Abstract
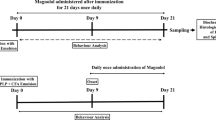
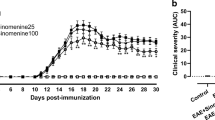
We aimed to determine the effect of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibition on chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a murine model of multiple sclerosis (MS), associated with changes in inflammasome-dependent and -independent inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways in the CNS of mice. C57BL/6 mice were used to induce chronic EAE by using an injection of MOG35–55 peptide/PT. Animals were observed daily and scored for EAE signs for 25 days after immunization. Following the induction of EAE, the scores were increased after 9 days and reached peak value as determined by ≥ 2 or ≤ 3 with 8% mortality rate on day 17. On day 17, mice were administered daily PBS, DMSO, or TPPU (a potent sEH inhibitor) (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) until the end of the study. TPPU only at 3 mg/kg dose decreased the AUC values calculated from EAE scores obtained during the disease compared to EAE and vehicle control groups. On day 25, TPPU also caused an increase in the PPARα/β/γ and NLRC3 proteins and a decrease in the proteins of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB p65, p-NF-κB p65, iNOS/nNOS, COX-2, NLRC4, ASC, caspase-1 p20, IL-1β, caspase-11 p20, NOX subunits (gp91phox and p47phox), and nitrotyrosine in addition to 14,15-DHET and IL-1β levels compared to EAE and vehicle control groups. Our findings suggest that pharmacological inhibition of sEH attenuates chronic EAE likely because of enhanced levels of anti-inflammatory EETs in addition to PPARα/β/γ and NLRC3 expression associated with suppressed inflammatory TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway, NLRC4/ASC/pro-caspase-1 inflammasome, caspase-11 inflammasome, and NOX activity that are responsible for inflammatory mediator formation in the CNS of mice.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson P, Gonzalez-Rey E, O’Valle F et al (2017) Allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating self-reactive t cell responses and dendritic cell function. Stem Cells Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2389753
Atone J, Wagner K, Hashimoto K et al (2019) Cytochrome P450 derived epoxidized fatty acids as a therapeutic tool against neuroinflammatory diseases. Prostaglandins Lipid Mediat 147:106385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.106385
Awad F, Assrawi E, Louvrier C et al (2018) Inflammasome biology, molecular pathology and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther 187:133–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.011
Ayoub SS, Wood EG, Hassan SU et al (2011) Cyclooxygenase expression and prostaglandin levels in central nervous system tissues during the course of chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Inflamm Res 60:919–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0352-3
Baecher-Allan C, Kaskow B, Weiner HL (2018) Multiple sclerosis: mechanisms and immunotherapy. Neuron 97:742–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.021
Basler M, Mundt S, Muchamuel T et al (2014) Inhibition of the immunoproteasome ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. EMBO Mol Med 6:226–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201303543
Bernales CQ, Encarnacion M, Criscuoli MG et al (2018) Analysis of NOD-like receptor NLRP1 in multiple sclerosis families. Immunogenetics 70:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-017-1034-2
Bittner S, Afzali AM, Wiendl H et al (2014) Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG35-55) induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in C57BL/6 mice. J Vis Exp 86:e51275. https://doi.org/10.3791/51275
Bloom J, Metz C, Nalawade S et al (2016) Identification of iguratimod as an inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) with steroid-sparing potential. J Biol Chem 291:26502–26514. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.743328
Boghozian R, McKenzie BA, Saito LB et al (2017) Suppressed oligodendrocyte steroidogenesis in multiple sclerosis: implications for regulation of neuroinflammation. Glia 65:1590–1606. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23179
Bogie JF, Jorissen W, Mailleux J et al (2013) Myelin alters the inflammatory phenotype of macrophages by activating PPARs. Acta Neuropathol Commun 1:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/2051-5960-1-43
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Chen Y, Tian H, Yao E et al (2017) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition promotes white matter integrity and long-term functional recovery after chronic hypoperfusion in mice. Sci Rep 7:7758. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08227-z
Chen Z, Tang Y, Yu J et al (2019) sEH inhibitor TPPU ameliorates cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis by regulating macrophage functions. Shock. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000001408
Cheng Y, Sun L, Xie Z et al (2017) Diversity of immune cell types in multiple sclerosis and its animal model: pathological and therapeutic implications. J Neurosci Res 95:1973–1983. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24023
Chiang CW, Lee HT, Tarng DC et al (2015) Genetic deletion of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates inflammation and fibrosis in experimental obstructive nephropathy. Mediators Inflamm 2015:693260. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/693260
Choi BY, Kim JH, Kho AR et al (2015) Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation reduces EAE-induced white matter damage in mice. J Neuroinflammation 12:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0325-5
Christmas P (2015) Role of cytochrome P450s in inflammation. Adv Pharmacol 74:163–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2015.03.005
Constantinescu CS, Farooqi N, O'Brien K et al (2011) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br J Pharmacol 164:1079–1106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01302.x
Cudrici C, Niculescu T, Niculescu F et al (2006) Oligodendrocyte cell death in pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: protection of oligodendrocytes from apoptosis by complement. J Rehabil Res Dev 43:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1682/jrrd.2004.08.0111
Darwesh AM, Keshavarz-Bahaghighat H, Jamieson KL et al (2019) Genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase ameliorates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int J Mol Sci 20:E3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143502
Derdelinckx J, Mansilla MJ, De Laere M et al (2019) Clinical and immunological control of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by tolerogenic dendritic cells loaded with MOG-encoding mRNA. J Neuroinflammation 16:167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1541-1
Dolunay A, Senol SP, Temiz-Resitoglu M et al (2017) Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome prevents LPS-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia in mice: contribution of NF-κB, caspase-1/11, ASC, NOX, and NOS isoforms. Inflammation 40:366–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0483-3
Dong L, Zhou Y, Zhu ZQ (2017) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor suppresses the expression of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 by inhibiting NF-kB activation in murine macrophage. Inflammation 40:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0448-6
Drohomyrecky PC, Doroshenko ER, Akkermann R et al (2019) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-δ acts within peripheral myeloid cells to limit th cell priming during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 203:2588–2601. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1801200
Duncan JA, Canna SW (2018) The NLRC4 inflammasome. Immunol Rev 281:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12607
Eitas TK, Chou WC, Wen H et al (2014) The nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) family member NLRX1 mediates protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and represses macrophage/microglia-induced inflammation. J Biol Chem 289:4173–4179. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.533034
Fakan B, Szalardy L, Vecsei L (2019) Exploiting the therapeutic potential of endogenous immunomodulatory systems in multiple sclerosis-special focus on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and the kynurenines. Int J Mol Sci 20:E426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020426
Freeman LC, Ting JP (2016) The pathogenic role of the inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 136:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13217
Freeman L, Guo H, David CN et al (2017) NLR members NLRC4 and NLRP3 mediate sterile inflammasome activation in microglia and astrocytes. J Exp Med 214:1351–1370. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20150237
Fu Y, Zhan X, Wang Y et al (2019) NLRC3 expression in dendritic cells attenuates CD4+ T cell response and autoimmunity. EMBO J 38:e101397. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018101397
Gajofatto A, Turatti M (2018) Investigational immunosuppressants in early-stage clinical trials for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 27:273–286. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2018.1442437
Gharagozloo M, Mahvelati TM, Imbeault E et al (2015) The Nod-like receptor, Nlrp12, plays an anti-inflammatory role in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0414-5
Gharagozloo M, Gris KV, Mahvelati T et al (2018a) NLR-dependent regulation of inflammation in multiple sclerosis-dependent regulation of inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.02012
Gharagozloo M, Gris KV, Mahvelati T et al (2018b) NLR-dependent regulation of inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 8:2012. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.02012
Gocke AR, Hussain RZ, Yang Y et al (2009) Transcriptional modulation of the immune response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-{alpha} agonists in autoimmune disease. J Immunol 182:4479–4487. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0713927
Hamidi V, Couto E, Ringerike T et al (2018) A multiple treatment comparison of eleven disease-modifying drugs used for multiple sclerosis. J Clin Med Res 10:88–105. https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr3168w
Hisahara S, Yuan J, Momoi T et al (2001) Caspase-11 mediates oligodendrocyte cell death and pathogenesis of autoimmune-mediated demyelination. J Exp Med 193:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.193.1.111
Hisahara S, Okano H, Miura M (2003) Caspase-mediated oligodendrocyte cell death in the pathogenesis of autoimmune demyelination. Neurosci Res 46:387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-0102(03)00127-5
Hung TH, Shyue SK, Wu CH et al (2017) Deletion or inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase protects against brain damage and reduces microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury. Oncotarget 8:103236–103260. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21139
Inojosa H, Proschmann U, Akgün K et al (2019) A focus on secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS): challenges in diagnosis and definition. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09489-5
Inoue M, Chen PH, Siecinski S et al (2016) An interferon-β-resistant and NLRP3 inflammasome-independent subtype of EAE with neuronal damage. Nat Neurosci 19:1599–1609. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4421
JahagirdarR AS, Marusic S et al (2017) RVX-297, a BET bromodomain ınhibitor, has therapeutic effects in preclinical models of acute ınflammation and autoimmune disease. Mol Pharmacol 92:694–706. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.117.110379
Kanakasabai S, Walline CC, Chakraborty S et al (2011) PPARδ deficient mice develop elevated Th1/Th17 responses and prolonged experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res 1376:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.12.059
Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Natteru PA et al (2016) Neuroinflammation induces neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Spine 1:1003
Kim S, Moon C, Wie MB et al (2000) Enhanced expression of constitutive and inducible forms of nitric oxide synthase in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Vet Sci 1:11–17
Kim J, Yoon SP, Toews ML et al (2015) Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase prevents renal interstitial fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 308:F131–F139. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00531.2014
Kipp M, Nyamoya S, Hochstrasser T et al (2017) Multiple sclerosis animal models: a clinical and histopathological perspective. Brain Pathol 27:123–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12454
Kodani SD, Morisseau C (2019) Role of epoxy-fatty acids and epoxide hydrolases in the pathology of neuro-inflammation. Biochimie 159:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.01.020
Kong X, Yuan Z, Cheng J (2017) The function of NOD-like receptors in central nervous system diseases. J Neurosci Res 95:1565–1573. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24004
Lakkappa N, Krishnamurthy PT, Hammock BD et al (2019) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, APAU, protects dopaminergic neurons against rotenone induced neurotoxicity: implications for Parkinson's disease. Neurotoxicology 70:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2018.11.010
Lassmann H (2019a) Pathogenic mechanisms associated with different clinical courses of multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 9:3116. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.03116
Lassmann H (2019b) The changing concepts in the neuropathology of acquired demyelinating central nervous system disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 32:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000685
Liang Z, Zhang B, Xu M et al (2019) 1-Trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea, a selective and potent dual inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase and p38 kinase intervenes in Alzheimer’s signaling in human nerve cells. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:4018–4030. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00271
Liu JY, Lin YP, Qiu H et al (2013) Substituted phenyl groups improve the pharmacokinetic profile and anti-inflammatory effect of urea-based soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in murine models. Eur J Pharm Sci 48:619–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2012.12.013
Liu CY, Guo SD, Yu JZ et al (2015) Fasudil mediates cell therapy of EAE by immunomodulating encephalomyelitic T cells and macrophages. Eur J Immunol 45:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201344429
Liu AH, Wu YT, Wang YP (2017) MicroRNA-129-5p inhibits the development of autoimmune encephalomyelitis-related epilepsy by targeting HMGB1 through the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull 132:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.05.004
Liu B, Gu Y, Pei S et al (2019) Interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase (IRAK)-M -mediated type 2 microglia polarization ameliorates the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Autoimmun 102:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2019.04.020
Lubina-Dabrowska N, Stepien A, Sulkowski G et al (2017) Effects of IFN-β1a and IFN-β1b treatment on the expression of cytokines, inducible NOS (NOS type II), and myelin proteins in animal model of multiple sclerosis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 65:325–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-017-0458-6
Macaron G, Ontaneda D (2019) Diagnosis and management of progressive multiple sclerosis. Biomedicines 7:E56. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7030056
Maillart E (2018) Treatment of progressive multiple sclerosis: challenges and promising perspectives. Rev Neurol 174:441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2018.01.370
Malhotra S, Rio J, Urcelay E et al (2015) NLRP3 inflammasome is associated with the response to IFN-β in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain 138:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu388
Malik A, Kanneganti TD (2017) Inflammasome activation and assembly at a glance. J Cell Sci 130:3955–3963. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.207365
Mamik MK, Power C (2017) Inflammasomes in neurological diseases: emerging pathogenic and therapeutic concepts. Brain 140:2273–2285. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx133
Man SM, Kanneganti TD (2016) Converging roles of caspases in inflammasome activation, cell death and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 16:7–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2015.7
Marta M, Andersson A, Isaksson M et al (2008) Unexpected regulatory roles of TLR4 and TLR9 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 38:565–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200737187
Mathur A, Hayward JA, Man SM (2018) Molecular mechanisms of inflammasome signaling. J Leukoc Biol 103:233–257. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.3MR0617-250R
Maver A, Lavtar P, Ristic S et al (2017) Identification of rare genetic variation of NLRP1 gene in familial multiple sclerosis. Sci Rep 7:3715. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03536-9
Mayer MC, Meinl E (2012) Glycoproteins as targets of autoantibodies in CNS inflammation: MOG and more. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 5:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756285611433772
Mendel I, Kerlero de Rosbo N, Ben-Nun A (1995) A myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide induces typical chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in H-2b mice: fine specificity and T cell receptor V beta expression of encephalitogenic T cells. Eur J Immunol 25:1951–1959. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830250723
Morris G, Walker AJ, Berk M et al (2017) Cell death pathways: a novel therapeutic approach for neuroscientists. Mol Neurobiol 55:5767–5786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0793-y
Narayan RN, Forsthuber T, Stüve O (2018) Emerging drugs for primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 23:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728214.2018.1463370
Navarro-Mabarak C, Camacho-Carranza R, Espinosa-Aguirre JJ (2018) Cytochrome P450 in the central nervous system as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. Drug Metab Rev 50:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602532.2018.1439502
Noroozi S, Meimand HAE, Arababadi MK et al (2017) The effects of IFN-β 1a on the expression of inflammasomes and apoptosis-associated speck-like proteins in multiple sclerosis patients. Mol Neurobiol 54:3031–3037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9864-8
Pachner AR (2011) Experimental models of multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol 24:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e328346c226
Pardeshi R, Bolshette N, Gadhave K et al (2019) Docosahexaenoic acid increases the potency of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor in alleviating streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease-like complications of diabetes. Front Pharmacol 10:288. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00288
Peschl P, Bradl M, Höftberger R et al (2017) Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein: deciphering a target in inflammatory demyelinating diseases. Front Immunol 8:529. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00529
Platnich JM, Muruve DA (2019) NOD-like receptors and inflammasomes: a review of their canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys 670:4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.02.008
Praet J, Guglielmetti C, Berneman Z et al (2014) Cellular and molecular neuropathology of the cuprizone mouse model: clinical relevance formultiple sclerosis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:485–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.10.004
Procaccini C, De Rosa V, Pucino V et al (2015) Animal models of multiple sclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol 759:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.042
Ren Q, Ma M, Ishima T et al (2016) Gene deficiency and pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase confers resilience to repeated social defeat stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E1944–E1952. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1601532113
Ren Q, Ma M, Yang J et al (2018) Soluble epoxide hydrolase plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E5815–E5823. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1802179115
Ruiz F, Vigne S, Pot C (2019) Resolution of inflammation during multiple sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol 41:711–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-019-00765-0
Schiffmann S, Weigert A, Mannich J et al (2014) PGE2/EP4 signaling in peripheral immune cells promotes development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biochem Pharmacol 87:625–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.006
Senol SP, Temiz M, Guden DS et al (2016) Contribution of PPARα/β/γ, AP-1, importin-α3, and RXRα to the protective effect of 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, against hypotension, tachycardia, and inflammation in a rat model of septic shock. Inflamm Res 65:367–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0922-5
Shrestha B, Jiang X, Ge S et al (2017) Spatiotemporal resolution of spinal meningeal and parenchymal inflammation during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurobiol Dis 108:159–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.08.010
Stys PK, Tsutsui S (2019) Recent advances in understanding multiple sclerosis. F1000Res 8 F1000 Faculty Rev 8:9–10 Doi: 10.12688/f1000research.20906.
Taguchi N, Nakayama S, Tanaka M (2016) Single administration of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor suppresses neuroinflammation and improves neuronal damage after cardiac arrest in mice. Neurosci Res 111:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2016.05.002
Takeuchi C, Matsumoto Y, Kohyama K et al (2013) Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 aggravates inflammation and demyelination in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Neurochem Int 62:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.12.007
Thomson S, Edin ML, Lih FB et al (2015) Intimal smooth muscle cells are a source but not a sensor of anti-inflammatory CYP450 derived oxylipins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 463:774–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.012
Tu R, Armstrong J, Lee KSS et al (2018) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition decreases reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia. Sci Rep 8:5279. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23504-1
Tunctan B, Korkmaz B, Yildirim H et al (2005) Increased production of nitric oxide contributes to renal oxidative stress in endotoxemic rat. Am J Infect Dis 1:111–115. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajidsp.2005.111.115
Tunctan B, Korkmaz B, Sari AN et al (2013a) 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, reverses hypotension and improves survival in a rodent model of septic shock: contribution of soluble epoxide hydrolase. CYP2C23, MEK1/ERK1/2/IKKβ/IκB-α/NF-κB pathway, and proinflammatory cytokine formation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 102–103:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2013.01.005
Tunctan B, Korkmaz B, Sari AN et al (2013b) Contribution of iNOS/sGC/PKG pathway, COX-2, CYP4A1, and gp91(phox) to the protective effect of 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, against vasodilation, hypotension, tachycardia, and inflammation in a rat model of septic shock. Nitric Oxide 33:18–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2013.05.001
Tunctan B, Kucukkavruk SP, Temiz-Resitoglu M et al (2018) Bexarotene, a selective RXRα agonist, reverses hypotension associated with inflammation and tissue injury in a rat model of septic shock. Inflammation 41:337–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0691-5
Uchimura T, Oyama Y, Deng M et al (2018) The innate immune sensor NLRC3 acts as a rheostat that fine-tunes T cell responses in infection and autoimmunity. Immunity 49:1049–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.10.008
Voet S, Srinivasan S, Lamkanfi M et al (2019) Inflammasomes in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. EMBO Mol Med 11:e10248. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201810248
Wagner KM, McReynolds CB, Schmidt WK et al (2017) Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for pain, inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. PharmacolTher 180:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.06.006
Wang L, Luo G, Zhang LF et al (2018) Neuroprotective effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Prostagland Lipid Mediat 138:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2018.07.002
Wang X, Li L, Wang H et al (2019) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids alleviate methionine-choline-deficient diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Scand J Immunol 90:e12791. https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.12791
Wen J, Ribeiro R, Tanaka M et al (2015) Activation of CB2 receptor is required for the therapeutic effect of ABHD6 inhibition in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neuropharmacology 99:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.07.010
Xu J, Racke MK, Drew PD (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist fenofibrate regulates IL-12 family cytokine expression in the CNS: relevance to multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem 103:1801–1810. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04875.x
Yang J, Liu Z, Xiao TS (2017) Post-translational regulation of inflammasomes. Cell Mol Immunol 14:65–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2016.29
Yeh CF, Chuang TY, Hung YW et al (2019) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition enhances anti-inflammatory and antioxidative processes, modulates microglia polarization, and promotes recovery after ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:2927–2941. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S210403
Yi YS (2019) Functional crosstalk between non-canonical caspase-11 and canonical NLRP3 inflammasomes during infection-mediated inflammation. Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13134
Yu JW, Li YH, Song GB et al (2016) Synergistic and superimposed effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with fasudil in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Mol Neurosci 60:486–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0819-3
Zhang W, Yang AL, Liao J et al (2012) Soluble epoxide hydrolase gene deficiency or inhibition attenuates chronic active inflammatory bowel disease in IL-10(-/-) mice. Dig Dis Sci 57:2580–2591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2217-1
Zhang L, Mo J, Swanson KV et al (2014) NLRC3, a member of the NLR family of proteins, is a negative regulator of innate immune signaling induced by the DNA sensor STING. Immunity 40:329–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.01.010
Zhou F, Ciric B, Zhang GX et al (2014) Immunotherapy using lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells to treat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol 178:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12440
Zhou Y, Yang J, Sun GY et al (2016) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor 1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Cell Tissue Res 363:399–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2262-0
Zhou Y, Liu T, Duan JX et al (2017) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and improves survival in mice. Shock 47:638–645. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000767
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by a grant from Mersin University (2019-1-TP2-3142). The results presented in this study were included in the Master’s Thesis of Pharm. M.S. Merve Biliktu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biliktu, M., Senol, S.P., Temiz-Resitoglu, M. et al. Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by modulating inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways in an inflammasome-dependent and -independent manner. Inflammopharmacol 28, 1509–1524 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00691-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00691-w