Abstract
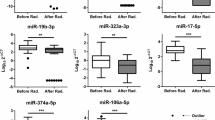
In recent years, scientists have found evidence confirming the aberrant expression of miRNAs in cancer patients compared to healthy individuals. The growing interest in the identification of non-invasive and specific diagnostic and prognostic molecular markers has identified microRNAs as potential candidates in cancer diagnosis, prognosis and treatment response. In the present study, we have analyzed the expression profile of circulating miR-21, -191 and -421 in peripheral blood of head and neck cancer patients (HNC) to investigate a possible modulation of mRNA levels by radiation and to identify the role of mRNA as biomarkers of cancer prognosis. Results showed a modulation of the microRNA expression at different time points after radiotherapy, suggesting that treatment may influence the release of circulating miRNAs depending also on the time interval elapsed since radiotherapy. The expression levels of miR-21, -191 and -421 were higher in blood of patients treated with radiotherapy alone after 6 months from the end of therapy and high levels of them seemed to correlate with the remission of the disease. The trends shown in this study confirmed that miRNAs could be useful prognosis markers and could provide preliminary data for further evaluation in predicting patients’ response to radiotherapy by developing miRNA-based treatments to improve the sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi CL, Chng WJ (2011) MiRNA deregulation in multiple myeloma. Chin Med J (Engl) 124:3164–3169
Cellini F, Morganti AG, Genovesi D, Silvestris N, Valentini V (2014) Role of microRNA in response to ionizing radiations: evidences and potential impact on clinical practice for radiotherapy. Molecules 19(4):5379–5401
Chen L, Wen Y, Zhang J, Sun W, Lui VWY, Wei Y, Chen F, Wen W (2018) Prediction of radiotherapy response with a 5-microRNA signature-based nomogram in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med 7(3):726–735. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1369
Courthod G, Franco P, Palermo L, Pisconti S, Numico G (2014) The role of microRNA in head and neck cancer: current knowledge and perspectives. Molecules 19(5):5704–5716. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19055704
Farooqi AA, Qureshi MZ, Coskunpinar E, Naqvi SK, Yaylim I, Ismail M (2014) MiR-421, miR-155 and miR-650: emerging trends of regulation of cancer and apoptosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(5):1909–1912
Gombos K, Horváth R, Szele E, Juhász K, Gőcze K, Somlai K, Pajkos G, And Ember I, Olasz L (2013) MiRNA expression profiles of oral squamous cell carcinomas. Anticancer Res 33:1511–1518
Hailiang H, Liutao D, Gindy N, Robert CS, Richard AG (2010) ATM is down-regulated by N-Myc–regulated microRNA-421. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(4):1506–1511
Halimi M, Asghari SM, Sariri R, Moslemi D, Parsian H (2012) Cellular response to ionizing radiation: a MicroRNA story. Int J Mol Cell Med 1(4):178–184
Han HS, Jo YN, Lee JY, Choi SY, Jeong Y, Yun J, Lee OJ (2014) Identification of suitable reference genes for the relative quantification of microRNAs in pleural effusion. Oncol Lett 8(4):1889–1895. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2014.2404
Hu H, Du L, Nagabayashi G, Seeger RC, Gatti RA (2010) ATM is down-regulated by N-Myc-regulated microRNA-421. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:1506–1511. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907763107
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Ochiya T (2010) Circulating microRNA in body fluid: new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci 101(10):2087–2092. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01650.x
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lubov J, Maschietto M, Ibrahim I, Mlynarek A, Hier M, Kowalski LP, Alaoui-Jamali MA, da Silva SD (2017) Meta-analysis of microRNAs expression in head and neck cancer: uncovering association with outcome and mechanisms. Oncotarget 8(33):55511–55524. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19224
Mansour WY, Bogdanova NV, Kasten-Pisula U, Rieckmann T, Köcher S, Borgmann K, Baumann M, Krause M, Petersen C, Hu H, Gatti RA, Dikomey E, Dörk T, Dahm-Daphi J (2013) Aberrant overexpression of miR-421 downregulates ATM and leads to a pronounced DSB repair defect and clinical hypersensitivity in SKX squamous cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 106(1):147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2012.10.020
Metheetrairut C, Slack FJ (2013) MicroRNAs in the ionizing radiation response and in radiotherapy. Curr Opin Genet Dev 23(1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2013.01.002
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10513–10518. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804549105
Nagpal N, Ahmad HM, Molparia B, Kulshreshtha R (2013) MicroRNA-191, an estrogen-responsive microRNA, functions as an oncogenic regulator in human breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 34:1889–1899. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgt107
Noren Hooten N, Fitzpatrick M, Wood WH 3rd, De S, Ejiogu N, Zhang Y, Mattison JA, Becker KG, Zonderman AB, Evans MK (2013) Age-related changes in microRNA levels in serum. Aging 5(10):725–740
Paolini A, Curti V, Pasi F, Mazzini G, Nano R, Capelli E (2015) Gallic acid exerts a protective or an anti-proliferative effect on glioma T98G cells via dose-dependent epigenetic regulation mediated by miRNAs. Int J Oncol 46(4):1491–1497. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.2864
Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Yendamuri S (2010) Overexpression of microRNA miR-30a or miR-191 in A549 lung cancer or BEAS-2B normal lung cell lines does not alter phenotype. PLoS ONE 5:e9219. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009219
Reddy K (2015) MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int 15:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-015-0185-1
Rusanova I, Diaz-Casado ME, Fernández-Ortiz M, Aranda-Martínez P, Guerra-Librero A, García-García FJ, Escames G, Mañas L, Acuña-Castroviejo D (2018) Analysis of plasma MicroRNAs as predictors and biomarkers of aging and frailty in humans. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:7671850. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7671850
Smith-Vikos T, Slack FJ (2012) MicroRNAs and their roles in aging. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 1):7–17. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.099200
Sundarbose K, Kartha RV, Subramanian S (2013) MicroRNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Diagnostics (Basel) 3(1):84–104. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3010084
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(7):2257–2261
Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X, Li H, Dulak A, Tomko RJJ, Lazo JS, Wang Z, Zhang L, Yu J (2009) MicroRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:8157–8165. https://doi.org/10.1158/00085472.CAN-09-1996
Wu DG, Wang YY, Fan LG, Luo H, Han B, Sun LH, Wang XF, Zhang JX, Cao L, Wang XR, You YP, Liu N (2011) MicroRNA-7 regulates glioblastoma cell invasion via targeting focal adhesion kinase expression. Chin Med J (Engl) 124:2616–2621
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY, Yang SL (2016) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol 37(9):12061–12070
Zhang X, Ng WL, Wang P, Tian L, Werner E, Wang H, Doetsch P, Wang Y (2012) MicroRNA-21 modulates the levels of reactive oxygen species levels by targeting SOD3 and TNF. Cancer Res 72(18):4707–4713. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0639
Zhao L, Lu X, Cao Y (2013) MicroRNA and signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response. Cell Signal 25(7):1625–1634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.004
Zhao J, Qiao CR, Ding Z, Sheng YL, Li XN, Yang Y, Zhu DY, Zhang CY, Liu DL, Wu K, Zhao S (2017) A novel pathway in NSCLC cells: miR-191, targeting NFIA, is induced by chronic hypoxia, and promotes cell proliferation and migration. Mol Med Rep 15(3):1319–1325
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Staff of Department of Radiation Oncology, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia for their support to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicting interests
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasi, F., Corbella, F., Baio, A. et al. Radiation-induced circulating miRNA expression in blood of head and neck cancer patients. Radiat Environ Biophys 59, 237–244 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-020-00832-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-020-00832-3