng, X. Kong et al., A simple two-step method to fabricate highly transparent ITO/polymer nanocomposite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(22), 8564–8569 (2012)
H. Tang, Y. Su, T. Hu et al., Synergetic effect of LaB6 and ITO nanoparticles on optical properties and thermal stability of poly (vinylbutyral) nanocomposite films. Appl. Phys. A 117(4), 2127–2132 (2014)
Q.X. He, W.P. Tu, J.Q. Hu, Synthesis and characterization of bismuth-doped tin dioxide nanometer powders. J. Central South Univ. 13(5), 519–524 (2006)
L. Cai, G. Jiang, C. Zhu et al., High quality Al-doped ZnO thin films deposited using targets prepared by chemical coprecipitation. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 206(7), 1461–1464 (2009)
G. Hu, Y. Ma, B. Wang, Mechanical properties and morphology of nylon 11/tetrapod-shaped zinc oxide whisker composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 504(1–2), 8–12 (2009)
S. Nie, X. Zhang, J. Luo et al., Synergistic effect of boron nitride and tetrapod-shaped zinc oxide whisker hybrid fillers on filler networks in thermal conductive HDPE composites. Polym. Compos. 38, 1902–1909 (2015)
F.Y. Yuan, H.B. Zhang, X. Li et al., Synergistic effect of boron nitride flakes and tetrapod-shaped ZnO whiskers on the thermal conductivity of electrically insulating phenol formaldehyde composites. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 53, 137–144 (2013)
Z.W. Zhou, S. Hu, L.S. Chu, Studies on tetrapod-shaped ZnO whisker modified polymer composites. Mater. Sci. Forum 475, 1033–1036 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program (No. 20180201075SF) and Jilin Province Development and Reform Commission (No. 2019C043-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Liu, C., Lu, C. et al. Lipophilic modification of T-ZnOw and optical properties of T-ZnOw/PVB composite films. Appl. Phys. A 126, 259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3436-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3436-5