Abstract
Background
Neuroinflammation plays a dominant role in the progression of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). This study was carried out to explore the neuroprotective effect of Chikusetsu saponin IVa (ChIV) against sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment.
Methods
The neuroprotective activity of ChIV against sevoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction in aged rats was evaluated by Morris water maze, NOR test and Y-maze test, respectively. The expression of NLRP3, ASC and caspase-1, pro-inflammatory cytokines and apoptotic-related protein were detected in the hippocampus and primary neurons using western blot. TUNEL assay and immunohistochemistry staining were applied to assess the apoptotic cell and number of NLRP3-positive cells in the hippocampus. The oxiSelectIn Vitro ROS/RNS assay kit was used to detect the ROS level. The CCK-8 assay was applied to measure the viability of primary neurons. Flow cytometry was carried out to determine cell apoptosis.
Results
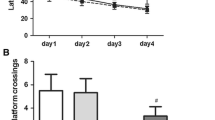
Pretreatment with ChIV significantly alleviated neurological dysfunction in aged rat exposure to sevoflurane. Mechanistically, ChIV treatment significantly alleviated sevoflurane-induced apoptotic cell and neuroinflammation. Of note, the neuroprotective effect of ChIV against sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity through blocking NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. In consistent with in vivo studies, ChIV was also able to repress sevoflurane-induced apoptosis and neuroinflammation in primary neurons. Furthermore, pretreatment with NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway inhibitor (MCC950) significantly augmented the neuroprotective effect of ChIV.
Conclusion
Our finding confirmed that ChIV provides a neuroprotective effect against sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment by blocking the NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway, which may be an effective strategy for the clinical treatment of elderly patients with POCD induced by anesthesia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feinkohl I, Winterer G, Spies CD, Pischon T. Cognitive reserve and the risk of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114(7):110–7. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0110.
Lachmann G, Kant I, Lammers F, Windmann V, Spies C, Speidel S, Borchers F, Hadzidiakos D, Hendrikse J, Winterer G, de Bresser J. Cerebral microbleeds are not associated with postoperative delirium and postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older individuals. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218411. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0218411.
Yang W, Kong LS, Zhu XX, Wang RX, Liu Y, Chen LR. Effect of dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive dysfunction and inflammation in patients after general anaesthesia: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(18):e15383. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000015383.
Quan C, Chen J, Luo Y, Zhou L, He X, Liao Y, Chou J, Guo Q, Chen AF, Wen O. BIS-guided deep anesthesia decreases short-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction and peripheral inflammation in elderly patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Brain Behav. 2019;9(4):e01238. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1238.
Yang F, Shan Y, Tang Z, Wu X, Bi C, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Liu H. The neuroprotective effect of hemin and the related mechanism in sevoflurane exposed neonatal rats. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:537. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00537.
Cao Y, Li Z, Ma L, Yang N, Guo X. Isoflurane-induced postoperative neurovascular and cognitive dysfunction is associated with VEGF overexpression in aged rats. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01350-8.
Nishigaki A, Kawano T, Iwata H, Aoyama B, Yamanaka D, Tateiwa H, Shigematsu-Locatelli M, Eguchi S, Locatelli FM, Yokoyama M. Acute and long-term effects of haloperidol on surgery-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits in aged rats. J Anesth. 2019;33(3):416–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-019-02646-0.
Li N, Zhang X, Dong H, Hu Y, Qian Y. Bidirectional relationship of mast cells-neurovascular unit communication in neuroinflammation and its involvement in POCD. Behav Brain Res. 2017;322(Pt A):60–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.01.006.
Kok WF, Koerts J, Tucha O, Scheeren TW, Absalom AR. Neuronal damage biomarkers in the identification of patients at risk of long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Anaesthesia. 2017;72(3):359–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/anae.13712.
Hovens IB, van Leeuwen BL, Mariani MA, Kraneveld AD, Schoemaker RG. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation; cardiac surgery and abdominal surgery are not the same. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;54:178–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.02.003.
Zhang Z, Li X, Li F, An L. Berberine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing neuroinflammation in aged mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;38:426–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.06.031.
Sha HY, Zhao JB, Sha MX, Guo SM. Effects of Vitamin B12 on postoperative cognitive dysfunction induced by isoflurane anesthesia in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(8):1959–66.
Ye JS, Chen L, Lu YY, Lei SQ, Peng M, Xia ZY. Honokiol-mediated mitophagy ameliorates postoperative cognitive impairment induced by surgery/sevoflurane via inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in the hippocampus. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8639618. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8639618.
Wei P, Yang F, Zheng Q, Tang W, Li J. The potential role of the NLRP3 inflammasome activation as a link between mitochondria ROS generation and neuroinflammation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:73. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00073.
Ashraf A, Mahmoud PA, Reda H, Mansour S, Helal MH, Michel HE, Nasr M. Silymarin and silymarin nanoparticles guard against chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in mice: involvement of neurogenesis and NLRP3 inflammasome. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(5):615–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881119836221.
Ystgaard MB, Scheffler K, Suganthan R, Bjoras M, Ranheim T, Sagen EL, Halvorsen B, Saugstad OD, Yndestad A. Neuromodulatory effect of NLRP3 and ASC in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Neonatology. 2019;115(4):355–62. https://doi.org/10.1159/000497200.
Peng J, Zhang P, Zheng H, Ren YQ, Yan H. Dexmedetomidine reduces hippocampal microglia inflammatory response induced by surgical injury through inhibiting NLRP3. Chin J Traumatol. 2019;22(3):161–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.03.002.
Detrait ER, Danis B, Lamberty Y, Foerch P. Peripheral administration of an anti-TNF-alpha receptor fusion protein counteracts the amyloid induced elevation of hippocampal TNF-alpha levels and memory deficits in mice. Neurochem Int. 2014;72:10–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.04.001.
Alam A, Hana Z, Jin Z, Suen KC, Ma D. Surgery, neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment. EBioMedicine. 2018;37:547–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.10.021.
Skvarc DR, Berk M, Byrne LK, Dean OM, Dodd S, Lewis M, Marriott A, Moore EM, Morris G, Page RS, Gray L. Post-operative cognitive dysfunction: an exploration of the inflammatory hypothesis and novel therapies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;84:116–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.11.011.
Locatelli FM, Kawano T, Iwata H, Aoyama B, Eguchi S, Nishigaki A, Yamanaka D, Tateiwa H, Shigematsu-Locatelli M, Yokoyama M. Resveratrol-loaded nanoemulsion prevents cognitive decline after abdominal surgery in aged rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;137(4):395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2018.08.006.
Qi D, Yang X, Chen J, Li F, Shi X, Zhang C, Yang Z. Determination of chikusetsusaponin V and chikusetsusaponin IV in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and its application to a preliminary pharmacokinetic study. Biomed Chromatogr. 2013;27(11):1568–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.2961.
Li Y, Zhang T, Cui J, Jia N, Wu Y, Xi M, Wen A. Chikusetsu saponin IVa regulates glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation: implications in antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015;67(7):997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12392.
Yang J, Qian S, Cai X, Lu W, Hu C, Sun X, Yang Y, Yu Q, Gao SP, Cao P. Chikusetsusaponin IVa butyl ester (CS-IVa-Be), a novel IL6R antagonist, inhibits IL6/STAT3 signaling pathway and induces cancer cell apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15(6):1190–200. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-15-0551.
Wang L, Yuan D, Zheng J, Wu X, Wang J, Liu X, He Y, Zhang C, Liu C, Wang T, Zhou Z. Chikusetsu saponin IVa attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in mice through activation autophagy mediated by AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling. Phytomedicine. 2019;58:152764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.024.
Yuan C, Liu C, Wang T, He Y, Zhou Z, Dun Y, Zhao H, Ren D, Wang J, Zhang C, Yuan D. Chikusetsu saponin IVa ameliorates high fat diet-induced inflammation in adipose tissue of mice through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NF-kappaB signaling. Oncotarget. 2017;8(19):31023–40. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16052.
Chen X, Wu QS, Meng FC, Tang ZH, Chen X, Lin LG, Chen P, Qiang WA, Wang YT, Zhang QW, Lu JJ. Chikusetsusaponin IVa methyl ester induces G1 cell cycle arrest, triggers apoptosis and inhibits migration and invasion in ovarian cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2016;23(13):1555–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2016.09.002.
Yuan D, Wan JZ, Deng LL, Zhang CC, Dun YY, Dai YW, Zhou ZY, Liu CQ, Wang T. Chikusetsu saponin V attenuates MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells via regulation of Sirt1/Mn-SOD and GRP78/caspase-12 pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8):13209–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150813209.
Fang X, Han Q, Li S, Zhao Y, Luo A. Chikusetsu saponin IVa attenuates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive deficits via SIRT1/ERK1/2 in developmental rats. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(9):4288–99.
Wan J, Deng L, Zhang C, Yuan Q, Liu J, Dun Y, Zhou Z, Zhao H, Liu C, Yuan D, Wang T. Chikusetsu saponin V attenuates H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells through Sirt1/PGC-1alpha/Mn-SOD signaling pathways. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;94(9):919–28. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2015-0262.
Zhou H, Li S, Wang G. Euxanthone ameliorates sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in neonatal mice. J Mol Neurosci. 2019;68(2):275–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01303-1.
Huang L, Huang K, Ning H. Hispidulin prevents sevoflurane- Induced memory dysfunction in aged rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:412–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.142.
Han M, Gao H, Xie J, Yuan YP, Yuan Q, Gao MQ, Liu KL, Chen XH, Han YT, Han ZW. Hispidulin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo by activating AMPK signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(5):666–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0159-7.
Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Antonioli L, Blandizzi C, Calderone V. Phytochemicals as novel therapeutic strategies for nlrp3 inflammasome-related neurological, metabolic, and inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122876.
Ai QD, Chen C, Chu S, Zhang Z, Luo Y, Guan F, Lin M, Liu D, Wang S, Chen N. IMM-H004 therapy for permanent focal ischemic cerebral injury via CKLF1/CCR4-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Transl Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2019.05.007.
Nakao S, Yamamoto T, Kimura S, Mino T, Iwamoto T. Brain white matter lesions and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a review. J Anesth. 2019;33(2):336–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-019-02613-9.
Safavynia SA, Goldstein PA. The role of neuroinflammation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction: moving from hypothesis to treatment. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:752. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00752.
Kotekar N, Shenkar A, Nagaraj R. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction—current preventive strategies. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:2267–73. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.s133896.
Luo A, Yan J, Tang X, Zhao Y, Zhou B, Li S. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the aged: the collision of neuroinflammaging with perioperative neuroinflammation. Inflammopharmacology. 2019;27(1):27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-00559-0.
Li D, Liu L, Li L, Li X, Huang B, Zhou C, Zhang Z, Wang C, Dong P, Zhang X, Yang B, Zhang L. Sevoflurane induces exaggerated and persistent cognitive decline in a type II diabetic rat model by aggregating hippocampal inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:886. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00886.
Lu WI, Lu DP. Impact of chinese herbal medicine on american society and health care system: perspective and concern. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:251891. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/251891.
Chen PJ, Shang AQ, Wang WW, Yang JP. Astragaloside suppresses tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 5 signaling pathway and alleviates neurodegenerative changes in retinal pigment epithelial cells induced by isoflurane. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(1):1028–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27599.
Song X, Wang W, Zhang X, Jiang Y, Yang X, Deng C, Yue Z, Tang Z. Deglucose chikusetsusaponin IVa isolated from rhizoma panacis majoris induces apoptosis in human HepG2 hepatoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(4):5494–500. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4035.
Wang H, Qi J, Li L, Wu T, Wang Y, Wang X, Ning Q. Inhibitory effects of chikusetsusaponin IVa on lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory responses in THP-1 cells. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015;28(3):308–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/0394632015589519.
Duan J, Yin Y, Wei G, Cui J, Zhang E, Guan Y, Yan J, Guo C, Zhu Y, Mu F, Weng Y, Wang Y, Wu X, Xi M, Wen A. Chikusetsu saponin IVa confers cardioprotection via SIRT1/ERK1/2 and homer1a pathway. Sci Rep. 2015;5:18123. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18123.
Yin J, Seo CS, Hwang IH, Lee MW, Song KH. Anti-obesity activities of chikusetsusaponin IVa and Dolichos lablab L. Seeds. Nutrients. 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091221.
Lee HJ, Shin JS, Lee WS, Shim HY, Park JM, Jang DS, Lee KT. Chikusetsusaponin IVa methyl ester isolated from the roots of achyranthes japonica suppresses LPS-induced iNOS, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1beta expression by NF-kappaB and AP-1 inactivation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(5):657–64. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b15-00572.
Li L, Yu Q, Liang W. Molecular pathways of mitochondrial dysfunctions: possible cause of cell death in anesthesia-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Brain Res Bull. 2015;110:14–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.10.011.
Li B, Feng XJ, Hu XY, Chen YP, Sha JC, Zhang HY, Fan HG. Effect of melatonin on attenuating the isoflurane-induced oxidative damage is related to PKCalpha/Nrf2 signaling pathway in developing rats. Brain Res Bull. 2018;143:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.09.018.
Duan J, Yin Y, Cui J, Yan J, Zhu Y, Guan Y, Wei G, Weng Y, Wu X, Guo C, Wang Y, Xi M, Wen A. Chikusetsu saponin IVa ameliorates cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in diabetic mice via adiponectin-mediated AMPK/GSK-3beta pathway in vivo and in vitro. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(1):728–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9033-x.
Chen X, Zhang X, Xue L, Hao C, Liao W, Wan Q. Treatment with enriched environment reduces neuronal apoptosis in the periinfarct cortex after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1445–566. https://doi.org/10.1159/000468368.
Hu X, Hu X, Huang G. LncRNA MALAT1 is involved in sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in developing rats. J Cell Biochem. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29127.
Chen Z, Wang E, Hu R, Sun Y, Zhang L, Jiang J, Zhang Y, Jiang H. Tetranectin gene deletion induces Parkinson's disease by enhancing neuronal apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;468(1–2):400–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.118.
Ye X, Shen T, Hu J, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Bao L, Cui C, Jin G, Zan K, Zhang Z, Yang X, Shi H, Zu J, Yu M, Song C, Wang Y, Qi S, Cui G. Purinergic 2X7 receptor/NLRP3 pathway triggers neuronal apoptosis after ischemic stroke in the mouse. Exp Neurol. 2017;292:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.03.002.
Zhang B, Zhang JW, Wang WP, Dong RF, Tian S, Zhang C. Effect of lamotrigine on epilepsy-induced cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in pentylenetetrazole-kindled animal model. Synapse. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21945.
Xu J, Huai Y, Meng N, Dong Y, Liu Z, Qi Q, Hu M, Fan M, Jin W, Lv P. L-3-n-butylphthalide activates Akt/mTOR signaling, inhibits neuronal apoptosis and autophagy and improves cognitive impairment in mice with repeated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(10):2968–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2328-3.
Elliott EI, Sutterwala FS. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1):35–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12286.
Liu Q, Zhang D, Hu D, Zhou X, Zhou Y. The role of mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol Immunol. 2018;103:115–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.09.010.
Wang Z, Meng S, Cao L, Chen Y, Zuo Z, Peng S. Critical role of NLRP3-caspase-1 pathway in age-dependent isoflurane-induced microglial inflammatory response and cognitive impairment. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1137-1.
Fan Y, Du L, Fu Q, Zhou Z, Zhang J, Li G, Wu J. Inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 ameliorates isoflurane-induced pyroptosis and cognitive impairment in aged mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00426.
Cieniewicz B, Dong Q, Li G, Forrest JC, Mounce BC, Tarakanova VL, van der Velden A, Krug LT. Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 pathogenesis is independent of caspase-1 and caspase-11 in mice and impairs interleukin-1beta production upon extrinsic stimulation in culture. J Virol. 2015;89(13):6562–74. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00658-15.
Xi G, Gao J, Wan B, Zhan P, Xu W, Lv T, Song Y. GSDMD is required for effector CD8(+) T cell responses to lung cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105713.
Lee C, Do HTT, Her J, Kim Y, Seo D, Rhee I. Inflammasome as a promising therapeutic target for cancer. Life Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116593.
Sun L, Ma W, Gao W, Xing Y, Chen L, Xia Z, Zhang Z, Dai Z. Propofol directly induces caspase-1-dependent macrophage pyroptosis through the NLRP3-ASC inflammasome. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(8):542. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1761-4.
Wilson KD, Ochoa LF, Solomon OD, Pal R, Cardona SM, Carpio VH, Keiser PH, Cardona AE, Vargas G, Stephens R. Elimination of intravascular thrombi prevents early mortality and reduces gliosis in hyper-inflammatory experimental cerebral malaria. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1207-4.
Funding
The study is supported by funding from hospital to young physicians.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS: designed the study, performed the experiments and wrote the paper. JF and SF: performed the experiments and collected the data. JW: analyzed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, A., Fei, J., Feng, S. et al. Chikusetsu saponin IVa alleviated sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment by blocking NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Pharmacol. Rep 72, 833–845 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00078-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00078-2