Abstract
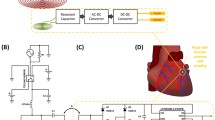
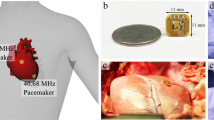
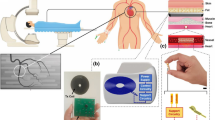
Despite numerous advancements in pacemaker technology for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction disorders, lead-related complications associated with these devices continue to compromise patient safety and survival. In this work, we present a system architecture that has the capacity to deliver power to a wireless, batteryless intravascular pacer. This was made possible through a three-tiered, dual-sub-system, four-coil design, which operates on two different frequencies through intermittent remote-controlled inductive power transfer. System efficiency was enhanced using coil design optimization, and validated using numerical simulations and experimental analysis. Our pacemaker design was concepted to achieve inductive power transfer over a 55 mm range to a microscale pacer with a 3 mm diameter. Thus, the proposed system design enabled long-range wireless power transfer to a small implanted pacer with the capacity for intravascular deployment to the anterior cardiac vein. This proposed stent-like fixation mechanism can bypass the multitude of complications associated with pacemaker wires while wireless power can eliminate the need for repeated procedures for battery replacement.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiri, P., A. Abiri, R. R. S. Packard, Y. Ding, A. Yousefi, J. Ma, M. Bersohn, K.-L. Nguyen, D. Markovic, S. Moloudi, and T. K. Hsiai. Inductively powered wireless pacing via a miniature pacemaker and remote stimulation control system. Sci. Rep. 7:6180, 2017.
Agrawal, D. R., Y. Tanabe, D. Weng, A. Ma, S. Hsu, S. Y. Liao, Z. Zhen, Z. Y. Zhu, C. Sun, Z. Dong, F. Yang, H. F. Tse, A. S. Y. Poon, and J. S. Ho. Conformal phased surfaces for wireless powering of bioelectronic microdevices. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-017-0043.
Ali, H., T. J. Ahmad, and S. A. Khan. Inductive Link Design for Medical Implants, 2009.
Auricchio, A., P. P. Delnoy, F. Regoli, M. Seifert, T. Markou, and C. Butter. First-in-man implantation of leadless ultrasound-based cardiac stimulation pacing system: novel endocardial left ventricular resynchronization therapy in heart failure patients. Europace 15:1191–1197, 2013.
Bakogianni, S., and S. Koulouridis. Sub-1 GHz far-field powering of implantable medical devices: design and safety considerations, 2015.
Chen, S. C. Q., and V. Thomas. Optimization of Inductive RFID Technology. In: Int. Symp. Electron. Environ, 2001, pp. 82–87.
Cleveland, R. F., D. M. Sylvar, and J. L. Ulcek. Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. Washington, D.C., 1997.
FDA Executive Summary Memorandum General Issues: Leadless Pacemaker Devices. Gaithersburg, 2016.
Finkenzeller, K. RFID Handbook: Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication. Chippenham: Wiley, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470665121.
Grandolfo, M., P. Vecchia, and O. P. Gandhi. Magnetic resonance imaging: calculation of rates of energy absorption by a human-torso model. Bioelectromagnetics 11:117–128, 1990.
Grover, F. W. Inductance calculations: working formulas and tables. Instrum. Soc. Am., 1946.
Heetderks, W. J. RF powering of millimeter- and submillimeter-sized neural prosthetic implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 35:323–327, 1988.
Ho, J. S., A. J. Yeh, E. Neofytou, S. Kim, Y. Tanabe, B. Patlolla, R. E. Beygui, and A. S. Y. Poon. Wireless power transfer to deep-tissue microimplants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111:7974–7979, 2014.
Hwang, G. T., H. Park, J. H. Lee, S. Oh, K. Il Park, M. Byun, H. Park, G. Ahn, C. K. Jeong, K. No, H. Kwon, S. G. Lee, B. Joung, and K. J. Lee. Self-powered cardiac pacemaker enabled by flexible single crystalline PMN-PT piezoelectric energy harvester. Adv. Mater. 26:4880–4887, 2014.
Jeon, D., Y. Chen, Y. Lee, Y. Kim, Z. Foo, G. Kruger, H. Oral, O. Berenfeld, Z. Zhang, D. Blaauw, and D. Sylvester. An implantable 64nW ECG-monitoring mixed-signal soc for arrhythmia diagnosis, 2014.
Jow, U., and M. Ghovanloo. Design and optimization of printed spiral coils for efficient transcutaneous inductive power transmission. Optimization 1:193–202, 2008.
Karami, M. A., and D. J. Inman. Powering pacemakers from heartbeat vibrations using linear and nonlinear energy harvesters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100:042901, 2012.
Kiani, M., U. M. Jow, and M. Ghovanloo. Design and optimization of a 3 coil inductive link for efficient wireless power transmission. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 5:579–591, 2011.
Kim, S., J. S. Ho, L. Y. Chen, and A. S. Y. Poon. Wireless power transfer to a cardiac implant. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101:1–5, 2012.
Kurs, A., A. Karalis, R. Moffatt, J. D. Joannopoulos, P. Fisher, and M. Soljacic. Wireless power transfer via strongly coupled magnetic resonances. Science 317:83–86, 2007.
Lee, H. M., and M. Ghovanloo. A power-efficient wireless capacitor charging system through an inductive link. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 60:707–711, 2013.
Lee, B., M. Kiani, and M. Ghovanloo. A triple-loop inductive power transmission system for biomedical applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 10:138–148, 2016.
Lee, S. Y., M. Y. Su, M. C. Liang, Y. Y. Chen, C. H. Hsieh, C. M. Yang, H. Y. Lai, J. W. Lin, and Q. Fang. A programmable implantable microstimulator soc with wireless telemetry: application in closed-loop endocardial stimulation for cardiac pacemaker. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 5:511–522, 2011.
Li, X., C. Y. Tsui, and W. H. Ki. A 13.56 MHz wireless power transfer system with reconfigurable resonant regulating rectifier and wireless power control for implantable medical devices. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 50:978–989, 2015.
Loeb, G. E., C. J. Zamin, J. H. Schulman, and P. R. Troyk. Injectable microstimulator for functional electrical stimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1991. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446097.
Mela, T., and J. P. Singh. Leadless pacemakers: leading us into the future? Eur. Heart J. 36:2520–2522, 2015.
MicraTM MC1VR01 Clinical Manual. Minneapolis, 2016.
Monti, G., L. Tarricone, and C. Trane. Experimental characterization of a 434 MHz wireless energy link for medical applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 30:53–64, 2012.
Neagu, C. R., H. V. Jansen, A. Smith, J. G. E. Gardeniers, and M. C. Elwenspoek. Characterization of a planar microcoil for implantable microsystems. Sens Actuators A 62:599–611, 1997.
Ouyang, H., Z. Liu, N. Li, B. Shi, Y. Zou, F. Xie, Y. Ma, Z. Li, H. Li, Q. Zheng, X. Qu, Y. Fan, Z. L. Wang, H. Zhang, and Z. Li. Symbiotic cardiac pacemaker. Nat. Commun. 10:1821, 2019.
Parramon, J., P. Doguet, D. Marin, M. Verleyssen, R. Munoz, L. Leija, and E. Valderrama. ASIC-based batteryless implantable telemetry microsystem for recording purposes, 1997.
RamRakhyani, A. K., S. Mirabbasi, and M. Chiao. Design and optimization of resonance-based efficient wireless power delivery systems for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 5:48–63, 2011.
Seol, S. J., H. Cho, D. H. Yoon, and S. H. Jang. Appropriate depth of needle insertion during rhomboid major trigger point block. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 38:72–76, 2014.
Sperzel, J., H. Burri, D. Gras, F. V. Y. Tjong, R. E. Knops, G. Hindricks, C. Steinwender, and P. Defaye. State of the art of leadless pacing. Europace 17:1508–1513, 2015.
Sun, J. P., X. S. Yang, Y. Y. Lam, M. J. Garcia, and C. M. Yu. Evaluation of coronary venous anatomy by multislice computed tomography. World J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2:91–95, 2012.
Udo, E. O., N. P. A. Zuithoff, N. M. Van Hemel, C. C. De Cock, T. Hendriks, P. A. Doevendans, and K. G. M. Moons. Incidence and predictors of short- and long-term complications in pacemaker therapy: the FOLLOWPACE study. Hear Rhythm 9:728–735, 2012.
Vest, A. N., L. Zhou, X. Huang, V. Norekyan, Y. Bar-Cohen, R. H. Chmait, and G. E. Loeb. Design and testing of a transcutaneous RF recharging system for a fetal micropacemaker. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2620805.
Von Arx, J. A., and K. Najafi. A wireless single-chip telemetry-powered neural stimulation system. In: 1999 IEEE Int. Solid-State Circuits Conf. Dig. Tech. Pap. ISSCC. First Ed. (Cat. No.99CH36278), pp. 214–215, 1999.https://doi.org/10.1109/isscc.1999.759199
Welsby, V. G. The Theory and Design of Inductance Coils. London: Wiley, 1960.
Wong, L. S. Y., S. Hossain, A. Ta, J. Edvinsson, D. H. Rivas, and H. Nääs. A very low-power CMOS mixed-signal IC for implantable pacemaker applications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 39:2446–2456, 2004.
Xi Nan, and C. R. Sullivan. An improved calculation of proximity-effect loss in high-frequency windings of round conductors, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1109/pesc.2003.1218168
Zhang, Z., K. T. Chau, C. Qiu, and C. Liu. Energy encryption for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30:5237–5246, 2015.
Zhong, W., C. K. Lee, and S. Y. Ron Hui. General analysis on the use of tesla’s resonators in domino forms for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 60:261–270, 2013.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health HL118650 (T.K. Hsiai), HL129727 (T.K. Hsiai), HL111437 (T.K. Hsiai), BX004356 (T.K. Hsiai), EB0220002 (T.K. Hsiai), GM008042 (P. Abiri), and UCLA David Geffen Scholarship (P. Abiri).
Conflicts of interest
No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Lakshmi Prasad Dasi oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abiri, P., Abiri, A., Gudapati, V. et al. Wireless Pacing Using an Asynchronous Three-Tiered Inductive Power Transfer System. Ann Biomed Eng 48, 1368–1381 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02450-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02450-y