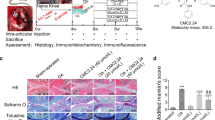
Abstract
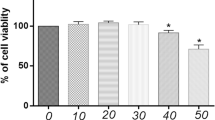
Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJ OA) is a complex multifactorial disease that can be induced by inflammation and oxidative stress. Curcumin has been reported to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Herein, the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms of curcumin in TMJ OA were investigated. Curcumin treatment inhibited the expression of the inflammation mediators IL-6, iNOS, and COX-2 and of the matrix-degrading proteinases MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5 and upregulated the mRNA levels of the cartilage anabolic factors COL2A1 and ACAN after IL-1β treatment. Curcumin treatment also decreased oxidative stress injury following IL-1β stimulation. Pathway analysis demonstrated that the ROS/Nrf2/HO-1-SOD2-NQO-1-GCLC signaling axis is a key axis through which curcumin activates the Nrf2/ARE pathway in TMJ inflammatory chondrocytes. Curcumin-induced anti-inflammatory and cartilage protective effects were significantly abrogated by specific Nrf2 siRNA. In vivo results demonstrated that curcumin treatment protected TMJ articular cartilage from progressive degradation. Our experimental results indicate that curcumin inhibits inflammation, oxidative stress, and the matrix degradation of TMJ inflammatory chondrocytes through the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway, thereby exerting cartilage protective effects. This study provides insight into potential therapeutic approaches for TMJ OA.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- ADAMTS:
-
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- COL2A1:
-
Type 2 collagen
- ACAN:
-
Aggrecan
- GCLC:
-
Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-Like 2
- NQO-1:
-
NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- SOD2:
-
Superoxide dismutase 2
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
References
Ahmed SMU, Luo L, Namani A, Wang XJ, Tang X, JB-MBoD (2016) Nrf2 signaling pathway: pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis 1863:585
Ahmed SM, Luo L, Namani A, Wang XJ, Tang X (2017) Nrf2 signaling pathway: pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis 1863:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.005
Altman RD, Gray R (1985) Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil 11:353–365
Clutterbuck AL, Mobasheri A, Shakibaei M, Allaway D, Harris P (2009) Interleukin-1β–induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:428–435
Clutterbuck AL, Mobasheri A, Shakibaei M, Allaway D, Harris P (2010) Interleukin-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:428–435
da Costa BR, Reichenbach S, Keller N, Nartey L, Wandel S, Jüni P, Trelle S (2017) Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet 390:e21–e33. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)31744-0
de Souza RF, Lovato da Silva CH, Nasser M, Fedorowicz Z, Al-Muharraqi MA (2012) Interventions for managing temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007261.pub2
Giannakopoulos NN, Keller L, Rammelsberg P, Kronmüller KT, Schmitter M (2010) Anxiety and depression in patients with chronic temporomandibular pain and in controls. J Dent 38:369–376
Goel A, Boland CR, Chauhan DP (2001) Specific inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression by dietary curcumin in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett 172:111–118
Goldring MB (2012) Articular cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis. HSS J 8:7–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-011-9250-z
Haseeb A, Haqqi TM (2013) Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol 146:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2012.12.011
Haseeb A, Chen D, Haqqi TM (2013) Delphinidin inhibits IL-1 -induced activation of NF- B by modulating the phosphorylation of IRAK-1Ser376 in human articular chondrocytes. Rheumatology 52:998–1008. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kes363
Khan NM, Sandur SK, Checker R, Sharma D, Poduval TB, Sainis KB (2011) Pro-oxidants ameliorate radiation-induced apoptosis through activation of the calcium-ERK1/2-Nrf2 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 51:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.03.037
Khan NM, Ansari MY, Haqqi TM (2017) Sucrose, but not glucose, blocks IL1-β-induced inflammatory response in human chondrocytes by inducing autophagy via AKT/mTOR pathway. J Cell Biochem 118:629
Kunnumakkara AB, Bordoloi D, Padmavathi G, Monisha J, Roy NK, Prasad S, Aggarwal BB (2017) Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases. Br J Pharmacol 174:1325–1348. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13621
Lavelle W, Lavelle ED, Lavelle L (2007) Intra-articular injections. Anesthesiol Clin 25:853–862
Lepetsos P, Papavassiliou AG (2016) ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:576–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.01.003
Moskovitz M, Sammara E, Holan G (2005) Success rate of root canal treatment in primary molars. J Dent 33:41–47
Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2004) Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med 10:549–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.003
Moussavi-Harami SF, Pedersen DR, Martin JA, Hillis SL, Brown TD (2009) Automated objective scoring of histologically apparent cartilage degeneration using a custom image analysis program. J Orthop Res 27:522–528. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.20779
Paniagua B et al (2017) Diagnostic Index: An open-source tool to classify TMJ OA condyles. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng 10137:101372H
Poulet B, Beier F (2016) Targeting oxidative stress to reduce osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 18:18–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0908-7
Prasad KN (2016) Simultaneous activation of Nrf2 and elevation of antioxidant compounds for reducing oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in human Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 153:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.01.002
Pritzker KPH et al (2006) Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthr Cartil 14:13–29
Shakibaei M, John T, Schulzetanzil G, Lehmann I, Mobasheri AJBP (2007) Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by curcumin leads to inhibition of expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human articular chondrocytes: implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol 73:1434–1445
Souza RFD, Silva CHLD, Nasser M, Fedorowicz Z, Al-Muharraqi MA (2008) Interventions for the management of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD007261
Tipton DA, Christian J, Blumer A (2016) Effects of cranberry components on IL-1β-stimulated production of IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF by human TMJ synovial fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol 68:88–96
Togni L, de Abreu MC, Augustin AH, da Silva RBM, Campos MM (2018) Characterization of a rat model with temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis following a surgical anterior disc displacement. Am J Transl Res 10:3806–3817
Yan-Qin Q, Pan-Feng J, Gao Y-Z (2018) Lutein prevents osteoarthritis through Nrf2 activation and downregulation of inflammation. Arch Med Sci 14:617–624
Zhang W et al (2010) OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: part III: changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthr Cartil 18:476–499
Zhang Z, Leong DJ, Xu L, He Z, Wang A, Navati M, Kim SJ, Hirsh DM, Hardin JA, Cobelli NJ, Friedman JM, Sun HB (2016) Curcumin slows osteoarthritis progression and relieves osteoarthritis-associated pain symptoms in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Arthritis Res Ther 18:128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-1025-y
Zhang G, Cao J, Yang E, Liang B, Ding J, Liang J, Xu J (2018) Curcumin improves age-related and surgically induced osteoarthritis by promoting autophagy in mice. Biosci Rep:38. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20171691
Zhou PH, Qiu B, Deng RH, Li HJ, Xu XF, Shang XF (2018) Chondroprotective effects of hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles containing plasmid DNA encoding cytokine response modifier A in a rat knee osteoarthritis model. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:1207–1216. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490217
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81800999), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2019 M653355), Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJQN201800414), and Program for Innovation Team Building at Institutions of Higher Education in Chongqing in 2016, Chongqing Medical Research Project (No. 2016MSXM046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The specific contributions of the authors are as follows:
(1) Study conception and design: Chao Jiang, Ping Luo, Xian Li, Ping Liu, Yong Li, Jie Xu.
(2) Data analysis and interpretation: Chao Jiang, Ping Luo, Xian Li, Ping Liu, Yong Li, Jie Xu.
(3) Data collection and management: Chao Jiang, Ping Luo.
(4) Drafting of the article: Chao Jiang, Ping Luo.
(5) Review of the article for important intellectual content and article revision: Xian Li, Ping Liu, Yong Li, Jie Xu.
(6) Final approval of the article: Chao Jiang, Ping Luo, Xian Li, Ping Liu, Yong Li, Jie Xu.
(7) Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work: Chao Jiang, Ping Luo, Xian Li, Ping Liu, Yong Li, Jie Xu.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were performed according to the terms of the Animal Committee.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval for the collection of human TMJ cartilage samples was obtained from the Committee of Chongqing Medical University.
Ethical statement
The collection of human TMJ cartilage samples conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
All the participants expressed informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Luo, P., Li, X. et al. Nrf2/ARE is a key pathway for curcumin-mediated protection of TMJ chondrocytes from oxidative stress and inflammation. Cell Stress and Chaperones 25, 395–406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01079-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01079-z