Abstract
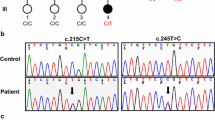
Reports of spectrum of clinical manifestations in PMP22 gene–associated neuropathies (duplication/mutations) are scarce. To identify the frequency of PMP22 gene variations and establish their genotype-phenotype correlation. Patients with suspected genetic demyelinating neuropathy (n = 128) underwent evaluation for copy number variations and point mutations in PMP22 gene by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) and direct sequencing respectively. Of these, only 27 patients (M:F:19:8) from 18 families had PMP22 gene–associated neuropathy; they were subsequently analyzed for genotype-phenotype correlation. Twenty-five patients had PMP22 duplication while two patients had PMP22 missense mutations (p.A114V and p.L80P). Age at onset of neuropathy ranged from infancy to 63 years and symptom duration ranged from 2 to 32 years. Cranial nerve dysfunction in the form of ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, bifacial weakness, and sensorineural hearing loss was observed in addition to a number of systemic features. Three patients were asymptomatic. All except one patient were ambulant. Velocity of median nerve and amplitude of evoked motor responses from common peroneal nerve were significantly reduced in male patients. There was significantly worse disability in the late-onset group as compared with the early-onset group. Otherwise, the mean age at onset, frequency of skeletal deformities, patterns of motor weakness, muscle stretch reflexes, sensory impairment, disability rating scales, and electrophysiological parameters were comparable irrespective of gender, onset age, family history and ulnar nerve conduction velocities. The relatively low frequency of PMP22 duplication in the present cohort warrants a more comprehensive search to establish the genetic etiology. Further research into the role of other genetic variants as well as modifier genes and their effect on phenotypic heterogeneity is indicated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe A, Numakura C, Kijima K, Hayashi M, Hashimoto T, Hayasaka K (2011) Molecular diagnosis and clinical onset of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Japan. J Hum Genet 56(5):364–368
Aho TR, Wallace RC, Pitt AM, Sivakumar K (2004) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: extensive cranial nerve involvement on CT and MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(3):494–497
Azevedo H, Pupe C, Pereira R, Nascimento OJM (2018) Pain in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an update. ArqNeuropsiquiatr. 76(4):273–276
Barreto LC, Oliveira FS, Nunes PS, de França Costa IM, Garcez CA, Goes GM, Neves EL, de Souza Siqueira Quintans J, de Souza Araújo AA (2016) Epidemiologic Study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: a systematic review. Neuroepidemiology. 46(3):157–165
Boerkoel CF, Takashima H, Garcia CA, Olney RK, Johnson J, Berry K, Russo P, Kennedy S, Teebi AS, Scavina M, Williams LL, Mancias P, Butler IJ, Krajewski K, Shy M, Lupski JR (2002) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related neuropathies: mutation distribution and genotype-phenotype correlation. Ann Neurol 51(2):190–201
Botsford B, Vuong LN, Hedges TR III, Mendoza-Santiesteban CE (2017) Characterization of Charcot-Marie-Tooth optic neuropathy. J Neurol 264(12):2431–2435
Chanson JB, Echaniz-Laguna A, Blanc F, Lacour A, Ballonzoli L, Kremer S, Namer IJ, Lannes B, Tranchant C, Vermersch P, de Seze J (2013) Central nervous system abnormalities in patients with PMP22 gene mutations: a prospective study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(4):392–397
Choi BO, Lee MS, Shin SH, Hwang JH, Choi KG, Kim WK, Sunwoo IN, Kim NK, Chung KW (2004) Mutational analysis of PMP22, MPZ, GJB1, EGR2 and NEFL in Korean Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy patients. Hum Mutat 24(2):185–186
Choi JE, Seok JM, Ahn J, Ji YS, Lee KM, Hong SH, Choi BO, Moon IJ (2018) Hidden hearing loss in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Sci Rep 8(1):10335
Coffey RJ, Fromm GH (1991) Familial trigeminal neuralgia and Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. Report of two families and review. Surg Neurol 35(1):49–53
Colomban C, Micallef J, Lefebvre MN, Dubourg O, Gonnaud PM, Stojkovic T, Jouve E, Blin O, Pouget J, Attarian S (2014) Clinical spectrum and gender differences in a large cohort of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A patients. J Neurol Sci 336(1–2):155–160
Das N, Kandalaft S, Wu X, Malhotra A (2017) Cranial nerve involvement inCharcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Clin Neurosci 37:59–62
Deymeer F, Matur Z, Poyraz M, Battaloglu E, Oflazer-Serdaroglu P, Parman Y (2011) Nerve conduction studies in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in a cohort from Turkey. Muscle Nerve 43(5):657–664
DiVincenzo C, Elzinga CD, Medeiros AC, Karbassi I, Jones JR, Evans MC, Braastad CD, Bishop CM, Jaremko M, Wang Z, Liaquat K, Hoffman CA, York MD, Batish SD, Lupski JR, Higgins JJ (2014) The allelic spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in over 17,000 individuals with neuropathy. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2(6):522–529
Gabreëls-Festen AA, Bolhuis PA, Hoogendijk JE, Valentijn LJ, Eshuis EJ, Gabreëls FJ (1995) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A: morphological phenotype of the 17p duplication versus PMP22 point mutations. Acta Neuropathol 90(6):645–649
Gadoth N, Gordon CR, Bleich N, Pratt H (1991) Three modality evoked potentials in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (HMSN-1). Brain Dev 13(2):91–94
Hermans G, Clerckx B, Vanhullebusch T, Segers J, Vanpee G, Robbeets C, Casaer MP, Wouters P, Gosselink R, Van Den Berghe G (2012) Interobserver agreement of Medical Research Council sum-score and handgrip strength in the intensive care unit. Muscle Nerve 45(1):18–25
Joo IS, Ki CS, Joo SY, Huh K, Kim JW (2004) A novel point mutation in PMP22 gene associated with a familial case of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A withsensorineural deafness. Neuromuscul Disord 14(5):325–328
Khadilkar SV, Patil ND, Kadam ND, Mansukhani KA, Patel BA (2017) Clinico-electrophysiological and genetic overlaps and magnetic resonance imaging findings in Charcot-Marie- Tooth disease: a pilot study from Western India. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 20(4):425–429
Knopp M, Leese RJ, Martin-Lamb D, Rajabally YA (2014) Optic and auditory pathway dysfunction in demyelinating neuropathies. Acta Neurol Scand 130(1):53–57
Kovach MJ, Lin JP, Boyadjiev S, Campbell K, Mazzeo L, Herman K, Rimer LA, Frank W, Llewellyn B, Jabs EW, Gelber D, Kimonis VE (1999) A unique point mutation in the PMP22 gene is associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and deafness. Am J Hum Genet 64(6):1580–1593
Kumagai-Eto R, Kaseda Y, Tobimatsu S, Uozumi T, Tsuji S, Nakamura S (2004) Subclinical cranial nerve involvement in hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy: a combined conduction study with electrical and magnetic stimulation. ClinNeurophysiol. 115(7):1689–1696
Li J, Parker B, Martyn C, Natarajan C, Guo J (2013) The PMP22 gene and its related diseases. Mol Neurobiol 47(2):673–698
Liu P, Gelowani V, Zhang F, Drory VE, Ben-Shachar S, Roney E, Medeiros AC, Moore RJ, DiVincenzo C, Burnette WB, Higgins JJ, Li J, Orr-Urtreger A, Lupski JR (2014) Mechanism, prevalence, and more severe neuropathy phenotype of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A triplication. Am J Hum Genet 94(3):462–469
Manganelli F, Pisciotta C, Reilly MM, Tozza S, Schenone A, Fabrizi GM, Cavallaro T, Vita G, Padua L, Gemignani F, Laurà M, Hughes RA, Solari A, Pareyson D, Santoro L, CMT-TRIAAL and CMT-TRAUK Group (2016) Nerve conduction velocity in CMT1A: what else can we tell? Eur J Neurol 23(10):1566–1571
Marlin S, Jonard L, Loundon N, Bonnet C, Leboulanger N, Van Maldergem L, Gherbi S, Louha M, Deltenre P, Collette JL, Couderc R, Garabedian EN, Denoyelle F (2011) Genetic update on auditory neuropathy. Audiol Neurotol Extra 1:20–29
Mathis S, Corcia P, Tazir M, Camu W, Magdelaine C, Latour P, Biberon J, Guennoc AM, Richard L, Magy L, Funalot B, Vallat JM (2014) Peripheral myelin protein 22 gene duplication with atypical presentations: a new example of the wide spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A disease. Neuromuscul Disord 24(6):524–528
Mersiyanova IV, Ismailov SM, Polyakov AV, Dadali EL, Fedotov VP, Nelis E, Löfgren A, Timmerman V, van Broeckhoven C, Evgrafov OV (2000) Screening for mutations in the peripheral myelin genes PMP22, MPZ and Cx32 (GJB1) in Russian Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy patients. Hum Mutat 15(4):340–347
Milley GM, Varga ET, Grosz Z, Nemes C, Arányi Z, Boczán J, Diószeghy P, Molnár MJ, Gál A (2018) Genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of the most common causative genesof Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Hungarian patients. Neuromuscul Disord 28(1):38–43
Murphy SM, Laura M, Fawcett K, Pandraud A, Liu YT, Davidson GL, Rossor AM, Polke JM, Castleman V, Manji H, Lunn MP, Bull K, Ramdharry G, Davis M, Blake JC, Houlden H, Reilly MM (2012) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: frequency of genetic subtypes and guidelines for genetic testing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(7):706–710
Numakura C, Lin C, Ikegami T, Guldberg P, Hayasaka K (2002) Molecular analysis in Japanese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: DGGE analysis for PMP22,MPZ,and Cx32/GJB1 mutations. Hum Mutat 20(5):392–398
Pareyson D, Scaioli V, Laurà M (2006) Clinical and electrophysiological aspects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neuromolecular Med 8(1-2):3–22
Piantino JA, Torres A (2007) Myoclonic seizures in a patient with Charcot-Marie-tooth disease. Pediatr Neurol 36(2):118–120
Posa A, Emmer A, Kornhuber ME (2017) Unilateral oculomotor palsy in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 1A (CMT 1A). Clin Neurol Neurosurg 155:20–21
Rajabally YA, Adams D, Latour P, Attarian S (2016) Hereditary and inflammatory neuropathies: a review of reported associations, mimics and misdiagnoses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87(10):1051–1060
Ramchandren S (2017) Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Other Genetic Polyneuropathies. Continuum (MinneapMinn) 23(5, Peripheral Nerve and Motor Neuron Disorders):1360–1377
Ribiere C, Bernardin M, Sacconi S, Delmont E, Fournier-Mehouas M, Rauscent H, Benchortane M, Staccini P, Lantéri-Minet M, Desnuelle C (2012) Pain assessment inCharcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 55(3):160–173
Russo M, Laurá M, Polke JM, Davis MB, Blake J, Brandner S, Hughes RA, Houlden H, Bennett DL, Lunn MP, Reilly MM (2011) Variable phenotypes are associated with PMP22 missense mutations. Neuromuscul Disord 21(2):106–114
Sambuughin N, de Bantel A, McWilliams S, Sivakumar K (2003) Deafness and CMT disease associated with a novel four amino acid deletion in the PMP22 gene. Neurology. 60(3):506–508
Saporta AS, Sottile SL, Miller LJ, Feely SM, Siskind CE, Shy ME (2011) Charcot-Marie-tooth disease subtypes and genetic testing strategies. Ann Neurol 69(1):22–33
Seeman P, Mazanec R, Huehne K, Suslíková P, Keller O, Rautenstrauss B (2004) Hearing loss as the first feature of late-onset axonal CMT disease due to a novel P0 mutation. Neurology. 63(4):733–735
Shy ME, Blake J, Krajewski K, Fuerst DR, Laura M, Hahn AF, Li J, Lewis RA, Reilly M (2005) Reliability and validity of the CMT neuropathy score as a measure of disability. Neurology. 64(7):1209–1214
Street VA, Meekins G, Lipe HP, Seltzer WK, Carter GT, Kraft GH, Bird TD (2002) Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy: clinical phenotypes of four novel mutations inthe MPZ and Cx 32 genes. Neuromuscul Disord 12(7–8):643–650
Stuppia L, Antonucci I, Palka G, Gatta V (2012) Use of the MLPA assay in the molecular diagnosis of gene copy number alterations in human genetic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 13(3):3245–3276
Swan ER, Fuerst DR, Shy ME (2007) Women and men are equally disabled byCharcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Neurology. 68(11):873
Tsao CY (2011) Intractable epilepsy, audio-visual hallucinations and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 1A in an African-American boy. Clin EEG Neurosci 42(3):206–208
Tyson J, Ellis D, Fairbrother U, King RH, Muntoni F, Jacobs J, Malcolm S, Harding AE, Thomas PK (1997) Hereditary demyelinating neuropathy of infancy. A genetically complex syndrome. Brain 120(Pt 1):47–63
Vaeth S, Christensen R, Dunø M, Lildballe DL, Thorsen K, Vissing J, Svenstrup K, Hertz JM, Andersen H, Jensen UB (2019) Genetic analysis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Denmark and the implementation of a next generation sequencingplatform. Eur J Med Genet 62(1):1–8
van Paassen BW, van der Kooi AJ, van Spaendonck-Zwarts KY, Verhamme C, Baas F, de Visser M (2014) PMP22 related neuropathies: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A and hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9:38
Verhagen WI, Huygen PL, Gabreëls-Festen AA, Engelhart M, van Mierlo PJ, van Engelen BG (2005) Sensorineural hearing impairment in patients with Pmp22 duplication,deletion, and frameshift mutations. Otol Neurotol 26(3):405–414
Verhamme C, van Schaik IN, Koelman JH, de Haan RJ, de Visser M (2009) The natural history of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A in adults: a 5-year follow-up study. Brain 132(Pt 12):3252–3262
Watila MM, Balarabe SA (2015) Molecular and clinical features of inheritedneuropathies due to PMP22 duplication. J Neurol Sci 355(1–2):18–24
Werheid F, Azzedine H, Zwerenz E, Bozkurt A, Moeller MJ, Lin L, Mull M, Häusler M, Schulz JB, Weis J, Claeys KG (2016) Underestimated associated features in CMT neuropathies: clinical indicators for the causative gene? Brain Behav 6(4):e00451
Wong RH, Farhat HI (2013) Charcot-Marie-tooth and trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(10):2234–2235
Zhan Y, Zi X, Hu Z, Peng Y, Wu L, Li X, Jiang M, Liu L, Xie Y, Xia K, Tang B, Zhang R (2015) PMP22-Related neuropathies and other clinical manifestations in Chinese Han patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. Muscle Nerve 52(1):69–75
Sources of Funding
The study is a part of a larger study funded by a grant from the Indian Council of Medical Research (BMS/TF/Trans-Neuro/2014-3389/July-15/16/KA/Govt dated 25th July 2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Institute Ethics Committee (NIMHANS/DO/103RDIEC/2016).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagappa, M., Sharma, S., Govindaraj, P. et al. PMP22 Gene–Associated Neuropathies: Phenotypic Spectrum in a Cohort from India. J Mol Neurosci 70, 778–789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01488-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01488-w