Abstract
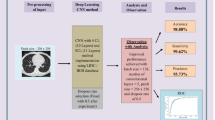
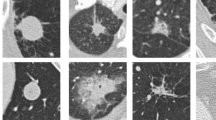
Convolutional neural network (CNN) is one of the deep structured algorithms widely applied to analyze the ability to visualize and extract the hidden texture features of image datasets. The study aims to automatically extract the self-learned features using an end-to-end learning CNN and compares the results with the conventional state-of-art and traditional computer-aided diagnosis system’s performance. The architecture consists of eight layers: one input layer, three convolutional layers and three sub-sampling layers intercepted with batch normalization, ReLu and max-pooling for salient feature extraction, and one fully connected layer that uses softmax function connected to 3 neurons as output layer, classifying an input image into one of three classes categorized as nodules \(\ge\) 3 mm as benign (low malignancy nodules), malignant (high malignancy nodules), and nodules < 3 mm and non-nodules \(\ge\) 3 mm combined as non-cancerous. For the input layer, lung nodule CT images are acquired from the Lung Image Database Consortium public repository having 1018 cases. Images are pre-processed to uniquely segment the nodule region of interest (NROI) in correspondence to four radiologists’ annotations and markings describing the coordinates and ground-truth values. A two-dimensional set of re-sampled images of size 52 \(\times\) 52 pixels with random translation, rotation, and scaling corresponding to the NROI are generated as input samples. In addition, generative adversarial networks (GANs) are employed to generate additional images with similar characteristics as pulmonary nodules. CNNs are trained using images generated by GAN and are fine-tuned with actual input samples to differentiate and classify the lung nodules based on the classification strategy. The pre-trained and fine-tuned process upon the trained network’s architecture results in aggregate probability scores for nodule detection reducing false positives. A total of 5188 images with an augmented image data store are used to enhance the performance of the network in the study generating high sensitivity scores with good true positives. Our proposed CNN achieved the classification accuracy of 93.9%, an average specificity of 93%, and an average sensitivity of 93.4% with reduced false positives and evaluated the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve with the highest observed value of 0.934 using the GAN generated images.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Lung Association Lung Cancer Fact Sheet (2019) https://www.lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/lung-cancer/resource-library/lung-cancer-fact-sheet.html
Abbas Q (2017) Segmentation of differential structures on computed tomography images for diagnosis lung-related diseases. Biomed Signal Process Control 33:325–334
Al-Fahoum AS, Jaber EB, Al-Jarrah MA (2014) Automated detection of lung cancer using statistical and morphological image processing techniques. J Biomed Graph Comput 4(2):33
Amer HM, Abou-Chadi FE, Kishk SS, Obayya MI (2018) A computer-aided early detection system of pulmonary nodules in CT scan images. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on software and information engineering. ACM, pp 81–86
Arabasadi Z, Alizadehsani R, Roshanzamir M, Moosaei H, Yarifard AA (2017) Computer aided decision making for heart disease detection using hybrid neural network-genetic algorithm. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 141:19–26
Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, Choi B, Reicher JJ, Peng L, Tse D, Etemadi M, Ye W, Corrado G et al (2019) End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med 25(6):954
Armato SG III, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP, Zhao B, Aberle DR, Henschke CI, Hoffman EA et al (2011) The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med Phys 38(2):915–931
Arulmurugan R, Anandakumar H (2018) Early detection of lung cancer using wavelet feature descriptor and feed forward back propagation neural networks classifier. In: Computational vision and bio inspired computing. Springer, Berlin, pp 103–110
Bhuvaneswari P, Therese AB (2015) Detection of cancer in lung with k-NN classification using genetic algorithm. Proc Mater Sci 10:433–440
Chuquicusma MJ, Hussein S, Burt J, Bagci U (2018) How to fool radiologists with generative adversarial networks? A visual Turing test for lung cancer diagnosis. In: 2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018). IEEE, pp 240–244
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M et al (2013) The cancer imaging archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging 26(6):1045–1057
da Nóbrega RVM, Rebouças Filho PP, Rodrigues MB, da Silva SP, Júnior CMD, de Albuquerque VHC (2018) Lung nodule malignancy classification in chest computed tomography images using transfer learning and convolutional neural networks. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3895-1
de Carvalho Filho AO, Silva AC, de Paiva AC, Nunes RA, Gattass M (2018) Classification of patterns of benignity and malignancy based on CT using topology-based phylogenetic diversity index and convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit 81:200–212
El-Sherbiny B, Nabil N, El-Naby S.H, Emad Y, Ayman N, Mohiy T, AbdelRaouf A (2018) BLB (brain/lung cancer detection and segmentation and breast dense calculation). In: Deep and representation learning (IWDRL), 2018 first international workshop on. IEEE, pp 41–47
Fernandes SL, Gurupur VP, Lin H, Martis RJ (2017) A novel fusion approach for early lung cancer detection using computer aided diagnosis techniques. J Med Imaging Health Inf 7(8):1841–1850
Firmino M, Morais AH, Mendoça RM, Dantas MR, Hekis HR, Valentim R (2014) Computer-aided detection system for lung cancer in computed tomography scans: review and future prospects. Biomed Eng Online 13(1):41
Ghosh S, Dubey SK (2013) Comparative analysis of k-means and fuzzy c-means algorithms. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 4(4):35–39
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2672–2680
Han H, Li L, Han F, Song B, Moore W, Liang Z (2015) Fast and adaptive detection of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT images using a hierarchical vector quantization scheme. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 19(2):648–659
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Muller NL, Remy J (2008) Fleischner society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246(3):697–722
Hochhegger B, Zanon M, Altmayer S, Pacini GS, Balbinot F, Francisco MZ, Dalla Costa R, Watte G, Santos MK, Barros MC et al (2018) Advances in imaging and automated quantification of malignant pulmonary diseases: a state-of-the-art review. Lung 196(6):633–642
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7132–7141
Hyvärinen A, Oja E (2000) Independent component analysis: algorithms and applications. Neural Netw 13(4–5):411–430
Jacobs C, van Rikxoort EM, Murphy K, Prokop M, Schaefer-Prokop CM, van Ginneken B (2016) Computer-aided detection of pulmonary nodules: a comparative study using the public LIDC/IDRI database. Eur Radiol 26(7):2139–2147
Javaid M, Javid M, Rehman MZU, Shah SIA (2016) A novel approach to CAD system for the detection of lung nodules in CT images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 135:125–139
Kalpana V, Rajini G (2016) Segmentation of lung lesion nodules using dicom with structuring elements and noise—a comparative study. In: Electrical, computer and electronics engineering (UPCON), 2016 IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section international conference on. IEEE, pp 252–257
Kaul C, Manandhar S, Pears N (2019) Focusnet: an attention-based fully convolutional network for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.03091
Korkmaz S.A, Akçiçek A, Bínol H, Korkmaz M.F (2017) Recognition of the stomach cancer images with probabilistic hog feature vector histograms by using hog features. In: Intelligent systems and informatics (SISY), 2017 IEEE 15th international symposium on. IEEE, pp 000339–000342
Kuruvilla J, Gunavathi K (2014) Lung cancer classification using neural networks for CT images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 113(1):202–209
Lampert TA, Stumpf A, Gançarski P (2016) An empirical study into annotator agreement, ground truth estimation, and algorithm evaluation. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(6):2557–2572
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Li C, Zhu G, Wu X, Wang Y (2018) False-positive reduction on lung nodules detection in chest radiographs by ensemble of convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 6:16060–16067
Lindsay W, Wang J, Sachs N, Barbosa E, Gee J (2018) Transfer learning approach to predict biopsy-confirmed malignancy of lung nodules from imaging data: a pilot study. In: Image analysis for moving organ, breast, and thoracic images. Springer, Berlin, pp 295–301
Lu L, Yapeng L, Hongyuan Z (2018) Benign and malignant solitary pulmonary nodules classification based on CNN and SVM. In: Proceedings of the international conference on machine vision and applications. ACM, pp 46–50
Makaju S, Prasad P, Alsadoon A, Singh A, Elchouemi A (2018) Lung cancer detection using CT scan images. Proc Comput Sci 125:107–114
Manikandan T, Bharathi N (2016) A survey on computer-aided diagnosis systems for lung cancer detection. Int Res J Eng Technol 3(5):1562–70
Masood A, Sheng B, Li P, Hou X, Wei X, Qin J, Feng D (2018) Computer-assisted decision support system in pulmonary cancer detection and stage classification on CT images. J Biomed Inf 79:117–128
Nguyen T, Khosravi A, Creighton D, Nahavandi S (2015) Classification of healthcare data using genetic fuzzy logic system and wavelets. Expert Syst Appl 42(4):2184–2197
Nishio M, Sugiyama O, Yakami M, Ueno S, Kubo T, Kuroda T, Togashi K (2018) Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodule classification between benign nodule, primary lung cancer, and metastatic lung cancer at different image size using deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning. PLoS ONE 13(7):e0200721
Obayya M, Ghandour M (2015) Lung cancer classification using curvelet transform and neural network with radial basis function. Int J Comput Appl 120(13):33–37
Orozco HM, Villegas OOV, Sánchez VGC, Domínguez HdJO, Alfaro MdJN (2015) Automated system for lung nodules classification based on wavelet feature descriptor and support vector machine. Biomed Eng Online 14(1):9
Ozekes S, Osman O (2010) Computerized lung nodule detection using 3D feature extraction and learning based algorithms. J Med Syst 34(2):185–194
Rastegari M, Ordonez V, Redmon J, Farhadi A (2016) Xnor-net: imagenet classification using binary convolutional neural networks. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Berlin, pp 525–542
Roth HR, Lu L, Liu J, Yao J, Seff A, Cherry K, Kim L, Summers RM (2015) Improving computer-aided detection using convolutional neural networks and random view aggregation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1170–1181
Roth HR, Lu L, Liu J, Yao J, Seff A, Cherry K, Kim L, Summers RM (2016) Improving computer-aided detection using convolutional neural networks and random view aggregation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1170–1181
Saad M.N, Muda Z, Ashaari N.S, Hamid H.A (2014) Image segmentation for lung region in chest X-ray images using edge detection and morphology. In: Control system, computing and engineering (ICCSCE), 2014 IEEE international conference on. IEEE, pp 46–51
Serj M.F, Lavi B, Hoff G, Valls D.P (2018) A deep convolutional neural network for lung cancer diagnostic. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.08170
Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Litjens G, Gerke P, Jacobs C, Van Riel SJ, Wille MMW, Naqibullah M, Sánchez CI, van Ginneken B (2016) Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1160–1169
Shen W, Zhou M, Yang F, Yu D, Dong D, Yang C, Zang Y, Tian J (2017) Multi-crop convolutional neural networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recognit 61:663–673
Shi Z, Hao H, Zhao M, Feng Y, He L, Wang Y, Suzuki K (2019) A deep cnn based transfer learning method for false positive reduction. Multimed Tools Appl 78(1):1017–1033
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Sun W, Zheng B, Qian W (2017) Automatic feature learning using multichannel roi based on deep structured algorithms for computerized lung cancer diagnosis. Comput Biol Med 89:530–539
Takahashi R, Kajikawa Y (2017) Computer-aided diagnosis: a survey with bibliometric analysis. Int J Med Inf 101:58–67
Tan J, Huo Y, Liang Z, Li L (2017) Apply convolutional neural network to lung nodule detection: recent progress and challenges. In: International conference on smart health. Springer, Berlin, pp 214–222
Team NLSTR (2011) Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med 365(5):395–409
Wan S, Lee HC, Huang X, Xu T, Xu T, Zeng X, Zhang Z, Sheikine Y, Connolly JL, Fujimoto JG et al (2017) Integrated local binary pattern texture features for classification of breast tissue imaged by optical coherence microscopy. Med Image Anal 38:104–116
Wikipedia Contributors (2018) Cellular neural network—Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cellular_neural_network&oldid=869201596. Accessed 31 Dec 2018
Wikipedia contributors (2018) Deep learning— Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Deep_learning&oldid=875207371. Accessed 31 Dec 2018
Woźniak M, Połap D, Capizzi G, Sciuto GL, Kośmider L, Frankiewicz K (2018) Small lung nodules detection based on local variance analysis and probabilistic neural network. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 161:173–180
Xie H, Yang D, Sun N, Chen Z, Zhang Y (2019) Automated pulmonary nodule detection in CT images using deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit 85:109–119
Zeng JY, Ye HH, Yang SX, Jin RC, Huang QL, Wei YC, Huang SG, Wang BQ, Ye JZ, Qin JY (2015) Clinical application of a novel computer-aided detection system based on three-dimensional CT images on pulmonary nodule. International J Clin Exp Med 8(9):16077
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh, S., Mohan, S. ROI-based feature learning for efficient true positive prediction using convolutional neural network for lung cancer diagnosis. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 15989–16009 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04787-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04787-w