Abstract
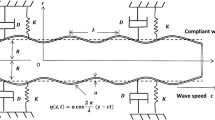
In the present investigation, we have studied the effects of heat transfer on the peristaltic flow considering the Phan-Thien–Tanner fluid model. The fluid is flowing in a uniform circular tube in the form of wave motion. The inner walls of the tube are considered to be ciliated with small hair-like structures. Exact solutions have been derived for velocity, temperature and pressure gradient. Mechanical properties of the fluid, such as velocity, temperature, pressure rise and pressure gradient, have been discussed graphically. Trapping phenomena due to the variation of physical parameters have been deliberated. It has been observed that when the viscous forces are greater than the elastic forces, the velocity of the fluid flow significantly decreases, thermal conductivity of the fluid improves and the pressure gradient along the tube increases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar NS, Butt AW (2016) Ferromagnetic effects for peristaltic flow of Cu–water nanofluid for different shapes of nanosize particles. Appl Nanosci 6(3):379–385
Akbar NS, Butt AW (2017) Entropy generation analysis for the peristaltic flow of Cu–water nanofluid in a tube with viscous dissipation. J Hydrodyn 29(1):135–143
Akbar NS, Butt AW (2018) Ferromagnetic nano model study for the peristaltic flow in a plumb duct with permeable walls. Microsyst Technol 25(4):1227–1234
Akbar NS, Nadeem S (2012) Peristaltic flow of a Phan-Thien–Tanner nanofluid in a diverging tube. Heat Transf Res 41(1):10–22
Akbar NS, Butt AW, Tripathi D (2017) Nanoparticle shapes effects on unsteady physiological transport of nanofluids through a finite length non-uniform channel. Res Phys 7:2477–2484
Akbarzadeh P (2018) Peristaltic biofluids flow through vertical porous human vessels using third-grade non-Newtonian fluids model. Biomech Model Mechan 17(1):71–86
Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R (2016) Heat transfer analysis on peristaltically induced motion of particle-fluid suspension with variable viscosity: clot blood model. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 137:115–124
Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R (2017) Heat transfer with thermal radiation on MHD particle-fluid suspension induced by metachronal wave. Pramana 89(3):0048
Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R, Shit GC (2018) Mathematical modeling of heat and mass transfer effects on MHD peristaltic propulsion of two-phase flow through a Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer porous medium. Adv Powder Technol 29(5):1189–1197
Bhatti MM, Zeshan A, Ellahi R, Beg OA, Kadir A (2019) Effects of coagulation on the two-phase peristaltic pumping of magnetized prandtl biofluid through an endoscopic annular geometry containing a porous medium. Chin J Phys 58:222–234
Blake JR (1971) A spherical envelope approach to ciliary propulsion. J Fluid Mech 46(1):199–208
Blake JR (1972) A model for the micro-structure in ciliated organisms. J Fluid Mech 55(1):1–23
El Naby AEHA (2009) Creeping flow of Phan-Thien–Tanner fluids in a peristaltic tube with an infinite long wavelength. J Appl Mech 76(6):064504
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hussain F, Asadollahi A (2019) Peristaltic blood flow of couple stress fluid suspended with nanoparticles under the influence of chemical reaction and activation energy. Symmetry 11(2):276
Hagen T, Renardy M (1997) Boundary layer analysis of the Phan-Thien–Tanner and Giesekus model in high Weissenberg number flow. J Non-Newton Fluid 73:181–189
Hanasoge S, Ballard MR, Hesketh PJ, Alexeev A (2017) Asymmetric motion of magnetically actuated artificial cilia. Lab Chip 17:3138–3145
Khan AU, Hussain ST, Nadeem S (2017) Existence and stability of heat and fluid flow in the presence of nanoparticles along a curved surface by mean of dual nature solution. Appl Math Comput 353:66–81
Miller CE (1967) An investigation of the movement of Newtonian liquids initiated and sustained by the oscillation of mechanical cilia. Aspen Emphysema Conf 10:309–321
Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT (1999) Analytical solution for fully developed channel and pipe flow of Phan-Thien–Tanner fluids. J Fluid Mech 387:271–280
Phan-Thien N, Tanner RI (1977) A new constitutive equation derived from network theory. J Non-Newtonian Fluid 2(4):353–365
Phan-Thien N, Tanner RI (1978) A nonlinear network viscoelastic model. J Rheol 22(3):259–283
Quinzani LM, Armstrong RC, Brown RA (1995) Use of coupled birefringence and LDV studies of flow through a planar contraction to test constitutive equations for concentrated polymer solutions. J Rheol 39:1201–1228
Riaz A, Ellahi R, Bhatti MM, Marin M (2019) Study of heat and mass transfer in the Eyring–Powell model of fluid propagating peristaltically through a rectangular compliant channel. Heat Trans Res 50(16):1539–1560
Sheikholeslami M, Rezaeianjouybari B, Darzi M, Shafee A, Li Z, Nguyen TK (2019a) Application of nano-refrigerant for boiling heat transfer enhancement employing an experimental study. Int J Heat Mass Transf 141:974–980
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Hedayat M, Shafee A, Li Z, Nguyen TK, Bakouri M (2019b) Heat transfer and turbulent simulation of nanomaterial due to compound turbulator including irreversibility analysis. Int J Heat Mass Transf 137:1290–1300
Sleigh MA (1962) The biology of cilia and flagella. MacMillian, New York
Sleigh MA, Aiello E (1972) The movement of water by cilia. Acta Protozool 11:265–277
Srinivas S, Gayathri R (2009) Peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in a vertical asymmetric channel with heat transfer and porous medium. Appl Math Comput 215(1):185–196
Vajravelu K, Radhakrishnamacharya G, Radhakrishnamurty V (2007) Peristaltic flow and heat transfer in a vertical porous annulus, with long wave approximation. Int J Nonlinear Mech 42(5):754–759
Waldrop L, Miller L (2016) Large-amplitude, short-wave peristalsis and its implications for transport. Biomech Model Mechan 15(3):629–642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butt, A.W., Akbar, N.S. & Mir, N.A. Heat transfer analysis of peristaltic flow of a Phan-Thien–Tanner fluid model due to metachronal wave of cilia. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 19, 1925–1933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-020-01317-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-020-01317-4