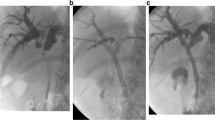
Abstract
Background
In patients with unresectable hilar malignant biliary obstruction (MBO), bilateral metal stent placement is recommended. However, treatment selection between partially stent-in-stent (SIS) and side-by-side (SBS) methods is still controversial.
Study
Clinical outcomes of bilateral metal stent placement by SBS and SIS methods for hilar MBO were retrospectively studied in four Japanese centers. While large-cell-type uncovered metal stents were placed above the papilla in SIS, braided-type uncovered metal stents were placed across the papilla in SBS.
Results
A total of 64 patients with hilar MBO (40 SIS and 24 SBS) were included in the analysis. Technical success rate was 100% in SIS and 96% in SBS. Functional success rate was 93% in SIS and 96% in SBS. Early adverse event rates were higher in SBS (46%) than in SIS (23%), though not statistically significant (P = 0.09). Post-procedure pancreatitis was exclusively observed in SBS group (29%). Recurrent biliary obstruction rates were 48% and 43%, and the median time to recurrent biliary obstruction was 169 and 205 days in SIS and SBS, respectively.
Conclusions
Other than a trend to higher adverse event rates including post-procedure pancreatitis in SBS, clinical outcomes of SIS and SBS methods were comparable in patients with unresectable hilar MBO.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perdue DG, Freeman ML, DiSario JA, et al. Plastic versus self-expanding metallic stents for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a prospective multicenter observational cohort study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;42:1040–1046.
Sangchan A, Kongkasame W, Pugkhem A, et al. Efficacy of metal and plastic stents in unresectable complex hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76:93–99.
Rerknimitr R, Angsuwatcharakon P, Ratanachu-ek T, et al. Asia-Pacific consensus recommendations for endoscopic and interventional management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:593–607.
Mukai T, Yasuda I, Nakashima M, et al. Metallic stents are more efficacious than plastic stents in unresectable malignant hilar biliary strictures: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2013;20:214–222.
Gao DJ, Hu B, Ye X, et al. Metal versus plastic stents for unresectable gallbladder cancer with hilar duct obstruction. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2017;29:97–103.
Dumonceau JM, Tringali A, Papanikolaou IS, et al. Endoscopic biliary stenting: indications, choice of stents, and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline—updated october 2017. Endoscopy. 2018;50:910–930.
Vienne A, Hobeika E, Gouya H, et al. Prediction of drainage effectiveness during endoscopic stenting of malignant hilar strictures: the role of liver volume assessment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:728–735.
Takahashi E, Fukasawa M, Sato T, et al. Biliary drainage strategy of unresectable malignant hilar strictures by computed tomography volumetry. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:4946–4953.
Chang WH, Kortan P, Haber GB. Outcome in patients with bifurcation tumors who undergo unilateral versus bilateral hepatic duct drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998;47:354–362.
De Palma GD, Galloro G, Siciliano S, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic hepatic duct drainage in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction: results of a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:547–553.
Naitoh I, Ohara H, Nakazawa T, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:552–557.
Iwano H, Ryozawa S, Ishigaki N, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral drainage using self-expandable metallic stent for unresectable hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2011;23:43–48.
Liberato MJ, Canena JM. Endoscopic stenting for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: efficacy of unilateral and bilateral placement of plastic and metal stents in a retrospective review of 480 patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:103.
Lee TH, Kim TH, Moon JH, et al. Bilateral versus unilateral placement of metal stents for inoperable high-grade malignant hilar biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective, randomized study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:817–827.
Kogure H, Isayama H, Nakai Y, et al. Newly designed large cell Niti-S stent for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a pilot study. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:463–467.
Kogure H, Isayama H, Nakai Y, et al. High single-session success rate of endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement with modified large cell Niti-S stents for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2014;26:93–99.
Lee JM, Lee SH, Chung KH, et al. Small cell-versus large cell-sized metal stent in endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2015;27:692–699.
Saleem A, Baron TH, Gostout CJ. Large-diameter therapeutic channel duodenoscope to facilitate simultaneous deployment of side-by-side self-expandable metal stents in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:628–631.
Naitoh I, Hayashi K, Nakazawa T, et al. Side-by-side versus stent-in-stent deployment in bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:3279–3285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2270-9.
Law R, Baron TH. Bilateral metal stents for hilar biliary obstruction using a 6Fr delivery system: outcomes following bilateral and side-by-side stent deployment. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:2667–2672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2671-4.
Yoshida T, Hara K, Imaoka H, et al. Benefits of side-by-side deployment of 6-mm covered self-expandable metal stents for hilar malignant biliary obstructions. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2016;23:548–555.
Kawakubo K, Kawakami H, Kuwatani M, et al. Single-step simultaneous side-by-side placement of a self-expandable metallic stent with a 6-Fr delivery system for unresectable malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a feasibility study. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:151–155.
Cosgrove N, Siddiqui AA, Adler DG, et al. A comparison of bilateral side-by-side metal stents deployed above and across the sphincter of oddi in the management of malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;51:528–533.
Hsieh J, Thosani A, Grunwald M, et al. Serial insertion of bilateral uncovered metal stents for malignant hilar obstruction using an 8 Fr biliary system: a case series of 17 consecutive patients. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2015;4:348–353.
Moon JH, Rerknimitr R, Kogure H, et al. Topic controversies in the endoscopic management of malignant hilar strictures using metal stent: side-by-side versus stent-in-stent techniques. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:650–656.
Lee TH, Moon JH, Choi JH, et al. Prospective comparison of endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent versus stent-by-stent deployment for inoperable advanced malignant hilar biliary stricture. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;90:222–230.
Ito K, Sakamoto Y, Isayama H, et al. The impact of MDCT and endoscopic transpapillary mapping biopsy to predict longitudinal spread of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract. 2018;22:1528–1537.
Isayama H, Hamada T, Yasuda I, et al. TOKYO criteria 2014 for transpapillary biliary stenting. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2015;27:259–264.
Nakai Y, Isayama H, Tsujino T, et al. Intraductal US in the assessment of tumor involvement to the orifice of the cystic duct by malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:78–83.
Kongkam P, Tasneem AA, Rerknimitr R. Combination of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage in malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2019;31:50–54.
Nakai Y, Kogure H, Isayama H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage for unresectable hilar malignant biliary obstruction. Clin Endosc. 2019;52:220–225.
Tarnasky PR, Cunningham JT, Hawes RH, et al. Transpapillary stenting of proximal biliary strictures: does biliary sphincterotomy reduce the risk of postprocedure pancreatitis? Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;45:46–51.
Kawakubo K, Isayama H, Nakai Y, et al. Risk factors for pancreatitis following transpapillary self-expandable metal stent placement. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:771–776.
Shiomi H, Matsumoto K, Isayama H. Management of acute cholangitis as a result of occlusion from a self-expandable metallic stent in patients with malignant distal and hilar biliary obstructions. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2017;29:88–93.
Inoue T, Naitoh I, Okumura F, et al. Reintervention for stent occlusion after bilateral self-expandable metallic stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2016;28:731–737.
Okuno M, Mukai T, Iwashita T, et al. Evaluation of endoscopic reintervention for self-expandable metallic stent obstruction after stent-in-stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2019;26:211–218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KI, TH, HI, and YN conceived and designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data, and drafted the article. TS, RH, KS, TS, NT, SM, HK, YI, HY, SM, DA, DM, MT, and KK critically revised the article for important intellectual content. All authors contributed to the final approval of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yousuke Nakai and Hiroyuki Isayama received research grant from Boston Scientific Japan. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishigaki, K., Hamada, T., Nakai, Y. et al. Retrospective Comparative Study of Side-by-Side and Stent-in-Stent Metal Stent Placement for Hilar Malignant Biliary Obstruction. Dig Dis Sci 65, 3710–3718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06155-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06155-z