Abstract
Background
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) had a great relationship with anesthesia during surgery, and miRNAs have been found involved in anesthesia-induced cognitive impairment.
Objective
To explore the role and potential mechanism of miR-106a in isoflurane anesthesia-induced cognitive impairment.
Methods
Adult male mice were treated with isoflurane anesthesia; Morris water maze tests and fear conditioning tests were performed; and expression levels of miR-106a and LIMK1 were determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blot. Dual luciferase reporter assay was used to determine the binding of miR-106a and 3’UTR of LIMK1. To verify the role of miR-106a, antagomir of miR-106a were intrahippocampally injected. Finally, expression of BCL2 apoptosis regulator (Bcl-2), LIM domain kinase 1 (LIMK1), BCL2-associated X, apoptosis regulator (Bax) and cleaved caspase3 was determined by western blot.
Results
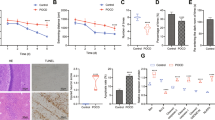
In isoflurane anesthesia-treated group (IS), the percentage of target quadrant dwell time was significantly lower and the escape latency was significantly higher than in the control group (sham), and the freezing behavior of IS was significantly less in contextual fear conditioning tests. Expression levels of miR-106a were increased and those of LIMK1 were decreased in response to IS. Dual luciferase reporter assay showed that miR-106a could bind with the 3’UTR of LIMK1. Decreased expression levels of miR-106a improved the cognitive impairment of the mice treated with isoflurane. Intrahippocampally injected antagomir of miR-106a also increased LIMK1 and Bcl-2 levels, decreased the BAX and cleaved caspase3 expression levels in the mice treated with isoflurane.
Conclusion
Decrease of LIMK1 expression by miR-106a played an important role in isoflurane anesthesia-induced cognitive impairment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Cao Y, Li Z, Ma L, Ni C, Li L, Yang N, Shi C, Guo X (2018) Isoflurane-induced postoperative cognitive dysfunction is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-dependent neuroinflammation in aged rats. Mol Med Rep 17:7730–7736
Chavan SS, Huerta PT, Robbiati S, Valdes-Ferrer SI, Ochani M, Dancho M, Frankfurt M, Volpe BT, Tracey KJ, Diamond B (2012) HMGB1 mediates cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors. Mol Med (Camb Mass) 18:930–937
Chen Y, Huang T, Yang X, Liu C, Li P, Wang Z, Zhi S (2018) MicroRNA-106a regulates the proliferation and invasion of human osteosarcoma cells by targeting VNN2. Oncol Rep 40:2251–2259
Cong J, Wang C, Pu D, Liu J, Hu G, Gao C, Wu J (2014) Expression of early growth response 1 affects miR-106a/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 regulating cognitive impairment in ovariectomized mice. Menopause 21:1143–1150
Dong Q, Ji Y-S, Cai C, Chen Z-Y (2012) LIM kinase 1 (LIMK1) interacts with tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) and Mediates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced axonal elongation. J Biol Chem 287:41720–41731
Fang Y, Shen H, Li H, Cao Y, Qin R, Long L, Zhu X, Xie C, Xu W (2013) miR-106a confers cisplatin resistance by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway in gastric cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 45:963–972
Geng Y-j, Wu Q-h, Zhang R-q (2017) Effect of propofol, sevoflurane, and isoflurane on postoperative cognitive dysfunction following laparoscopic cholecystectomy in elderly patients: A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth 38:165–171
Goto G, Hori Y, Ishikawa M, Tanaka S, Sakamoto A (2014) Changes in the gene expression levels of microRNAs in the rat hippocampus by sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Mol Med Rep 9:1715–1722
Hackl M, Brunner S, Fortschegger K, Schreiner C, Micutkova L, Muck C, Laschober GT, Lepperdinger G, Sampson N, Berger P et al (2010) miR-17, miR-19b, miR-20a, and miR-106a are down-regulated in human aging. Aging Cell 9:291–296
Hu B, Cai H, Zheng R, Yang S, Zhou Z, Tu J (2017) Long non-coding RNA 657 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-106a-5p to regulate PTEN expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 92:34–42
Issler O, Chen A (2015) Determining the role of microRNAs in psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:201–212
Knafo S, Sánchez-Puelles C, Palomer E, Delgado I, Draffin JE, Mingo J, Wahle T, Kaleka K, Mou L, Pereda-Perez I et al (2016) PTEN recruitment controls synaptic and cognitive function in Alzheimer's models. Nat Neurosci 19:443
Kong F, Chen S, Cheng Y, Ma L, Lu H, Zhang H, Hu W (2013) Minocycline attenuates cognitive impairment induced by isoflurane anesthesia in aged rats. PLoS ONE 8:e61385–e61385
Li GF, Li ZB, Zhuang SJ, Li GC (2018) Inhibition of microRNA-34a protects against propofol anesthesia-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive dysfunction via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett 675:152–159
Liu A, Zhou Z, Dang R, Zhu Y, Qi J, He G, Leung C, Pak D, Jia Z, Xie W (2016) Neuroligin 1 regulates spines and synaptic plasticity via LIMK1/cofilin-mediated actin reorganization. J Cell Biol 212:449–463
Liu L, Zhao Z, Lu L, Liu J, Wu X, Sun J, Wei Y, Dong J (2018a) The role of HMGB1 in neuroinflammation and tissue repair: A potential therapeutic target for depression? Tradit Med Mod Med 01:85–93
Liu R, Luo Q, You W, Jin M (2018b) MicroRNA-106 attenuates hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting HMGB1. Gene 677:142–148
Lu Y, Xu X, Dong R, Sun L, Chen L, Zhang Z, Peng M (2019) MicroRNA-181b-5p attenuates early postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice. Cytokine 120:41–53
Pan Y, Zhuang Y, Zheng J, Pei D (2016) MiR-106a: Promising biomarker for cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26:5373–5377
Piscopo P, Lacorte E, Feligioni M, Mayer F, Crestini A, Piccolo L, Bacigalupo I, Filareti M, Ficulle E, Confaloni A et al (2019) MicroRNAs and mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev 50:131–141
Qiao Y, Feng H, Zhao T, Yan H, Zhang H, Zhao X (2015) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after inhalational anesthesia in elderly patients undergoing major surgery: the influence of anesthetic technique, cerebral injury and systemic inflammation. BMC Anesthesiology 15:154–154
Rosso S, Bollati F, Bisbal M, Peretti D, Sumi T, Nakamura T, Quiroga S, Ferreira A, Cáceres A (2004) LIMK1 regulates Golgi dynamics, traffic of Golgi-derived vesicles, and process extension in primary cultured neurons. Mol Biol Cell 15:3433–3449
Rundshagen I (2014) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int 111:119–125
Shi B, Ma C, Liu G, Guo Y (2019) MiR-106a directly targets LIMK1 to inhibit proliferation and EMT of oral carcinoma cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:1
Shoji H, Takao K, Hattori S, Miyakawa T (2014) Contextual and cued fear conditioning test using a video analyzing system in mice. J Visualized Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/50871
Su B, Su J, Zeng Y, Liu F, Xia H, Ma Y-H, Zhou Z-G, Zhang S, Yang B-M, Wu Y-H et al (2016) Diallyl disulfide suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and proliferation by downregulation of LIMK1 in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 7:10498–10512
Sun W-C, Pei L (2016) rno-miR-665 targets BCL2L1 (Bcl-xl) and increases vulnerability to propofol in developing astrocytes. J Neurochem 138:233–242
Sun E, Shi Y (2015) MicroRNAs: Small molecules with big roles in neurodevelopment and diseases. Exp Neurol 268:46–53
Todorovski Z, Asrar S, Liu J, Saw NMN, Joshi K, Cortez MA, Snead OC, Xie W, Jia Z (2015) LIMK1 regulates long-term memory and synaptic plasticity via the transcriptional factor CREB. Mol Cell Biol 35:1316–1328
Wang W, Wang Y, Wu H, Lei L, Xu S, Shen X, Guo X, Shen R, Xia X, Liu Y et al (2014) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: current developments in mechanism and prevention. Med Sci Monit 20:1908–1912
Wang H, Ban W, Wang T, Li Z, Dang X (2017) miR-20b/106a modulate Ngn2 gene expression during neural differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Neuro Report 28:1225–1231
Wang L, Zheng M, Wu S, Niu Z (2018) MicroRNA-188-3p is involved in sevoflurane anesthesia-induced neuroapoptosis by targeting MDM2. Mol Med Rep 17:4229–4236
Ward CG, Eckenhoff RG (2016) Neurocognitive adverse effects of anesthesia in adults and children: gaps in knowledge. Drug Saf 39:613–626
Wei C, Luo T, Zou S, Zhou X, Shen W, Ji X, Li Q, Wu A (2017) Differentially expressed lncRNAs and miRNAs with associated ceRNA networks in aged mice with postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Oncotarget 8:55901–55914
Yu Y, Zhang P, Yan J, Sun Y, Wu X, Xi S, Zhang L, Sun Y, Hu R, Jiang H (2016) Sevoflurane induces cognitive impairments via the MiR-27b/LIMK1-signaling pathway in developing rats. Inhalation Toxicol 28:731–738
Yuan R, Wang G, Xu Z, Zhao H, Chen H, Han Y, Wang B, Zhou J, Hu H, Guo Z (2016) Up-regulated circulating miR-106a by DNA methylation promised a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 16:1093–1100
Zhang Q, Li Y, Bao Y, Yin C, Xin X, Guo Y, Gao F, Huo S, Wang X, Wang Q (2018) Pretreatment with nimodipine reduces incidence of POCD by decreasing calcineurin mediated hippocampal neuroapoptosis in aged rats. BMC Anesthesiol 18:42
Zhao Y, Wang J, Du J, Li B, Gou X, Liu J, Hou L, Sang H, Deng B (2018) TAT-Ngn2 enhances cognitive function recovery and regulates caspase-dependent and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways after experimental stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 12:475. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00475
Zuo C-L, Wang C-M, Liu J, Shen T, Zhou J-P, Hao X-R, Pan Y-Z, Liu H-C, Lian Q-Q, Lin H (2018) Isoflurane anesthesia in aged mice and effects of A1 adenosine receptors on cognitive impairment. CNS Neurosci Ther 24:212–221
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NZ and LY conceived and designed the experiments, WGY analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments, TLW and HW performed the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests, and all authors should confirm its accuracy.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal use peotocol listed below has been reviewde and approved by the Animal Ethical and Welfaer Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Ye, W., Wang, T. et al. Up-regulation of miR-106a targets LIMK1 and contributes to cognitive impairment induced by isoflurane anesthesia in mice. Genes Genom 42, 405–412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00913-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00913-8