Abstract
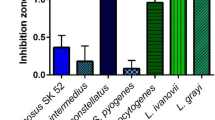
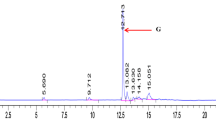
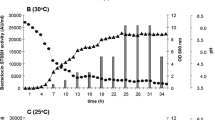
Streptomyces spp. are Gram-positive bacteria well-known for their ability to produce antibiotics and other metabolites, but few studies on bacteriocins produced by these bacteria have been reported. We tested eight Streptomyces strains against different pathogenic bacteria, and selected S. griseus, S. nigrescens, S. bottroprensis, and S. violaceoruber for further study based on their inhibitory effects against bacteria, including human pathogens. S. bottropensis reached its highest activity at 312 h and was higher than the activities of S. violaceoruber and S. nigrescens. The best condition for bacteriocin precipitation was using diammonium sulfate at 50% saturation. Bacteriocins were susceptible to proteinase treatments and stable at high temperature (up to 100 °C). The highest inhibitory activities were observed between pH 5 and 6. Cross-activity assays indicated that each Streptomyces strain produced different bacteriocins. When preparations of S. griseus and S. nigrescens were subjected to SDS-PAGE, bands of inhibition were observed in the gel overlay assay at a position corresponding to ~ 2 and 3 kDa, respectively, suggesting that both strains are potential sources for novel bacteriocins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson-Borge GI, Skeie M, Sørhaug T, Langsrud T, Granum PE (2001) Growth and toxin profiles of Bacillus cereus isolated from different food sources. Int J Food Microbiol 69(3):237–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(01)00500-1
Antony-Babu S, Stach JEM, Goodfellow M (2008) Genetic and phenotypic evidence for Streptomyces griseus ecovars isolated from a beach and dune sand system. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 94:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-008-9246-y
Barboza-Corona JE, Vázquez-Acosta H, Bideshi-Dennis K, Salcedo-Hernández R (2007) Bacteriocin-like inhibitor substances produced by Mexican strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Arch Microbiol 187:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0178-5
Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K, Villebro R, Ziemert N, Lee SY, Medema MH, Weber T (2019) antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz310
Brooke D, Movahed N, Bothner B (2015) Universal buffers for use in biochemistry and biophysical experiments. AIMS Biophysics 2(3):336–342. https://doi.org/10.3934/biophy.2015.3.336
Brückner R, Titgemeyer F (2002) Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: choice of the carbon source and autoregulatory limitation of sugar utilization. FEMS Microbiol Lett 209:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11123.x
Castañeda-Ramírez C, Cortes-Rodríguez V, de la Fuente-Salcido N, Bideshi DK, Barboza-Corona JE (2011) Isolation of Salmonella spp. from lettuce and evaluation of its susceptibility to novel bacteriocins synthesized by Bacillus thuringiensis and antibiotics. J Food Prot 74:274–278. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-10-324
Claesen J, Bibb M (2010) Genome mining and genetic analysis of cypemycin biosynthesis reveal an unusual class of posttranslationally modified peptides. PNAS 107(37):16297–16302. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008608107
Claesen J, Bibb M (2011) Biosynthesis and regulation of grisemycin, a new member of the linaridin family of ribosomally synthesized peptides produced by Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J Bacteriol 193(10):2510–2516. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00171-11
Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP (2005) Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(10):777–788. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1273
Demain AL (1999) Pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites of microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051
Deutscher J (2008) The mechanisms of carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 11(2):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2008.02.007
Dimitrov TS, Dicks LMT (2005) Effect of growth medium on bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum ST194BZ, a strain isolated from boza. Food Technol Biotech 43(2), 165-173.
Farris MH, Duffy C, Findlay RH, Olson JB (2011) Streptomyces scopuliridis sp. nov., a bacteriocin-producing soil streptomycete. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(9):2112–2116. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.023192-0
Garsa AK, Kumariya R, Sood SK, Kumar A, Kapila S (2014) Bacteriocin production and different strategies for their recovery and purification. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 6(1):47–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-013-9153-z
Gautam N, Sharma N (2015) A study on characterization of new bacteriocin produced from a novel strain of Lactobacillus spicheri G2 isolated from Gundruk-a fermented vegetable product of North East India. J Food Sci Technol 52(9):5808–5816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1710-x
Granum PE, Lund T (1997) Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol Lett 57:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb12776.x
Hopwood DA, Bibb MJ, Chater KF, Kieser T, Bruton CJ, Kieser HM, Lydiate DJ, Smith CP, Ward JM, Schrempf H (1985) Genetic manipulation of Streptomyces. A laboratory manual. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Hou Y, Tianero MDB, Kwan JC, Wyche TP, Michel CR, Ellis GA, Bugni TS (2012) Structure and biosynthesis of the antibiotic bottromycin D. Org Lett 14(19):5050–5053. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol3022758
Islas-Rodríguez AE, Marcellini L, Orioni B, Barra D, Stella L, Mangoni ML (2009) Esculentin 1–21: a linear antimicrobial peptide from frog skin with inhibitory effect on bovine mastitis-causing bacteria. J Pept Sci 15:607–614. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.1148
Jankovic I, Brückner R (2007) Carbon catabolite repression of sucrose utilization in Staphylococcus xylosus: catabolite control protein CcpA ensures glucose preference and autoregulatory limitation of sucrose utilization. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 12(1–2):114–120. https://doi.org/10.1159/000096466
Jiang Y, Cao YR, Wiese J, Tang SK, Xu LH, Imhoff JF, Jiang CL (2011) Streptomyces sparsus sp. nov., isolated from a saline and alkaline soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(Pt 7):1601–1605. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.020669-0
Kirk S, Avignone-Rossa AC, Bushell ME (2000) Growth limiting substrate effects antibiotic production and associated metabolic fluxes in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biotechnol Lett 22:1803–1822. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:100567060
Kobayashi Y, Ichioka M, Hirose T, Nagai K, Matsumoto A, Matsui H, Hanaki H, Masuma R, Takahashi Y, Omura S, Sunazuka T (2010) Bottromycin derivatives: efficient chemical modifications of the ester moiety and evaluation of anti-MRSA and anti-VRE activities. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(20):6116–6120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.08.037
Komiyama K, Otoguro K, Segawa T, Shiomi K, Yang H, Takahashi Y, Hayashi M, Otani T, Omura S (1993) A new antibiotic, cypemycin. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological characteristics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 46(11):1666–1671. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.46.1666
Leroy F, De Vuyst L (2001) Growth of the bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus sakei strain CTC 494 in MRS broth is strongly reduced due to nutrient exhaustion: a nutrient depletion model for the growth of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(10):4407–4413. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.10.4407-4413.2001
Li R, Townsend C (2006) Rational strain improvement for enhanced clavulanic acid production by genetic engineering of the glycolytic pathway in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Metab Eng 8(3):240–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2006.01.003
Masurekar PS (2008) Nutritional and engineering aspects of microbial process development. Prog Drug Res 65:291–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8117-2_8
Miller RA, Beno SM, Kent DJ, Carroll LM, Martin NH, Boor KJ, Kovac J (2016) Bacillus wiedmannii sp. nov., a psychrotolerant and cytotoxic Bacillus cereus group species isolated from dairy foods and dairy environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(11):4744–4753. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001421
Murphy CJ, Foster BA, Mannis MJ, Selsted ME, Reid TW (1993) Defensins are mitogenic for epithelial cells and friboblast. J Cell Physiol 155:408–413. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1041550223
Onaka H, Nakaho M, Hayashi K, Igarashi Y, Furumai T (2005) Cloning and characterization of the goadsporin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. TP-A0584. Microbiol 151(Pt 12):3923–3933. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28420-0
Orsaria L, Paoletti L, Gramajo HC (1998) Characterization of stationary-phase proteins in Streptomyces coelicolor A3. FEMS Microbiol Lett 162:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13009.x
Peces R, Gago E, Tejada F, Laures AS, Alvarez-Grande J (1997) Relapsing bacteraemia due to Micrococcus luteus in a haemodialysis patient with a Perm-Cath catheter. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12(11):2428–2429. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/12.11.2428
Reid KC, Cockerill FR III, Patel R (2001) Clinical and epidemiological features of Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens and Enterococcus gallinarum bacteremia: a report of 20 cases. Clin Infect Dis 32(11):1540–1546. https://doi.org/10.1086/320542
Rintala H, Nevalainen A, Rönkä E, Suutari M (2001) PCR primers targeting the 16S rRNA gene for the specific detection of streptomycetes. Mol Cell Probes 15(6):337–347. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcpr.2001.0379
Rodríguez E, Arques JL, Gaya P, Tomillo J, Nuñez M, Medina M (2000) Behaviour of Staphylococcus aureus in semi-hard cheese made from raw milk with nisin-producing starter cultures. Milchwissenschaft 55:633–635
Shepherd MD, Kharel MK, Bosserman MA, Rohr J (2010) Laboratory maintenance of Streptomyces species. Curr Protoc Microbiol 18(E:10E.1):10E.1.1–10E.1.8. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mc10e01s18
Shimamura H, Gouda H, Nagai K, Hirose T, Ichioka M, Furuya Y, Kobayashi Y, Hirono S, Sunazuka T, Omura S (2009) Structure determination and total synthesis of bottromycin A2:a potent antibiotic against MRSA and VRE. Angew Chem 48:914–917. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200804138
Smith MH (1966) The amino acid composition of proteins. J Theor Biol 13:261–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(66)90021-X
Soohyun U, Joon Choi T, Kim H, Yong Kim B, Seong-Hwan K, Sang Kook L, Ki-Bong O, Jongheon S, Dong-Chan O (2013) Ohmyungsamycins A and B: cytotoxic and antimicrobial cyclic peptides produced by Streptomyces sp. from a volcanic island. J Org Chem 78(24):12321–12329. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo401974g
Tanasupawat S, Phongsopitanun W, Suwanborirux K, Ohkuma M, Kudo T (2016) Streptomyces actinomycinicus sp. nov., isolated from soil of a peat swamp forest. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:290–295. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000716
Verluyten J, Leroy F, De Vuyst L (2004) Influence of complex nutrient source on growth of and curvacin A production by sausage isolate Lactobacillus curvatus LTH 1174. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5081–5088. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.9.5081-5088.2004
Vivier D, Ratomahenina R, Galzy P (1994) Characteristics of micrococci from the surface of Roquefort cheese. J Appl Microbiol 76(6):546–552. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1994.tb01651.x
Waksman SA, Henrici AT (1943) The nomenclature and classification of the actinomycetes. J Bacteriol 46(4):337–341
Watve MG, Tickoo R, Jog MM, Bhole BD (2001) How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces? Arch Microbiol 176(5):386–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030100345
Yang E, Fan L, Yan J, Jiang Y, Doucette C, Fillmore S, Walker B (2018) Influence of culture media, pH and temperature on growth and bacteriocin production of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria. AMB Express 8(1):10–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0536-0
Zhao XQ, Li WJ, Jiao WC, Li Y, Yuan WJ, Zhang YQ, Klenk HP, Suh JW, Bai FW (2009) Streptomyces xinghaiensis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2870–2874. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.009878-0
Funding
This research was supported partially by Grant SEP-CONACYT (258220), México, to J.E. B.-C and partially supported by “Problemas Nacionales CONACYT (3664),” México, to L.E.C-V. Oscar Hernández Saldaña is a doctoral student in Biosciences graduate program in the University of Guanajuato, México, and he is supported by CONACYT with a doctoral fellowship. L.E. C.-V is an Associate Researcher supported by Grant 2069 from Cátedras-CONACYT, México.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
N/A. In this study, there were no study subjects, so no informed consent was obtained.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 31 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Saldaña, O.F., Barboza-Corona, J.E., Bideshi, D.K. et al. New bacteriocin-like substances produced by Streptomyces species with activity against pathogens. Folia Microbiol 65, 669–678 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00770-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00770-z