Abstract
Background
A limited number of publications correlate bidimensional shear-wave elastography (2-D SWE) and stages of liver fibrosis in children.
Objective
To correlate liver elastography values using 2-D SWE and liver biopsy classified by Knodell–Ishak score to evaluate fibrosis in pediatric patients with liver disease, and to propose values of 2-D SWE (kPa) correlating with Knodell–Ishak score, which have not been defined in the literature.
Materials and methods
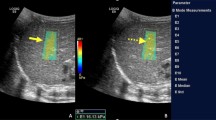
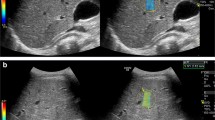
We conducted a prospective cross-sectional observational study on the performance of diagnostic tests. Between June 2016 and June 2018, elastography was performed in 213 children and young adults who had undergone liver biopsy. B mode, Doppler and 2-D SWE were performed using an Aixplorer (SuperSonic Imagine, Aix-en-Provence, France). Histology samples were classified using the Knodell–Ishak score. We evaluated performance by assessing sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value. To determine cut-off points for the continuous variables, we used receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. All the cutoff values we established apply only to the SuperSonic Aixplorer system.
Results
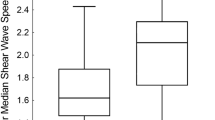
Measurement with 2-D SWE was successful, with a good correlation with fibrosis stage. The area under the curve (AUC) to differentiate between early (Stages 1–2) and moderate (Stages 3–4) fibrosis was 0.91 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.87–0.96), with a sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 86%, with a cutoff value 12 kPa (2 m/s). The AUC of severe fibrosis (early stages of cirrhosis; Stage 5) was 0.95 (95% CI: 0.92–0.97), with a sensitivity of 94% and specificity of 90%, with a cutoff value 18.5 kPa (2.48 m/s). In two patients with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and suspicion of graft versus host disease we found high 2-D SWE values in correlation with the fibrosis stages (Stage 0 with a median of 13 kPa [2.08 m/s] with hemosiderosis Grade 2 in one child and Stage 2 with a median of 46 kPa [3.91 m/s] and hemosiderosis Grade 4 in the other).
Conclusion
Our study shows the usefulness and accuracy of 2-D SWE for detecting liver fibrosis in pediatric patients. We propose reference values for Knodell–Ishak Stages 1 and 5. We found hemosiderosis as a possible confounding factor that hasn’t been described with 2-D SWE.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mews C, Sinatra F (1993) Chronic liver disease in children. Pediatr Rev 14:436–444
Belei O, Sporea I, Gradinaru-Tascau O et al (2016) Comparison of three ultrasound based elastographic techniques in children and adolescents with chronic diffuse liver diseases. Med Ultrason 18:145–150
Shiha G, Zalata K (2011) Ishak versus METAVIR: terminology, convertibility and correlation with laboratory changes in chronic hepatitis C. In: Takahashi H (ed) Liver biopsy. https://www.intechopen.com/books/liver-biopsy. Accessed 22 Dec 2019
Barr RG, Ferraioli G, Palmeri ML et al (2015) Elastography assessment of liver fibrosis: Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound consensus conference statement. Radiology 276:845–861
Dillman JR, Heider A, Bilhartz JL et al (2015) Ultrasound shear wave speed measurements correlate with liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 45:1480–1488
Dhyani M, Gee MS, Misdraji J et al (2015) Feasibility study for assessing liver fibrosis in paediatric and adolescent patients using real-time shear wave elastography. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 59:687–694
Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC et al (1981) Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology 1:431–435
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L et al (1995) Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22:9696–9999
Abdall AF, Zalata KR, Ismail AF (2009) Regression of fibrosis in paediatric autoimmune hepatitis: morphometric assessment of fibrosis versus semiquantiatative methods. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2:2
Cohen MB, A-Kader HH, Lambers D, Heubi JE (1992) Complications of percutaneous liver biopsy in children. Gastroenterology 102:629–632
Serai SD, Trout AT, Miethke A et al (2018) Putting it all together: established and emerging MRI techniques for detecting and measuring liver fibrosis. Pediatr Radiol 48:1256–1272
Hwang JY, Yoon HM, Kim JR et al (2018) Diagnostic performance of transient elastography for liver fibrosis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 211:W257–W266
De Ledinghen V, Le Bail B, Rebouissoux L et al (2007) Liver stiffness measurement in children using FibroScan: feasibility study and comparison with Fibrotest, aspartate transaminase to platelets ratio index, and liver biopsy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 45:443–450
Engelmann G, Gebhardt C, Wenning D et al (2012) Feasibility study and control values of transient elastography in healthy children. Eur J Pediatr 171:353–360
Fitzpatrick E, Quaglia A, Vimalesvaran S et al (2013) Transient elastography is a useful noninvasive tool for the evaluation of fibrosis in paediatric chronic liver disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 56:72–76
Goldschmidt I, Stieghorst H, Munteanu M et al (2013) The use of transient elastography and non-invasive serum markers of fibrosis in pediatric liver transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant 17:525–534
Goldschmidt I, Streckenbach C, Dingemann C et al (2013) Application and limitations of transient liver elastography in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 57:109–113
Noruegas MJ, Matos H, Goncalves I et al (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging in the assessment of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 42:201–204
Hanquinet S, Rougemont AL, Courvoisier D et al (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 43:545–551
Pinto J, Matos H, Nobre S et al (2014) Comparison of acoustic radiation force impulse/serum noninvasive markers for fibrosis prediction in liver transplant. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 58:382–386
Kim JR, Suh CH, Yoon HM et al (2017) The diagnostic performance of shear wave elastography for liver fibrosis in children and adolescents: systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 28:1175–1186
Tutar O, Beser OF, Adaletli I et al (2014) Shear wave elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 58:750–755
Shin HJ, Kim MJ, Kim HY et al (2016) Optimal acquisition number for hepatic shear wave velocity measurements in children. PLoS One 11:e0168758
Franchi-Abella S, Corno L, Gonzales E et al (2016) Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of supersonic shear-wave elastography for the assessment of liver stiffness and liver fibrosis in children: a pilot study of 96 patients. Radiology 278:554–562
Garcovich M, Veraldi S, Di Stasio E et al (2016) Liver stiffness in pediatric patients with fatty liver disease: diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility of shear-wave elastography. Radiology 283:820–827
Galina P, Alexopoulou E, Zellos A et al (2019) Performance of two-dimensional ultrasound shear wave elastography: reference values of normal liver stiffness in children. Pediatr Radiol 49:91–98
Barr RG (2017) Shear wave liver elastography. Abdom Radiol 3:800–807
Behairy E, Sira M, Zalata K et al (2016) Transient elastography compared to liver biopsy and morphometry for predicting fibrosis in pediatric chronic liver disease: does etiology matter? World J Gastroenterol 22:4238–4249
Sporea I, Gradinaru-Tascaū O, Bota S et al (2013) How many measurements are needed for liver stiffness assessment by 2D-elastography (2D-SWE) and which value should be used: the mean or median? Med Ultrason 15:268–272
Ferraioli G, Wong VW, Castera L et al (2018) Liver ultrasound elastography: an update to the World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology guidelines and recommendations. Ultrason Med Biol 44:2419–2440
Goodman ZD (2007) Grading and staging systems for inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol 47:598–607
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dardanelli, E.P., Orozco, M.E., Lostra, J. et al. Bidimensional shear-wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in children: a proposal of reference values that correlate with the histopathological Knodell–Ishak score. Pediatr Radiol 50, 817–826 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04632-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04632-1