Abstract
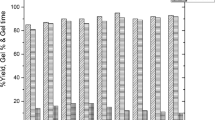
The TiO2 dispersed physically cross-linked polymer hydrogels were synthesized through a single step free radical addition polymerization mechanism based on acrylic acid and gum Arabic (GA) as polymer constituents, and ferric ions (Fe3+) as physical cross-linker. The effect of TiO2 powder was investigated on thermal and mechanical properties of the hydrogels by dispersion of 0.01, 0.02 and 0.03 g of TiO2 in hydrogels. The prepared hydrogels were successfully characterized through FTIR, XRD, SEM and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). For the mechanical properties, dynamic mechanical analysis and universal testing machine (UTM) were used. The DMA results showed that the storage modulus was increased with the TiO2, while UTM results showed that 0.02 g of TiO2 powder significantly enhanced the fracture stress, elastic modulus, toughness and stretchability by 4514%, 4328%, 4124% and 20%, respectively, compared to the virgin hydrogels. Cole–Cole plot confirmed the homogeneity and viscoelastic behavior of the system, while manual load bearing and shape memory test showed that the hydrogels bear a load of 2.5 kg for a long time and it is recovered within 10 s to its original state. The materials can be applied for the synthesis of artificial body parts in the field of bio-engineering. The use of un-modified GA for the synthesis of hydrogels will open a new window for the researchers working in this field.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudnik E (2019) Compostable polymer materials. Newnes, Elseveir
Hajebi S, Rabiee N, Bagherzadeh M, Ahmadi S, Rabiee M, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Tahriri M, Tayebi L, Hamblin MR (2019) Stimulus-responsive polymeric nanogels as smart drug delivery systems. Acta Biomater 92:1–18
Rabiee N, Rabiee M, Bagherzadeh M, Hamblin MR (2019) Stimuli-responsive polymers: nano-dimension. Morgan & Claypool Publishers, San Rafael
Cheng C, Xia D, Zhang X, Chen L, Zhang Q (2015) Biocompatible poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-g-carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels as carriers for sustained release of cisplatin. J Mater Sci 50:4914–4925
Patil SB, Inamdar SZ, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Soni SK, Kulkarni RV (2019) Novel biocompatible poly(acrylamide)-grafted-dextran hydrogels: synthesis, characterization and biomedical applications. J Microbiol Methods 159:200–210
Strange DG, Oyen ML (2012) Composite hydrogels for nucleus pulposus tissue engineering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 11:16–26
Jia H, Huang Z, Fei Z, Dyson PJ, Zheng Z, Wang X (2016) Unconventional tough double-network hydrogels with rapid mechanical recovery, self-healing, and self-gluing properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:31339–31347
Hu Y, Du Z, Deng X, Wang T, Yang Z, Zhou W, Wang C (2016) Dual physically cross-linked hydrogels with high stretchability, toughness, and good self-recoverability. Macromolecules 49:5660–5668
Shah M, Shah LA, Khan MS, Nasar MQ, Rasheed S (2019) Synthesis, fabrication and characterization of polymer microgel/photochromic dye-based sandwiched sensors. Iran Polym J 28:1–11
Shah LA, Haleem A, Sayed M, Siddiq M (2016) Synthesis of sensitive hybrid polymer microgels for catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3492–3497
Shah LA (2019) Developing Ag-tercopolymer microgels for the catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol and EosinY throughout the entire pH range. J Mol Liq 288:111045
Javed R, Shah LA, Sayed M, Khan MS (2018) Uptake of heavy metal ions from aqueous media by hydrogels and their conversion to nanoparticles for generation of a catalyst system: two-fold application study. RSC Adv 8:14787–14797
Xing L, Ma Y, Tan H, Yuan G, Li S, Li J, Jia Y, Zhou T, Niu X, Hu X (2019) Alginate membrane dressing toughened by chitosan floccule to load antibacterial drugs for wound healing. Polym Test 79:106039
Smith TJ, Kennedy JE, Higginbotham CL (2010) Rheological and thermal characteristics of a two phase hydrogel system for potential wound healing applications. J Mater Sci 45:2884–2891
Li J, Illeperuma WR, Suo Z, Vlassak JJ (2014) Hybrid hydrogels with extremely high stiffness and toughness. ACS Macro Lett 3:520–523
Chavoshi S, Rabiee M, Rafizadeh M, Rabiee N, Shamsabadi AS, Bagherzadeh M, Salarian R, Tahriri M, Tayebi L (2019) Mathematical modeling of drug release from biodegradable polymeric microneedles. Bio-Design Manuf 2:96–107
Bian H, Jiao L, Wang R, Wang X, Zhu W, Dai H (2018) Lignin nanoparticles as nano-spacers for tuning the viscoelasticity of cellulose nanofibril reinforced polyvinyl alcohol-borax hydrogel. Eur Polym J 107:267–274
Jiang H, Duan L, Ren X, Gao G (2018) Hydrophobic association hydrogels with excellent mechanical and self-healing properties. Eur Polym J 112:660–669
Liu C, Tan Y, Xu K, Hua M, Huo X-H, Sun Y-S (2018) A novel designed high strength and thermoresponsive double network hydrogels cross-linked by starch-based microspheres. Iran Polym J 27:889–897
Li X, Zhang Y, Yang Q, Li D, Zhang G, Long S (2018) Agar/PAAc-Fe3+ hydrogels with pH-sensitivity and high toughness using dual physical cross-linking. Iran Polym J 27:829–840
Shah LA, Khan M, Javed R, Sayed M, Khan MS, Khan A, Ullah M (2018) Superabsorbent polymer hydrogels with good thermal and mechanical properties for removal of selected heavy metal ions. J Clean Prod 201:78–87
Hu J, Kurokawa T, Hiwatashi K, Nakajima T, Wu ZL, Liang SM, Gong JP (2012) Structure optimization and mechanical model for microgel-reinforced hydrogels with high strength and toughness. Macromolecules 45:5218–5228
Martin N, Youssef G (2018) Dynamic properties of hydrogels and fiber-reinforced hydrogels. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 85:194–200
Zhou C, Wu Q, Yue Y, Zhang Q (2011) Application of rod-shaped cellulose nanocrystals in polyacrylamide hydrogels. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 353:116–123
Huang T, Xu H, Jiao K, Zhu L, Brown HR, Wang H (2007) A novel hydrogel with high mechanical strength: a macromolecular microsphere composite hydrogel. Adv Mater 19:1622–1626
Xing L, Hu C, Zhang Y, Wang X, Shi L, Ran R (2019) A mechanically robust double-network hydrogel with high thermal responses via doping hydroxylated boron nitride nanosheets. J Mater Sci 54:3368–3382
Le X, Lu W, Xiao H, Wang L, Ma C, Zhang J, Huang Y, Chen T (2017) Fe3+-, pH-, thermoresponsive supramolecular hydrogel with multishape memory effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:9038–9044
Sun J-Y, Zhao X, Illeperuma WR, Chaudhuri O, Oh KH, Mooney DJ, Vlassak JJ, Suo Z (2012) Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 489:133–136
Lin P, Ma S, Wang X, Zhou F (2015) Molecularly engineered dual-crosslinked hydrogel with ultrahigh mechanical strength, toughness, and good self-recovery. Adv Mater 27:2054–2059
Huang S, Zhao Z, Feng C, Mayes E, Yang J (2018) Nanocellulose reinforced P(AAm-co-AAc) hydrogels with improved mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Compos A 112:395–404
Chen Q, Zhu L, Chen H, Yan H, Huang L, Yang J, Zheng J (2015) A novel design strategy for fully physically linked double network hydrogels with tough, fatigue resistant, and self-healing properties. Adv Funct Mater 25:1598–1607
Wu D, Xu J, Chen Y, Yi M, Wang Q (2018) Gum Arabic: a promising candidate for the construction of physical hydrogels exhibiting highly stretchable, self-healing and tensility reinforcing performances. Carbohydr Polym 181:167–174
Reddy KR, Karthik K, Prasad SB, Soni SK, Jeong HM, Raghu AV (2016) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of nanostructured titanium dioxide/polyaniline hybrid photocatalysts. Polyhedron 120:169–174
Basavarajappa PS, Patil SB, Ganganagappa N, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Reddy CV (2019) Recent progress in metal-doped TiO2, non-metal doped/codoped TiO2 and TiO2 nanostructured hybrids for enhanced photocatalysis. Int J Hydrogen Energy (in press)
Patil SB, Basavarajappa PS, Ganganagappa N, Jyothi M, Raghu A, Reddy KR (2019) Recent advances in non-metals-doped TiO2 nanostructured photocatalysts for visible-light driven hydrogen production, CO2 reduction and air purification. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:13022–13039
Chougale R, Kasai D, Nayak S, Masti S, Nasalapure A, Raghu AV (2019) Design of eco-friendly PVA/TiO2-based nanocomposites and their antifungal activity study. Green Mater. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgrma.19.00002
Sarika P, Cinthya K, Jayakrishnan A, Anilkumar P, James NR (2014) Modified gum arabic cross-linked gelatin scaffold for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C 43:272–279
Tsai R-Y, Kuo T-Y, Hung S-C, Lin C-M, Hsien T-Y, Wang D-M, Hsieh H-J (2015) Use of gum arabic to improve the fabrication of chitosan–gelatin-based nanofibers for tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 115:525–532
Fan J, Shi Z, Wang J, Yin J (2013) Glycidyl methacrylate-modified gum arabic mediated graphene exfoliation and its use for enhancing mechanical performance of hydrogel. Polymer 54:3921–3930
Reis AV, Moia TA, Sitta DL, Mauricio MR, Tenório-Neto ET, Guilherme MR, Rubira AF, Muniz EC (2016) Sustained release of potassium diclofenac from a pH-responsive hydrogel based on gum arabic conjugates into simulated intestinal fluid. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43319
Suhas D, Jeong H, Aminabhavi T, Raghu A (2014) Preparation and characterization of novel polyurethanes containing 4,4′-{oxy-1,4-diphenyl bis(nitromethylidine)} diphenol schiff base diol. Polym Eng Sci 54:24–32
Raghu A, Gadaginamath G, Priya M, Seema P, Jeong HM, Aminabhavi T (2008) Synthesis and characterization of novel polyurethanes based on N1, N4-bis[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylene] succinohydrazide hard segment. J Appl Polym Sci 110:2315–2320
Liew CW, Ng HM, Numan A, Ramesh S (2016) Poly(acrylic acid)-based hybrid inorganic-organic electrolytes membrane for electrical double layer capacitors application. Polymers 8:179
Zohuriaan-Mehr MJ, Motazedi Z, Kabiri K, Ershad-Langroudi A (2005) New super-absorbing hydrogel hybrids from gum arabic and acrylic monomers. J Macromol Sci 42:1655–1666
Begum R, Naseem K, Ahmed E, Sharif A, Farooqi ZH (2016) Simultaneous catalytic reduction of nitroarenes using silver nanoparticles fabricated in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-acrylic acid-acrylamide) microgels. Colloid Surf A 511:17–26
Nesrinne S, Djamel A (2017) Synthesis, characterization and rheological behavior of pH sensitive poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Arab J Chem 10:539–547
Killion JA, Geever LM, Devine DM, Kennedy JE, Higginbotham CL (2011) Mechanical properties and thermal behaviour of PEGDMA hydrogels for potential bone regeneration application. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4:1219–1227
Ornaghi HL, Zattera AJ, Amico SC (2015) Dynamic mechanical properties and correlation with dynamic fragility of sisal reinforced composites. Polym Compos 36:161–166
Rolere S, Cartault M, Sainte-Beuve J, Bonfils F (2017) A rheological method exploiting Cole-Cole plot allows gel quantification in natural rubber. Polym Test 61:378–385
Pothan LA, Oommen Z, Thomas S (2003) Dynamic mechanical analysis of banana fiber reinforced polyester composites. Compos Sci Technol 63:283–293
Acknowledgement
The authors are highly grateful to Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan for financial support under Grant No. 7309.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Shah, L.A., Rehman, T. et al. Synthesis of physically cross-linked gum Arabic-based polymer hydrogels with enhanced mechanical, load bearing and shape memory behavior. Iran Polym J 29, 351–360 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-020-00801-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-020-00801-z