Abstract
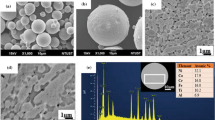
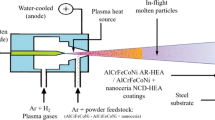
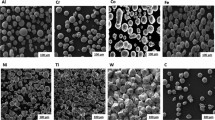
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have been deliberated as potential matrix material for self-lubricating composites due to their excellent mechanical properties. In this study, the Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti HEA powders with a face-centered cubic structure were prepared by mechanical alloying. Then, the alloyed HEA powders were sintered at 700 °C to achieve sprayed powder with suitable particle size. Next, the Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti HEA-based composite coating was plasma sprayed on carbon steel by combining Ag. Dry friction experiment was applied in order to investigate the tribological properties of HEA − Ag composite coating at temperatures ranging from 25 to 750 °C. The composite coating that was sprayed with HEA − Ag exhibited a low friction coefficient (0.253) and a relatively low wear rate (8.9 × 10−6 mm3/Nm) at 750 °C. Furthermore, the HEA + Ag coating obtained an increased hardness and superior tribological properties after high temperature annealing. The dense, continuous oxide layer that was formed tightly covered the coating surface and combined with the lubrication of Ag clusters to protect the underlying materials from wear loss at high temperatures.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.E. Sliney, Solid Lubricant Materials for High Temperatures: A Review, Tribol. Int., 1985, 15(5), p 303–315
C.C. Baker, R.R. Chromik, K.J. Wahl et al., Preparation of Chameleon Coatings for Space and Ambient Environments, Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(17), p 6737–6743
W. Wang, Application of a High Temperature Self-lubricating Composite Coating on Steam Turbine Components, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2004, 177, p 12–17
Z. Xu, Q. Zhang, X. Huang et al., An Approximate Model for the Migration of Solid Lubricant on Metal Matrix Self-lubricating Composites, Tribol. Int., 2016, 93, p 104–114
J.E. Mogonye, A. Srivastava, S. Gopagoni et al., Solid/Self-lubrication Mechanisms of an Additively Manufactured Ni-Ti-C Metal Matrix Composite, Tribol. Lett., 2016, 64(3), p 37
H.S. Maharana, A. Basu, and K. Mondal, Structural and Tribological Correlation of Electrodeposited Solid Lubricating Ni-WSe2 Composite Coating, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 349, p 328–339
J. Zhen, J. Cheng, M. Li et al., Lubricating Behavior of Adaptive Nickel Alloy Matrix Composites with Multiple Solid Lubricants from 25 to 700 °C, Tribol. Int., 2017, 109, p 174–181
B. Li, J. Jia, Y. Gao et al., Microstructural and Tribological Characterization of NiAl Matrix Self-lubricating Composite Coatings by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying, Tribol. Int., 2017, 109, p 563–570
Y. Xiao, X. Shi, W. Zhai et al., Effect of Temperature on Tribological Properties and Wear Mechanisms of NiAl Matrix Self-lubricating Composites Containing Graphene Nanoplatelets, Tribol. Trans., 2015, 58(4), p 729–735
S. Zhu, F. Li, J. Ma et al., Tribological Properties of Ni3Al Matrix Composites with Addition of Silver and Barium Salt, Tribol. Int., 2015, 84, p 118–123
M.H. Chuang, M.H. Tsai, W.R. Wang et al., Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 6308–6317
C.J. Tong, Y.L. Chen, J.W. Yeh et al., Microstructure Characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy System with Multiprincipal Elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36(4), p 881–893
X.W. Qiu and C.G. Liu, Microstructure and Properties of Al2CrFeCoCuTiNix High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Laser Cladding, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 553, p 216–220
S. Zhang, C.L. Wu, J.Z. Yi et al., Synthesis and Characterization of FeCoCrAlCu High-Entropy Alloy Coating by Laser Surface Alloying, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 262, p 64–69
S. Varalakshmi, G.A. Rao, M. Kamaraj et al., Hot Consolidation and Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline Equiatomic AlFeTiCrZnCu High Entropy Alloy after Mechanical Alloying, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45(19), p 5158–5163
F. He, Z. Wang, Q. Wu et al., Phase Separation of Metastable CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy at Intermediate Temperatures, Scr. Mater., 2017, 126, p 15–19
S. Praveen, J. Basu, S. Kashyap et al., Exceptional Resistance to Grain Growth in Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy at High Homologous Temperatures, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 662, p 361–367
S. Jiang, Z. Lin, H. Xu et al., Studies on the Microstructure and Properties of AlxCoCrFeNiTi1−x High Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 741, p 826–833
T. Fujieda, H. Shiratori, K. Kuwabara et al., CoCrFeNiTi-Based High-Entropy Alloy with Superior Tensile Strength and Corrosion Resistance Achieved by a Combination of Additive Manufacturing Using Selective Electron Beam Melting and Solution Treatment, Mater. Lett., 2017, 189, p 148–151
T.T. Shun, L.Y. Chang, and M.H. Shiu, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Multiprincipal Component CoCrFeNiTix Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 556, p 170–174
P.K. Huang, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun et al., Multi Principal Element Alloys with Improved Oxidation and Wear Resistance for Thermal Spray Coating, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6(1–2), p 74–78
D.J.M. King, S.C. Middleburgh, A.G. Mcgregor et al., Predicting the Formation and Stability of Single Phase High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2016, 104, p 172–179
A.S.M. Ang, C.C. Berndt, M.L. Sesso et al., Plasma-Sprayed High Entropy Alloys: Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNi and MnCoCrFeNi, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46(2), p 791–800
W. Ji, W. Wang, H. Wang et al., Alloying Behavior and Novel Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering, Intermetallics, 2015, 56, p 24–27
P.F. Yu, L.J. Zhang, H. Cheng et al., The High-Entropy Alloys with High Hardness and Soft Magnetic Property Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and High-Pressure Sintering, Intermetallics, 2016, 70, p 82–87
L.S. Wang, S.L. Zhang, T. Liu et al., Dominant Effect of Particle Size on the CeO2 Preferential Evaporation During Plasma Spraying of La2Ce2O7, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 37(4), p 1577–1585
I. Hwang, J. Jeong, K. Lim et al., Microstructural Characterization of Spray-Dried NiO-8YSZ Particles as Plasma Sprayable Anode Materials for Metal-Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cell, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43(10), p 7728–7735
S. Sivakumar, K. Praveen, and G. Shanmugavelayutham, Preparation and Thermophysical Properties of Plasma Sprayed Lanthanum Zirconate, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2018, 204, p 67–71
J.W. Yeh, S.Y. Chang, Y.D. Hong et al., Anomalous Decrease in X-Ray Diffraction Intensities of Cu-Ni-Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Si Alloy Systems with Multi-principal Elements, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2007, 103(1), p 41–46
H.X. Sui, M. Zhu, M. Qi et al., Erratum: The Enhancement of Solid Solubility Limits of AlCo Intermetallic Compound by High-Energy Ball Milling, J. Appl. Phys., 1993, 71, p 2945
B.L. Huang, R.J. Perez, E.J. Lavernia et al., Formation of Supersaturated Solid Solutions by Mechanical Alloying, Nanostruct. Mater., 1996, 7, p 67–79
A.R. Yavari, P.J. Desrã, and T. Benameur, Mechanically Driven Alloying of Immiscible Elements, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1992, 68(14), p 2235–2238
S. Guo, C. Ng, Z. Wang et al., Solid Solutioning in Equiatomic Alloys: Limit Set by Topological Instability, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 583(1), p 410–413
K. Radil and C. DellaCorte, The Performance of PS400 Subjected to Sliding Contact at Temperatures from 260 to 927 K, Tribol. Trans., 2017, 60(6), p 957–964
C.D. Corte, M.K. Stanford, F. Thomas, and B.J. Edmonds, “The Effect of Composition on the Surface Finish of PS400: A New High Temperature Solid Lubricant Coating,” NASA-TM-2010-216774, 2010.
F.H. Stott, The Role of Oxidation in the Wear of Alloys, Tribol. Int., 1998, 31(1–3), p 61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(98)00008-5
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51101087) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 30917014106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Li, J., Yan, C. et al. Microstructure and Tribological Properties of Plasma-Sprayed Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti-Ag Composite Coating from 25 to 750 °C. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 1640–1649 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04700-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04700-5