Abstract
Objective
To determine bacteriocin producers and the prevalence of structural enterocin genes and to detect the spectrum of activity against foodborne pathogens, from isolates of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis that were isolated from food and the environment.
Results
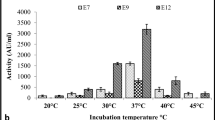
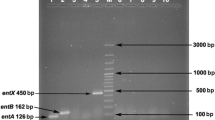
The entA, entB, entP, ent1071 and entX genes, which encode enterocins were the most frequently observed. Enterocins were thermostable, proteinaceous, and resistant to catalase. None of the isolates produced hemolysin, and inhibition resulting from bacteriophage lysis was excluded. The bactericidal effect of enterocins against L. innocua 12612 was determined by optical density and colony forming units. For the activity spectrum, elimination of mainly Listeria strains, Bacillus sp. and clinical enterococci, was observed. Imaging with scanning electron microscopy after treatment with enterocin Efm22 showed irregular rod-shaped cells and loss of cellular integrity.
Conclusions
The isolates evaluated in this study are candidates for the production of enterocins that will be used as food biopreservatives, because they have high anti-listerial activity even after 24 h of experimentation, and used in the pharmaceutical area because they inhibit clinical microorganisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avci M, Özden TB (2017) Safety evaluation of enterocin producer Enterococcus sp. strains isolated from traditional turkish cheeses. Pol J Microbiol 6:223–233
Ben Braïek O, Cremonesi P, Morandi S, Smaoui S, Hani K, Ghrairi T (2018) Safety characterisation and inhibition of fungi and bacteria by a novel multiple enterocin-producing Enterococcus lactis 4CP3 strain. Microb Pathogenesis 118:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.005
Benz J, Meinhart A (2014) Antibacterial effector/immunity systems: it's just the tip of the iceberg. Curr Opin Microbiol 17:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2013.11.002
Citti L, Rovero P, Colombo MG, Mariani L, Poliseno L, Rainaldi G (2002) Efficacy of an amphipathic oligopeptide to shuttle and release a cis-acting DNA decoy into human cells. Biotechniques 32:172–177. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00782
De Vuyst L, Moreno MF, Revets H (2003) Screening for enterocins and detection of hemolysin and vancomycin resistance in enterococci of different origins. Int J Food Microbiol 84:299–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00425-7
Du Toit M, Franz CMAP, Dicks LMT, Holzapfel WH (2000) Preliminary characterization of bacteriocins produced by Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis isolated from pig faeces. J Appl Microbiol 88:482–494. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00986.x
Eaton TJ, Gasson MJ (2001) Molecular screening of Enterococcus virulence determinants and potential for genetic exchange between food and medical isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1628–1635. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.4.1628-1635.2001
Edalatian MR, Najafi MBH, Mortazavi SA, Alegría Á, Delgado S, Bassami MR, Mayo B (2012) Production of bacteriocins by Enterococcus spp. isolated from traditional, Iranian, raw milk cheeses, and detection of their encoding genes. Eur Food Res Technol 234:789–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-011-0045-2
Furlaneto-Maia L, Rocha KR, Henrique FC, Giazzi A, Furlaneto MC (2014) Antimicrobial resistance in Enterococcus sp isolated from soft cheese in Southern Brazil. Adv Microbiol 4:175–181. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2014.43023
Hassan M, Diep DB, Javadzadeh Y, Dastmalchi S, Nes IF, Sharifi Y, Saber Y, Safar F, Lotfipour F (2012) Prevalence of bacteriocin activities and bacteriocin-encoding genes in enterococcal clinical isolates in Iran. Can J Microbiol 58:359–368. https://doi.org/10.1139/W11-136
Jaouani I, Abbassi MS, Alessandria V, Bouraoui J, Ben SR, Kilani H, Mansouri R, Messadi L, Cocolin L (2014) High inhibition of Paenibacillus larvae and Listeria monocytogenes by Enterococcus isolated from different sources in Tunisia and identification of their bacteriocin genes. Lett Appl Microbiol 59:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12239
Kaur B, Garg N (2013) Characteristics of bacteriocin BA28 produced by Pediococcus acidi lactici BA28. Mintage J Pharm Med Sci 2:17–20
Khademi F, Sahebkar A (2019) A systematic review and meta-analysis on the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Listeria species in food, animal and human specimens in Iran. J Food Sci Technol 56:5167–5183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04040-w
Maia LF, Costa LC, Rocha KR, Schueller J, Tosoni NF, Furlaneto MC (2019) Influence of optimised commercial medium on bacteriocin production by Enterococcus faecium. Acta Sci Technol 41:e42324. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascitechnol.v41i1.42324
Martin M, Gutierrez J, Criado R, Herranz C, Cintas LM, Hernandez PE (2006) Genes encoding bacteriocins and their expression and potential virulence factors of enterococci isolated from wood pigeons (Columba palumbus). J Food Prot 69:520–531. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x-69.3.520
Masias E, Dupuy FG, da Silva Sanches PR, Farizano JV, Cilli E, Bellomio A, Minahk C (2017) Impairment of the class IIa bacteriocin receptor function and membrane structural changes are associated to enterocin CRL35 high resistance in Listeria monocytogenes. BBA 1861:1770–1776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.03.014
Mogoşanu GD, Grumezescu AM, Bejenaru C, Bejenaru LE (2017) Natural products used for food preservation, food preservation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 365–411. eBook ISBN: 9780128043745
Ogaki MB, Rocha KR, Terra MR, Furlaneto MC, Furlaneto-Maia L (2016) Screening of the enterocin-encoding genes and antimicrobial activity in Enterococcus species. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1509.09020
Özdemir GB, Oryaşın E, Bıyık HH, Özteber M, Bozdoğan B (2011) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of bacteriocins in enterococcal isolates of different sources. Indian J Microbiol 51:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0143-0
Perin LM, Miranda RO, Camargo AC, Colombo M, Carvalho AF, Nero LA (2013) Antimicrobial activity of the Nisin Z producer Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Lc08 against Listeria monocytogenes in skim milk. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 65:1554–1560. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-09352013000500037
Pingitore EV, Todorov SD, Sesma F, Franco BDGM (2012) Application of bacteriocinogenic Enterococcus mundtii CRL35 and Enterococcus faecium ST88Ch in the control of Listeria monocytogenes in fresh Minas cheese. Food Microbiol 32:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2012.04.005
Rehaiem A, Martínez B, Manai M, Rodríguez A (2012) Technological performance of the enterocin A producer Enterococcus faecium MMRA as a protective adjunct culture to enhance hygienic and sensory attributes of traditional fermented milk ‘Rayeb’. Food Bioprocess Technol 5:2140–2150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0501-7
Rocha KR, Perini HF, Souza CM, Schueler J, Tosoni NF, Furlaneto MC, Furlaneto-Maia L (2019) Inhibitory effect of bacteriocins from enterococci on developing and preformed biofilms of Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria ivanovii and Listeria innocua. World J Microb Biot 35:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2675-0
Schittler L, Perin LM, de Lima MJ, Lando V, Todorov SD, Nero LA, da Silva WP (2019) Isolation of Enterococcus faecium, characterization of its antimicrobial metabolites and viability in probiotic Minas Frescal cheese. J Food Sci Technol 56:5128–5137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03985-2
Tomé E, Todorov SD, Gibbs PA, Teixeira PC (2009) Partial characterization of nine bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from cold-smoked salmon with activity against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Biotechnol 23:50–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/08905430802671956
Vandera E, Tsirka G, Kakouri A, Koukkou AI, Samelis J (2018) Approaches for enhancing in situ detection of enterocin genes in thermized milk, and selective isolation of enterocin-producing Enterococcus faecium from Baird-Parker agar. Int J Food Microbiol 281:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.05.020
Vandera E, Parapouli M, Kakouri A, Koukkou AI, Hatziloukas E, Samelis J (2020) Structural enterocin gene profiles and mode of antilisterial activity in synthetic liquid media and skim milk of autochthonous Enterococcus spp. isolates from artisan Greek Graviera and Galotyri cheeses. Food Microbiol 86:103335.
Zhang F, Jiang M, Wan C, Chen X, Chen X, Tao X, Shah NP, Wei H (2016) Screening probiotic strains for safety: evaluation of virulence and antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococci from healthy Chinese infants. Dairy Sci 99:4282–4290. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10690
Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang H, Bu Y, Yi H, Zhang L, Han X, Ai L (2018) Purification and partial characterization of bacteriocin Lac-B23, a novel bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum J23, isolated from Chinese traditional fermented milk. Front Microbiol 9:2165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02165
Zommiti M, Cambronel M, Maillot O, Barreau M, Sebei K, Feuilloley M, Ferchichi M, Connil N (2018) Evaluation of probiotic properties and safety of Enterococcus faecium isolated from artisanal tunisian meat “Dried Ossban”. Front Microbiol 6:1685. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01685
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Fundação Araucária/ Governo do Paraná – Brazil, PROPPG/ UTFPR. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, nor in the data collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript, nor the decision to publish the results.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furlaneto-Maia, L., Ramalho, R., Rocha, K.R. et al. Antimicrobial activity of enterocins against Listeria sp. and other food spoilage bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 42, 797–806 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02810-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02810-7