Abstract
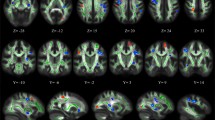
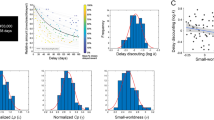
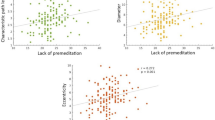
Studies that investigated neurobiological parameters subtended to impulsivity trait found their relationship with structural and functional brain alterations. No studies investigated the white matter microstructural attributes of impulsivity in a large sample of healthy subjects. In the present study 1007 subjects from Human Connectome Project public dataset were divided in two groups, impulsive and not impulsive, basing on Delay Discounting task score. For both groups brain morphometric and microstructural characteristics were investigated. A t-test (correct for multiple comparisons) was performed for each brain parcel and impulsivity measure. Magnetic resonance diffusion images were pre-processed and selected to perform a voxelwise analysis on the fractional anisotropy (FA) maps between impulsive and not impulsive groups. Group analysis showed significant differences in morphometric brain data mainly for temporal and frontal lobes. The impulsive group presented higher FA values in four regions: bilateral medial lemniscus and midbrain reticular formation, right superior longitudinal fasciculus, left forceps major, right corticospinal tract. Not impulsive group showed higher FA values in two significant regions: right and left anterior thalamus radiation. Concluding, macroscopic and microstructural brain alterations were assessed, identifying new neuroanatomical substrates for multidimensional impulsivity construct in a large sample of healthy subjects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achterberg, M., Peper, J. S., van Duijvenvoorde, A. C., Mandl, R. C., & Crone, E. A. (2016). Frontostriatal white matter integrity predicts development of delay of gratification: A longitudinal study. Journal of Neuroscience, 10(6), 1954–1961. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3459-15.2016.
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., & Field, A. S. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics, 4, 316–329.
Alicata, D., Chang, L., Cloak, C., Abe, K., & Ernst, T. (2009). Higher diffusion in striatum and lower fractional anisotropy in white matter of methamphetamine users. Psychiatry Research, 174, 1–8.
Amlung, M., Vedelago, L., Acker, J., Balodis, I., & Mackillop, J. (2017). Steep delay discounting and addictive behavior: A meta-analysis of continuous associations. Addiction, 112(1), 51–62.
Andres, T., Ernst, T., Oishi, K., Greenstein, D., Nakama, H., & Chang, L. (2016). Brain microstructure and impulsivity differ between current and past methamphetamine users. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology, 11(3), 531–541.
Bari, A., & Robbins, T. W. (2013). Inhibition and impulsivity: Behavioral and neural basis of response control. Progress in Neurobiology, 108, 44–79.
Bartra, O., McGuire, J. T., & Kable, J. W. (2013). The valuation system: A coordinate-based meta-analysis of BOLD fMRI experiments examining neural correlates of subjective value. Neuroimage, 76, 412–427.
Basser, P. J., Mattiello, J., & LeBihan, D. (1994). MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophysical Journal, 66(1), 259–267.
Bjork, J. M., Momenan, R., & Hommer, D. W. (2009). Delay discounting correlates with proportional lateral frontal cortex volumes. Biological Psychiatry, 65, 710–713.
van den Bos, W., Rodriguez, C.A., Schweitzer, J.B., McClure, S.M. (2015), Adolescent impatience decreases with increased frontostriatal connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 112:E3765–E3774.
Blair RJ. (2004). The roles of orbital frontal cortex in the modulation of antisocial behavior. Brain Cogn, 55(1), 198–208.
Burnette, E. M., Grodin, E. N., Lim, A. C., MacKillop, J., Karno, M. P., & Ray, L. A. (2019). Association between impulsivity and neural activation to alcohol cues in heavy drinkers. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 30(293), 110986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2019.110986.
Cavedini P., Riboldi G., Keller R., D'Annucci A., Bellodi L. (2002). Frontal lobe dysfunction in pathological gambling patients. Biol Psychiatry, 51(4), 334–41.
Chib, V. S., Rangel, A., Shimojo, S., & O’Doherty, J. P. (2009). Evidence for a common representation of decision values for dissimilar goods in human ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 12315–12320.
Cho, S. S., Pellecchia, G., Aminian, K., Ray, N., Segura, B., Obeso, I., & Strafella, A. P. (2013). Morphometric correlation of impulsivity in medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Topography, 26, 479–487.
Dombrovski, A. Y., Siegle, G. J., Szanto, K., Clark, L., Reynolds, C. F., & Aizenstein, H. (2012). The temptation of suicide: Striatal gray matter, discounting of delayed rewards, and suicide attempts in late-life depression. Psychological Medicine, 42(6), 1203–1215.
Du, X., Liu, L., Yang, Y., Qi, X., Gao, P., Zhang, Y., Zhu, J., Du, G., Dai, S., Li, X., & Zhang, Q. (2017). Diffusion tensor imaging of the structural integrity of white matter correlates with impulsivity in adolescents with internet gaming disorder. Brain and Behavior, 21(8), e00753. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.753.
Elliott, R., & Deakin, B. (2005). Role of the orbitofrontal cortex in reinforcement processing and inhibitory control: Evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging studies in healthy human subjects. International Review of Neurobiology, 715(65), 89–116.
Estle, S. J., Green, L., Myerson, J., & Holt, D. D. (2006). Differential effects of amount on temporal and probability discounting of gains and losses. Memory & Cognition, 34, 914.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., Tootell, R. B., & Dale, A. M. (1999). High-resolution intersubject averaging and a coordinate system for the cortical surface. Human Brain Mapping, 8, 272–284.
GarciaRill, E. (1997). Disorders of the reticular activating system. Medical Hypotheses., 49(5), 379–387.
Gavazzi, G., Rossi, A., Orsolini, S., Diciotti, S., Giovannelli, F., Salvadori, E., Pantoni, L., Mascalchi, M., & Viggiano, M. P. (2019). Impulsivity trait and proactive cognitive control: An fMRI study. European Journal of Neuroscience, 49(9), 1171–1179. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14301.
Glasser, M. F., Sotiropoulos, S. N., Wilson, J. A., Coalson, T. S., Fischl, B., Andersson, J. L., Xu, J., Jbabdi, S., Webster, M., Polimeni, J. R., Van Essen, D. C., & Jenkinson, M. (2013). The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the human Connectome project. Neuroimage, 80, 105–124.
Gray, J. C., MacKillop, J., Weafer, J., Hernandez, K. M., Gao, J., Palmer, A. A., & de Wit, H. (2018). Genetic analysis of impulsive personality traits: Examination of a priori candidates and genome-wide variation. Psychiatry Research, 259, 398–404.
Green, L., Myerson, J., Shah, A. K., Estle, S. J., & Holt, D. D. (2007). Do adjusting-amount and adjusting-delay procedures produce equivalent estimates of subjective value in pigeons? Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 87, 337–347.
Gupta, R., Koscik, T. R., Bechara, A., & Tranel, D. (2010). The amygdala and decision-making. Neuropsychologia, 49(4), 760–766.
Hampton, W. H., Alm, K. H., Venkatraman, V., Nugiel, T., & Olson, I. R. (2017). Dissociable frontostriatal white matter connectivity underlies reward and motor impulsivity. NeuroImage, 1590, 336–343.
Herting, M. M., Schwartz, D., Mitchell, S. H., & Nagel, B. J. (2010). Delay discounting behavior and white matter microstructure abnormalities in youth with a family history of alcoholism. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 34, 1590–1602.
Herrera-Díaz A., Mendoza-Quiñones R., Melie-Garcia L., Martínez-Montes E., Sanabria-Diaz G., Romero-Quintana Y., Salazar-Guerra I., Carballoso-Acosta M., Caballero-Moreno A. (2016). Functional Connectivity and Quantitative EEG in Women with Alcohol Use Disorders: A Resting-State Study. Brain Topogr, 29(3):368–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-015-0467-x.
Hester R., Garavan H. (2004). Executive dysfunction in cocaine addiction: evidence for discordant frontal, cingulate, and cerebellar activity. J Neurosci, 24(49), 11017–22.
Horn, N. R., Dolan, M., Elliott, R., Deakin, J. F. W., & Woodruff, P. W. R. (2003). Response Inhibition and Impulsivity: An FMRI Study. Neuropsychologia, 41(n.14), 1959–1966. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(03)00077-0.
Ikuta, T., del Arco, A., & Karlsgodt, K. H. (2018). White matter integrity in the fronto-striatal accumbofrontal tract predicts impulsivity. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 12(5), 1524–1528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9820-x.
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S. M. (2012). FSL. Neuroimage, 62, 782–790.
Jiang, Y., Guo, X., Zhang, J., Gao, J., Wang, X., Situ, W., Yi, J., Zhang, X., Zhu, X., Yao, S., & Huang, B. (2015). Abnormalities of cortical structures in adolescent-onset conduct disorder. Psychological Medicine, 45(16), 3467–3479.
Jones, B. E. (2008). Modulation of cortical activation and behavioral arousal by cholinergic and orexinergic systems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1129(1), 26–34.
Kable, J. W., & Glimcher, P. W. (2007). The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice. Nature Neuroscience, 10, 1625–1633.
Kable, J. W., & Glimcher, P. W. (2009). The neurobiology of decision: Consensus and controversy. Neuron, 63, 733–745.
Kubera, K. M., Schmitgen, M. M., Nagel, S., Hess, K., Herweh, C., Hirjak, D., Sambataro, F., & Wolf, R. C. (2018). A search for cortical correlates of trait impulsivity in Parkinson’s disease. Behavioral Brain Research, 13(369), 111911.
Lederer, K., Fouche, J. P., Wilson, D., Stein, D. J., & Uhlmann, A. (2016). Frontal white matter changes and aggression in methamphetamine dependence. Metabolic Brain Disease, 31, 53–62.
Mackillop, J., Weafer, J., Gray, J. C., Oshri, A., Palmer, A., & Wit, H. D. (2016). The latent structure of impulsivity: Impulsive choice, impulsive action, and impulsive personality traits. Psychopharmacology, 3361–3370.
Madden, G., & Bickel, W. K. (Eds.). (2009). Impulsivity: The behavioural and neurological science of discounting. Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association.
McClure, S. M., Laibson, D. I., Loewenstein, G., & Cohen, J. D. (2004). Separate neural systems value immediate and delayed monetary rewards. Science, 15(5695), 503–507.
McDonald, V., Hauner, K. K., Chau, A., Krueger, F., & Grafman, J. (2017). Networks underlying trait impulsivity: Evidence from voxel-based lesion-symptoms mapping. Human Brain Mapping, 38(2), 656–665.
Mills, I. H. (1985). The neuronal basis of compulsive behavior in anorexia nervosa. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 19(2–3), 231–235.
Moeller, F. G., Dougherty, D. M., Barratt, E. S., Schmitz, J. M., Swann, A. C., & Grabowsky, J. (2001). The impact of impulsivity on cocaine use and retention in treatment. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 21(4), 193–198.
Moeller, F. G., Hasan, K. M., Steinberg, J. L., Kramer, L. A., Dougherty, D. M., Santos, R. M., Valdes, I., Swann, A. C., Barratt, E. S., & Narayana, P. A. (2005). Reduced anterior corpus callosum white matter integrity is related to increased impulsivity and reduced discriminability in cocaine-dependent subjects: Diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology, 30(3), 610–617.
Mohammadi, B., Hammer, A., Miedl, S. F., Wiswede, D., Marco-Pallares, J., Herrmann, M., & Munte, T. F. (2015). Intertemporal choice behavior is constrained by brain structure in healthy participants and pathological gamblers. Brain Structure and Function, 3157–3170.
Myerson, J., Green, L., & Warusawitharana, M. (2001). Area under the curve as a measure of discounting. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 76(2), 235–243.
Navarro-Orozco, D., & Bollu, P. C. (2019). Neuroanatomy, Medial Lemniscus (Reils band, Reils ribbon). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
O’Doherty, J. P. (2004). Reward representations and reward-related learning in the human brain: Insights from neuroimaging. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 14, 769–776.
O’Doherty, J., Kringelbach, M. L., Rolls, E. T., Hornak, J., & Andrews, C. (2001). Abstract reward and punishment representations in the human orbitofrontal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 4(840), 95–102.
O'Halloran, L., Nymberg, C., Jollans, L., Garavan, H., & Whelan, R. (2017). The potential of neuroimaging for identifying predictors of adolescent alcohol use initiation and misuse. Addiction, 112(4), 719–726. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13629 Epub 2016 Dec 5.
Olson, E. A., Collins, P. F., Hooper, C. J., Muetzel, R., Lim, K. O., & Luciana, M. (2009). White matter integrity predicts delay discounting behavior in 9-to 23-year- olds: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21, 1406–1421.
Owens, M.M., Gray, J.C., Amlung, M.T., Oshri, A., Sweet, L.H., & MacKillop, J. (2017). Neuroanatomical foundations of delayed reward discounting decision making. Neuroimage, 1;161:261-270.
Pehlivanova, M., Wolf, D. H., Sotiras, A., Kaczkurkin, A. N., Moore, T. M., Ciric, R., Cook, P. A., Garcia de La Garza, A., Rosen, A. F. G., Ruparel, K., Sharma, A., Shinohara, R. T., Roalf, D. R., Gur, R. C., Davatzikos, C., Gur, R. E., Kable, J. W., & Satterthwaite, T. D. (2018). Diminished Cortical Thickness Is Associated with Impulsive Choice in Adolescence. Journal of Neuroscience, 7(10), 2471–2481.
Peper, J. S., Mandl, R. C., Braams, B. R., de Water, E., Heijboer, A. C., Koolschijn, P. C., & Crone, E. A. (2013). Delay discounting and frontostriatal fiber tracts: A combined DTI and MTR study on impulsive choices in healthy young adults. Cerebral Cortex, 23, 1695–1702.
Peters, J., & Buchel, C. (2010). Neural representations of subjective reward value. Behavioral Brain Research, 213, 135–141.
Peters, J., & Buchel, C. (2011). The neural mechanism of inter-temporal decision-making: Understanding variability. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15, 227–239.
Romero, M. J., Asensio, S., Palau, C., Sanchez, A., & Romero, F. J. (2010). Cocaine addiction: Diffusion tensor imaging study of the inferior frontal and anterior cingulate white matter. Psychiatry Research, 30(1), 57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.07.004.
Rossi, A., F. Giovannelli, G. Gavazzi, S. Righi, M. Cincotta, e M. P. Viggiano. «Electrophysiological activity prior to self-initiated movements is related to impulsive personality traits». Neuroscience 372 (2018): 266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.01.011.
Sanfey, A. G., Loewenstein, G., McClure, S. M., & Cohen, J. D. (2006). Neuroeconomics: Cross-currents in research on decision-making. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10(3), 108–116.
Schwartz, D. L., Mitchell, A. D., Lahna, D. L., Luber, H. S., Huckans, M. S., Mitchell, S. H., & Hoffman, W. F. (2010). Global and local morphometric differences in recently abstinent methamphetamine-dependent individuals. Neuroimage, 50, 1392–1401.
Siegel, A., & Victoroff, J. (2009). Understanding human aggression: New insights from neuroscience. International Journal of Law Psychiatry., 32(4), 209–215.
Steward, T., Mestre-Bach, G., Fernàndez-Aranda, F., Granero, R., Perales, J. C., Navas, J. F., Soriano-Mas, C., Bano, M., Fernàndez-Formoso, J. A., Martìn-Romera, V., Mnechòn, J. M., & Jiménez-Murcia, S. (2017). Delay discounting and impulsivity traits in young and older gambling disorder patients. Addcitive Behaviors, 71, 96–103.
Uhlmann, A., Fouche, J. P., Lederer, K., Meintjes, E. M., Wilson, D., & Stein, D. J. (2016). White matter microstructure and impulsivity in methamphetamine dependence with and without a history of psychosis. Human Brain Mapping, 37(6), 2055–2067.
Van Essen, D. C., Smith, S., Barch, D., Behrens, T. E. J., Yacoub, E., & Ugurbil, K. (2013). The WU-Minn human Connectome project: An overview. Special issue Mapping the Connectome: NeuroImage.
Veraart, J., Sijbers, J., Sunaert, S., Leemans, A., & Jeurissen, B. (2013). Weighted linear least squares estimation of diffusion MRI parameters: Strengths, limitations, and pitfalls. NeuroImage, 81, 335–346.
Vollstädt-Klein S1, Hermann D, Rabinstein J, Wichert S, Klein O, Ende G, Mann K. (2010). Increased activation of the ACC during a spatial working memory task in alcohol-dependence versus heavy social drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 34(5), 771–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01149.x.
Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Nagae-Poetscher, L. M., van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2004). Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology, 230, 77–87.
Wang, J., Fan, Y., Dong, Y., Ma, M., Ma, Y., Dong, Y., Niu, Y., Jiang, Y., Wang, H., Wang, Z., Wu, L., Sun, H., & Cui, C. (2016). Alterations in brain structure and functional connectivity in alcohol dependent patients and possible association with impulsivity. PLoS One, 30(8), e0161956. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161956.
Wang, S., Kong, F., Zhou, M., Chen, T., Yang, X., Chen, G., & Gong, Q. (2017). Brain structure linking delay discounting and academic performance. Human Brain Mapping, 38, 3917–3926.
Acknowledgments
These data were provided by the Human Connectome Project, WU-Minn Consortium (Principal Investigators: David Van Essen and KamilUgurbil; 1U54MH091657) funded by the 16 NIH Institutes and Centers that support the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research; and by the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience at Washington University in St. Louis. The authors are deeply appreciative to the Human Connectome Project for open access to its data.
This work was supported by RC projects of the Italian MOH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they had no financial or non-financial conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfano, V., Longarzo, M., Aiello, M. et al. Cerebral microstructural abnormalities in impulsivity: a magnetic resonance study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 346–354 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00261-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00261-2