Abstract
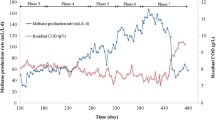
Sludge reduction performance and bacterial community dynamics in a pilot-scale multi-stage digester system with prolonged sludge retention time were characterized. Throughout the operation period of 281 days, the total loading sludge and the total digested sludge were 4700 and 3300 kg-MLSS. After 114 days of operation, the residual MLSS (RMLSS) in the reactors for sludge treatment was maintained at 18–25 kg-RMLSS m−3, and the sludge reduction efficiency achieved 95% under the F/M ratio (kg-loading MLSS kg-RMLSS−1) of less than 0.018. Also, among the sludge components, both fixed suspended solids and volatile suspended solids were reduced. Based on the sludge reduction performance and the RNA-based bacterial community characteristics, the combined action of the maintenance metabolism, lysis–cryptic growth, and particulate inorganic matter is proposed as the sludge reduction mechanism in the multi-stage sludge treatment process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pérez-Rodrígueza M, Canob A, Durána U, Barriosa JA (2019) Solubilization of organic matter by electrochemical treatment of sludge: influence of operating conditions. J Environ Manag 236:317–322
Zhang Q, Hu J, Lee DJ, Chang Y, Lee YJ (2017) Sludge treatment: current research trends. Bioresour Technol 243:1159–1172
Wang Z, Yu H, Ma J, Zheng X, Wu Z (2013) Recent advances in membrane bio-technologies for sludge reduction and treatment. Biotechnol Adv 31:1187–1199
Jiang LM, Zhou Z, Cheng C, Li J, Huang C, Niu T (2018) Sludge reduction by a micro-aerobic hydrolysis process: a full-scale application and sludge reduction mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 268:684–691
Seo KW, Choi YS, Gu MB, Kwon EE, Tsang YF, Rinklebe J, Park C (2017) Pilot-scale investigation of sludge reduction in aerobic digestion system with endospore-forming bacteria. Chemosphere 186:202–208
Banaei FK, Zinatizadeh AAL, Mesgar M, Salari Z (2013) Dynamic performance analysis and simulation of a full scale activated sludge system treating an industrial wastewater using artificial neural network. Int J Eng Trans A Basics 26:465–472
Guo W-Q, Yang S-S, Xiang W-S, Wang X-J, Ren N-Q (2013) Minimization of excess sludge production by in-situ activated sludge treatment processes—a comprehensive review. Biotechnol Adv 31:1386–1396
Kim TG, Moon K-E, Yun J, Cho K-S (2013) Comparison of RNA-and DNA-based bacterial communities in a lab-scale methane-degrading biocover. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:171–3181
Delforno TP, Macedo TZ, Midoux C, Lacerda GV Jr, Rué O, Mariadassou M, Loux V, Varesche MB, Bouchez T, Bize A, Oliveira VM (2019) Comparative metatranscriptomic analysis of anaerobic digesters treating anionic surfactant contaminated wastewater. Sci Total Environ 649:482–494
Xia Y, Yang C, Zhang T (2018) Microbial effects of part-stream low-frequency ultrasonic pretreatment on sludge anaerobic digestion as revealed by high-throughput sequencing-based metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:47–60
Korean Ministry of Environment (2017) Korean Standard Methods for Examinations of Water Quality. Korean Ministry of Environment. Revised in 2017. Seoul, Republic of Korea. https://www.me.go.kr. Accessed 19 Aug 2019
Korean Ministry of Environment (2015) Korean Standard Soil Analysis Method. Korean Ministry of Environment. Seoul, Republic of Korea. https://www.me.go.kr. Accessed 19 Aug 2019
Pollice A, Laera G, Saturno D, Giordano C, Sandulli R (2008) Optimal sludge retention time for a bench scale MBR treating municipal sewage. Water Sci Technol 57:319–322
Yoon S-H, Kim H-S, Yeom I-T (2004) The optimum operational condition of membrane bioreactor (MBR): cost estimation of aeration and sludge treatment. Water Res 38:37–46
Heran M, Wisniewski C, Orantes J, Grasmick A (2008) Measurement of kinetic parameters in a submerged aerobic membrane bioreactor fed on acetate and operated without biomass discharge. Biochem Eng J 38:70–77
Laera G, Pollice A, Saturno D, Giordano C, Lopez A (2005) Zero net growth in a membrane bioreactor with complete sludge retention. Water Res 39:5241–5249
Rosenberger S, Witzig R, Manz W, Szewzyk U, Kraume M (2000) Operation of different membrane bioreactors: experimental results and physiological state of the microorganisms. Water Sci Technol 41:269–277
Huang X, Gui P, Qian Y (2001) Effect of sludge retention time on microbial behavior in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 36:1001–1006
Teck HC, Loong KS, Sun DD, Leckie JO (2009) Influence of a prolonged solid retention time environment on nitrification/denitrification and sludge production in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Desalination 245:28–43
Sun DD, Khor SL, Hay CT, Leckie JO (2007) Impact of prolonged sludge retention time on the performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor. Desalination 208:101–112
Lozupone CA, Stombaugh JI, Gordon JI, Jansson JK, Knight R (2012) Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489:220–230
Briones A, Raskin L (2003) Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in engineered environments and their implications for process stability. Curr Opin Biotech 14:270–276
Kulichevskaya IS, Suzina NE, Rijpstra WIC, Damste JSS, Dedysh SN (2014) Paludibaculum fermentans gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultative anaerobe capable of dissimilatory iron reduction from subdivision 3 of the Acidobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2857–2864
Kojima H, Tokizawa R, Fukui M (2014) Mizugakiibacter sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3983–3987
Yan ZF, Lin P, Wang YS, Gao W, Li CT, Kook MC, Yi TH (2016) Niastellahibisci sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Mugunghwa, the Korean national flower. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:5218–5222
Qu Y, Ma Q, Deng J, Shen W, Zhang X, He Z, Nostrand JDV, Zhou J, Zhou J (2015) Responses of microbial communities to single-walled carbon nanotubes in phenol wastewater treatment systems. Environ Sci Technol 49:4627–4635
Lau KW, Ng CY, Ren J, Lau SC, Qian PY, Wong PK, Lau TC, Wu M (2005) Owenweeksia hongkongensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel marine bacterium of the phylum ‘Bacteroidetes’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1051–1057
Hedaoo M, Gore D, Fadnavis S, Dange M, Soni MA, Kopulwar AP (2018) Bioinformatics approach in speciation of oil degrading uncultured bacterium and its frequency recording. J Pharm Res 12:628–635
Bondoso J, Albuquerque L, Nobre MF, Lobo-da-Cunha A, da Costa MS, Lage OM (2011) Aquisphaera giovannonii gen. nov., sp. nov., a planctomycete isolated from a freshwater aquarium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2844–2850
Miller RA, Beno SM, Kent DJ, Carroll LM, Martin NH, Boor KJ, Kovac J (2016) Bacillus wiedmannii sp. nov., a psychrotolerant and cytotoxic Bacillus cereus group species isolated from dairy foods and dairy environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4744–4753
Zhu J (2000) A review of microbiology in swine manure odor control. Agric Ecosyst Environ 78:93–106
Song YL, Liu CX, McTeague M, Summanen P, Finegold SM (2004) Clostridium bartlettii sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Anaerobe 10:179–184
Kodama Y, Watanabe K (2011) Rhizomicrobium electricum sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic, fermentative, prosthecate bacterium isolated from a cellulose-fed microbial fuel cell. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1781–1785
Osman NI, Yin S (2018) Isolation and characterization of pea plant (Pisum sativum L.) growth-promoting Rhizobacteria. Afr J Microbiol Res 12:820–828
Illham M, Aurelio S, Abdelaziz S (2013) Solubilization of inorganic phosphate and production of organic acids by bacteria isolated from a Moroccan mineral phosphate deposit. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:626–635
Kim SJ, Ahn JH, Weon HY, Hong SB, Seok SJ, Kim JS, Kwon SW (2015) Chujaibacter soli gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from soil. J Microbiol 53:592–597
Lee Y-Y, Hong S, Cho K-S (2019) Design and shelf stability assessment of bacterial agents for simultaneous removal of methane and odors. J Environ Sci Health Part A 54:906–913
Yun J, Jung H, Ryu H-W, Oh K-C, Jeon J-M, Cho K-S (2018) Odor mitigation and bacterial community dynamics in on-site biocovers at a sanitary landfill in South Korea. Environ Res 166:516–528
Gu Q, Wu Q, Zhang J, Guo W, Wu H, Sun M (2016) Community analysis and recovery of phenol-degrading bacteria from drinking water biofilters. Front Microbiol 7:495
Deng L, Ren Y, Wei C (2012) Pyrene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. and Burkholderia sp. enriched from coking wastewater sludge. J Environ Sci Health A 47:1984–1991
Kristiansen A, Pedersen KH, Nielsen PH, Nielsen LP, Nielsen JL, Schramm A (2011) Bacterial community structure of a full-scale biofilter treating pig house exhaust air. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:344–352
Monot F, Abbad-Andaloussi S, Warzywoda M (2002) Biological culture containing Rhodococcus erythropolis and/or Rhodococcus rhodnii and process for desulfurization of petroleum fraction. US Patent No 6337204
Oldfield C, Pogrebinsky O, Simmonds J, Olson ES, Kulpa CF (1997) Elucidation of the metabolic pathway for dibenzothiophene desulphurization by Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8 (ATCC 53968). Microbiology 143:2961–2973
Benning MM, Meyer TE, Holden HM (1996) Molecular structure of a high potential cytochrome c2 isolated from Rhodopila globiformis. Ach Biochem Biophys 333:338–348
Guo JS, Xu YF (2011) Review of enzymatic sludge hydrolysis. J Bioremed Biodegrad 2:130
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Global Eco Technology Company (Incheon, Republic of Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, J., Ryu, HW., Kim, H.P. et al. Characterization of sludge reduction and bacterial community dynamics in a pilot-scale multi-stage digester system with prolonged sludge retention time. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 1171–1183 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02312-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02312-w