Abstract
Background
The transformation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) into collagen-producing myofibroblasts is a key event in hepatic fibrogenesis. Recent studies have shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) play a critical role in the transformation of HSCs. However, the function of miR-489-3p in liver fibrosis remains unclear.
Methods
Here, we detected the levels of miR-489-3p and jagged canonical Notch ligand 1 (JAG1) in liver fibrosis by using CCl4-treated rats as an in vivo model and transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1)-treated HSC cell lines LX-2 and HSC-T6 as in vitro models. The expression of profibrotic markers was affected by transfecting LX-2 cells with either miR-489-3p mimic or si-JAG1. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was carried out to study the interaction of JAG1 with miR-489-3p.
Results
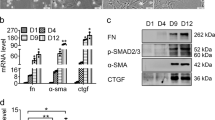
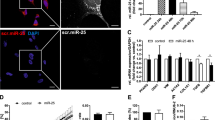
We found that miR-489-3p was remarkably decreased while JAG1 was increased in liver fibrosis models both in vivo and in vitro. Overexpression of miR-489-3p reduced the expression of profibrotic markers and the activation of LX-2 cells induced by TGF-β1. Moreover, miR-489-3p decreased the expression of jagged canonical Notch ligand 1 (JAG1) in LX-2 cells by interacting with its 3ʹ-UTR. As JAG1 is a Notch ligand, decreased JAG1 by miR-489-3p inhibited the Notch signaling pathway. Moreover, the downregulation of JAG1 inhibited the expression of fibrotic markers.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that miR-489-3p can inhibit HSC activation by inhibiting the JAG1/Notch3 signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet (London, England). 2014;383:1749–1761. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60121-5.
Pimpin L, Cortez-Pinto H, Negro F, et al. Burden of liver disease in Europe: epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention policies. J Hepatol. 2018;69:718–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.011.
Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:397–411. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.38.
Puche JE, Saiman Y, Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr Physiol. 2013;3:1473–1492. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c120035.
Tsukada S, Parsons CJ, Rippe RA. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Clinica chimica acta. Int J Clin Chem. 2006;364:33–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2005.06.014.
Pinheiro D, Dias I, Ribeiro Silva K, et al. Mechanisms underlying cell therapy in liver fibrosis: an overview. Cells.. 2019;. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111339.
Meurette O, Mehlen P. Notch Signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell.. 2018;34:536–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.07.009.
Hu B, Phan SH. Notch in fibrosis and as a target of anti-fibrotic therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2016;108:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.04.010.
Edeling M, Ragi G, Huang S, Pavenstadt H, Susztak K. Developmental signalling pathways in renal fibrosis: the roles of Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog. Nature Reviews Nephrology.. 2016;12:426–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.54.
Chen Y, Zheng S, Qi D, et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling by a gamma-secretase inhibitor attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. PloS ONE. 2012;7:e46512. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046512.
Chen YX, Weng ZH, Zhang SL. Notch3 regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:1397–1403. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i12.1397.
Huang M, Chang A, Choi M, Zhou D, Anania FA, Shin CH. Antagonistic interaction between Wnt and Notch activity modulates the regenerative capacity of a zebrafish fibrotic liver model. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md).. 2014;60:1753–1766. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27285.
Condorelli AG, Logli E, Cianfarani F, et al. MicroRNA-145-5p regulates fibrotic features of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa skin fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1017–1027. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.17840.
Chen X, Xiao W, Chen W, et al. MicroRNA-26a and -26b inhibit lens fibrosis and cataract by negatively regulating Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24:1431–1442. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.152.
Zhao S, Xiao X, Sun S, et al. MicroRNA-30d/JAG1 axis modulates pulmonary fibrosis through Notch signaling pathway. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214:1315–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.02.014.
Sawitza I, Kordes C, Reister S, Haussinger D. The niche of stellate cells within rat liver. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md).. 2009;50:1617–1624. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23184.
Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol cell Biol. 2014;15:509–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3838.
Gebert LFR, MacRae IJ. Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol cell Biol. 2019;20:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0045-7.
Piperigkou Z, Gotte M, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK. Insights into the key roles of epigenetics in matrix macromolecules-associated wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;129:16–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.10.008.
Wei S, Wang Q, Zhou H, et al. miR-455-3p alleviates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing HSF1 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;16:758–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.001.
Li J, Qu W, Jiang Y, et al. miR-489 Suppresses proliferation and invasion of human bladder cancer cells. Oncol Res. 2016;24:391–398. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504016x14666990347518.
Wu Q, Han L, Yan W, et al. miR-489 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting MyD88 and Smad3 and is negatively regulated by lncRNA CHRF. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30921. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30921.
Wang K, Liu F, Zhou LY, et al. The long noncoding RNA CHRF regulates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting miR-489. Circ Res. 2014;114:1377–1388. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.302476.
Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet (London, England).. 2013;381:468–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(12)61425-1.
Guruharsha KG, Kankel MW, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The Notch signalling system: recent insights into the complexity of a conserved pathway. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:654–666. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3272.
Huang S, Park J, Qiu C, et al. Jagged1/Notch2 controls kidney fibrosis via Tfam-mediated metabolic reprogramming. PLoS Biol. 2018;16:e2005233. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2005233.
Kopan R, Ilagan MX. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell. 2009;137:216–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.045.
Zhang K, Zhang YQ, Ai WB, et al. Hes1, an important gene for activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and TGF-beta/BMP signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:878–887. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.878.
Guo X, Wang XF. Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 2009;19:71–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.302.
Dewidar B, Meyer C, Dooley S, Meindl-Beinker AN. TGF-beta in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis-updated 2019. Cells. 2019;. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111419.
Funding
This work was supported by the Innovation Cultivation Program of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University [znpy2018095] and the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81670554].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
Ethical approval
The Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Wuhan University School of Medicine approved the animal experimental procedures (permit number: 2017055).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Dong, S., Ye, M. et al. MicroRNA-489-3p Represses Hepatic Stellate Cells Activation by Negatively Regulating the JAG1/Notch3 Signaling Pathway. Dig Dis Sci 66, 143–150 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06174-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06174-w