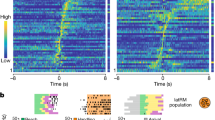
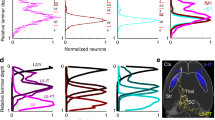
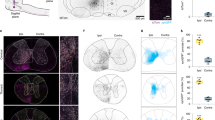
Abstract
The caudal forelimb area (CFA) of the mouse cortex is essential in many forelimb movements, and diverse types of GABAergic interneuron in the CFA are distinct in the mediation of cortical inhibition in motor information processing. However, their long-range inputs remain unclear. In the present study, we combined the monosynaptic rabies virus system with Cre driver mouse lines to generate a whole-brain map of the inputs to three major inhibitory interneuron types in the CFA. We discovered that each type was innervated by the same upstream areas, but there were quantitative differences in the inputs from the cortex, thalamus, and pallidum. Comparing the locations of the interneurons in two sub-regions of the CFA, we discovered that their long-range inputs were remarkably different in distribution and proportion. This whole-brain mapping indicates the existence of parallel pathway organization in the forelimb subnetwork and provides insight into the inhibitory processes in forelimb movement to reveal the structural architecture underlying the functions of the CFA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwaniuk AN, Whishaw IQ. On the origin of skilled forelimb movements. Trends Neurosci 2000, 23: 372–376.
Lemon RN. Descending pathways in motor control. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008, 31: 195–218.
Wang X, Liu Y, Li X, Zhang Z, Yang H, Zhang Y, et al. Deconstruction of corticospinal circuits for goal-directed motor skills. Cell 2017, 171: 440–455 e14.
Tennant KA, Adkins DL, Donlan NA, Asay AL, Thomas N, Kleim JA, et al. The organization of the forelimb representation of the C57BL/6 mouse motor cortex as defined by intracortical microstimulation and cytoarchitecture. Cereb Cortex 2011, 21: 865–876.
Touvykine B, Mansoori BK, Jean-Charles L, Deffeyes J, Quessy S, Dancause N. The effect of lesion size on the organization of the ipsilesional and contralesional motor cortex. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2016, 30: 280–292.
Zingg B, Hintiryan H, Gou L, Song MY, Bay M, Bienkowski MS, et al. Neural networks of the mouse neocortex. Cell 2014, 156: 1096–1111.
Ramanathan D, Conner JM, Tuszynski MH. A form of motor cortical plasticity that correlates with recovery of function after brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103: 11370–11375.
Harrison TC, Ayling OG, Murphy TH. Distinct cortical circuit mechanisms for complex forelimb movement and motor map topography. Neuron 2012, 74: 397–409.
Hira R, Terada S, Kondo M, Matsuzaki M. Distinct functional modules for discrete and rhythmic forelimb movements in the mouse motor cortex. J Neurosci 2015, 35: 13311–13322.
Sachidhanandam S, Sermet BS, Petersen CCH. Parvalbumin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex contribute to gating a goal-directed sensorimotor transformation. Cell Rep 2016, 15: 700–706.
Nelson A, Schneider DM, Takatoh J, Sakurai K, Wang F, Mooney R. A circuit for motor cortical modulation of auditory cortical activity. J Neurosci 2013, 33: 14342–14353.
Lee S, Kruglikov I, Huang ZJ, Fishell G, Rudy B. A disinhibitory circuit mediates motor integration in the somatosensory cortex. Nat Neurosci 2013, 16: 1662–1670.
Zhang S, Xu M, Kamigaki T, Hoang Do JP, Chang WC, Jenvay S, et al. Selective attention. Long-range and local circuits for top-down modulation of visual cortex processing. Science 2014, 345: 660–665.
Wickersham IR, Lyon DC, Barnard RJ, Mori T, Finke S, Conzelmann KK, et al. Monosynaptic restriction of transsynaptic tracing from single, genetically targeted neurons. Neuron 2007, 53: 639–647.
Wang X, Yang H, Pan L, Hao S, Wu X, Zhan L, et al. Brain-wide mapping of mono-synaptic afferents to different cell types in the laterodorsal tegmentum. Neurosci Bull 2019, 35: 781–790.
Wall NR, De La Parra M, Sorokin JM, Taniguchi H, Huang ZJ, Callaway EM. Brain-wide maps of synaptic input to cortical interneurons. J Neurosci 2016, 36: 4000–4009.
Zhang S, Xu M, Chang WC, Ma C, Hoang Do JP, Jeong D, et al. Organization of long-range inputs and outputs of frontal cortex for top-down control. Nat Neurosci 2016, 19: 1733–1742.
Su YT, Gu MY, Chu X, Feng X, Yu YQ. Whole-brain mapping of direct inputs to and axonal projections from GABAergic neurons in the parafacial zone. Neurosci Bull 2018, 34: 485–496.
Li Z, Chen Z, Fan G, Li A, Yuan J, Xu T. Cell-type-specific afferent innervation of the nucleus accumbens core and shell. Front Neuroanat 2018, 12: 84.
Luo P, Li A, Zheng Y, Han Y, Tian J, Xu Z, et al. Whole brain mapping of long-range direct input to glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in motor cortex. Front Neuroanat 2019, 13: 44.
Sun Q, Li X, Ren M, Zhao M, Zhong Q, Ren Y, et al. A whole-brain map of long-range inputs to GABAergic interneurons in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 2019, 22: 1357–1370.
Jiang T, Long B, Gong H, Xu T, Li X, Duan Z, et al. A platform for efficient identification of molecular phenotypes of brain-wide neural circuits. Sci Rep 2017, 7: 13891.
Oh SW, Harris JA, Ng L, Winslow B, Cain N, Mihalas S, et al. A mesoscale connectome of the mouse brain. Nature 2014, 508: 207–214.
Xu X, Roby KD, Callaway EM. Immunochemical characterization of inhibitory mouse cortical neurons: three chemically distinct classes of inhibitory cells. J Comp Neurol 2010, 518: 389–404.
Hooks BM, Mao T, Gutnisky DA, Yamawaki N, Svoboda K, Shepherd GM. Organization of cortical and thalamic input to pyramidal neurons in mouse motor cortex. J Neurosci 2013, 33: 748–760.
Li X, Yu B, Sun Q, Zhang Y, Ren M, Zhang X, et al. Generation of a whole-brain atlas for the cholinergic system and mesoscopic projectome analysis of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115: 415–420.
Saunders A, Oldenburg IA, Berezovskii VK, Johnson CA, Kingery ND, Elliott HL, et al. A direct GABAergic output from the basal ganglia to frontal cortex. Nature 2015, 521: 85–89.
Feldmeyer D, Qi G, Emmenegger V, Staiger JF. Inhibitory interneurons and their circuit motifs in the many layers of the barrel cortex. Neuroscience 2018, 368: 132–151.
Tremblay R, Lee S, Rudy B. GABAergic interneurons in the neocortex: from cellular properties to circuits. Neuron 2016, 91: 260–292.
Lee S, Hjerling-Leffler J, Zagha E, Fishell G, Rudy B. The largest group of superficial neocortical GABAergic interneurons expresses ionotropic serotonin receptors. J Neurosci 2010, 30: 16796–16808.
Schmitz Y, Luccarelli J, Kim M, Wang M, Sulzer D. Glutamate controls growth rate and branching of dopaminergic axons. J Neurosci 2009, 29: 11973–11981.
Melzer S, Gil M, Koser DE, Michael M, Huang KW, Monyer H. Distinct corticostriatal GABAergic neurons modulate striatal output neurons and motor activity. Cell Rep 2017, 19: 1045–1055.
Mandelbaum G, Taranda J, Haynes TM, Hochbaum DR, Huang KW, Hyun M, et al. Distinct cortical-thalamic-striatal circuits through the parafascicular nucleus. Neuron 2019, 102: 636–652.e7.
Aronoff R, Matyas F, Mateo C, Ciron C, Schneider B, Petersen CC. Long-range connectivity of mouse primary somatosensory barrel cortex. Eur J Neurosci 2010, 31: 2221–2233.
Audette NJ, Urban-Ciecko J, Matsushita M, Barth AL. POm thalamocortical input drives layer-specific microcircuits in somatosensory cortex. Cereb Cortex 2018, 28: 1312–1328.
Sumser A, Mease RA, Sakmann B, Groh A. Organization and somatotopy of corticothalamic projections from L5B in mouse barrel cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114: 8853–8858.
Acknowledgements
We thank Qingtao Sun, Pan Luo, Mei Yao, and Peilin Zhao for help with experiments and data analysis. We thank the Optical Bioimaging Core Facility of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for providing support with data acquisition. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61721092, 91749209, and 31871088) and the Director Fund of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, Z., Li, A., Gong, H. et al. A Whole-brain Map of Long-range Inputs to GABAergic Interneurons in the Mouse Caudal Forelimb Area. Neurosci. Bull. 36, 493–505 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-019-00458-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-019-00458-6