Abstract
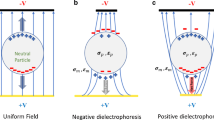
Phenotypic quantification of cells based on their plasma membrane capacitance and cytoplasmic conductivity, as determined by their dielectrophoretic frequency dispersion, is often used as a marker for their biological function. However, due to the prevalence of phenotypic heterogeneity in many biological systems of interest, there is a need for methods capable of determining the dielectrophoretic dispersion of single cells at high throughput and without the need for sample dilution. We present a microfluidic device methodology wherein localized constrictions in the microchannel are used to enhance the field delivered by adjoining planar electrodes, so that the dielectrophoresis level and direction on flow-focused cells can be determined on each traversing cell in a high-throughput manner based on their deflected flow streamlines. Using a sample of human red blood cells diluted to 2.25 × 108 cells/mL, the dielectrophoretic translation of single cells traversing at a flow rate of 1.68 μL/min is measured at a throughput of 1.1 × 105 cells/min, to distinguish positive versus negative dielectrophoresis and determine their crossover frequency in media of differing conductivity for validation of the computed membrane capacitance to that from prior methods. We envision application of this dynamic dielectrophoresis (Dy-DEP) method towards high-throughput measurement of the dielectric dispersion of single cells to stratify phenotypic heterogeneity of a particular sample based on their DEP crossover frequency, without the need for significant sample dilution.

Grapical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perkins TJ, Swain PS. Strategies for cellular decision-making. Mol Syst Biol. 2009;5(1):326.
Klepárník, K, F. Foret. Recent advances in the development of single cell analysis—a review. Anal Chim Acta 2013;800:12–21.
Adan A, Alizada G, Kiraz Y, Baran Y, Nalbant A. Flow cytometry: basic principles and applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017;37(2):163–76.
Grover P, Cummins A, Price T, Roberts-Thomson I, Hardingham J. Circulating tumour cells: the evolving concept and the inadequacy of their enrichment by EpCAM-based methodology for basic and clinical cancer research. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(8):1506–16.
Mitchell JB, McIntosh K, Zvonic S, Garrett S, Floyd ZE, Kloster A, et al. Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell–associated markers. Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):376–85.
Wlodkowic D, Skommer J, Darzynkiewicz Z. Cytometry in cell necrobiology revisited. Recent advances and new vistas. Cytom A. 2010;77(7):591–606.
Lee WC, Shi H, Poon Z, Nyan LM, Kaushik T, Shivashankar G, et al. Multivariate biophysical markers predictive of mesenchymal stromal cell multipotency. PNAS. 2014;111(42):E4409–18.
Gascoyne PR, Shim S, Noshari J, Becker FF, Stemke-Hale K. Correlations between the dielectric properties and exterior morphology of cells revealed by dielectrophoretic field-flow fractionation. Electrophoresis. 2013;34(7):1042–50.
Moore JH, Varhue WB, Su Y-H, Linton SS, Farmehini V, Fox TE, et al. Conductance-based biophysical distinction and microfluidic enrichment of nanovesicles derived from pancreatic tumor cells of varying invasiveness. Anal Chem. 2019;91(16):10424–31.
Elitas M, Martinez-Duarte R, Dhar N, McKinney JD, Renaud P. Dielectrophoresis-based purification of antibiotic-treated bacterial subpopulations. Lab Chip. 2014;14(11):1850–7.
Su Y-H, Rohani A, Warren CA, Swami NS. Tracking inhibitory alterations during interstrain Clostridium difficile interactions by monitoring cell envelope capacitance. ACS Infect Dis. 2016;2(8):544–51.
Honrado C, Ciuffreda L, Spencer D, Ranford-Cartwright L, Morgan H. Dielectric characterization of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells using microfluidic impedance cytometry. J R Soc Interface. 2018;15(147):20180416.
Gascoyne, P, S. Shim. Isolation of circulating tumor cells by dielectrophoresis. Cancers. 2014;6(1):545–579.
Yale AR, Nourse JL, Lee KR, Ahmed SN, Arulmoli J, Jiang AY, et al. Cell surface N-glycans influence electrophysiological properties and fate potential of neural stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2018;11(4):869–82.
Pohl, H. A, J.S. Crane. Dielectrophoresis of cells. Biophys J 1971;11(9):711–727.
Jones TB. Electromechanics of particles. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2005.
Morgan, H, N.G. Green. AC electrokinetics. Philadelphia: Research Studies Press; 2003.
Fernandez RE, Rohani A, Farmehini V, Swami NS. Microbial analysis in dielectrophoretic microfluidic systems. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;966:11–33.
Gagnon ZR. Cellular dielectrophoresis: applications to the characterization, manipulation, separation and patterning of cells. Electrophoresis. 2011;32(18):2466–87.
Wang X-B, Yang J, Huang Y, Vykoukal J, Becker FF, Gascoyne PR. Cell separation by dielectrophoretic field-flow-fractionation. Anal Chem. 2000;72(4):832–9.
Vahey MD, Voldman J. High-throughput cell and particle characterization using isodielectric separation. Anal Chem. 2009;81(7):2446–55.
Wang L, Lu J, Marchenko SA, Monuki ES, Flanagan LA, Lee AP. Dual frequency dielectrophoresis with interdigitated sidewall electrodes for microfluidic flow-through separation of beads and cells. Electrophoresis. 2009;30(5):782–91.
Lewpiriyawong N, Yang C, Lam YC. Continuous sorting and separation of microparticles by size using AC dielectrophoresis in a PDMS microfluidic device with 3-D conducting PDMS composite electrodes. Electrophoresis. 2010;31(15):2622–31.
Lewpiriyawong N, Kandaswamy K, Yang C, Ivanov V, Stocker R. Microfluidic characterization and continuous separation of cells and particles using conducting poly (dimethyl siloxane) electrode induced alternating current-dielectrophoresis. Anal Chem. 2011;83(24):9579–85.
Lapizco-Encinas, B. H, B.A. Simmons, E.B. Cummings, Y. Fintschenko. Insulator-based dielectrophoresis for the selective concentration and separation of live bacteria in water. Electrophoresis. 2004;25(10–11):1695–1704.
Bhattacharya S, Chao T-C, Ariyasinghe N, Ruiz Y, Lake D, Ros R, et al. Selective trapping of single mammalian breast cancer cells by insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(7):1855–65.
Su Y-H, Tsegaye M, Varhue W, Liao K-T, Abebe LS, Smith JA, et al. Quantitative dielectrophoretic tracking for characterization and separation of persistent subpopulations of Cryptosporidium parvum. Analyst. 2014;139(1):66–73.
Farmehini V, Rohani A, Su Y-H, Swami NS. A wide-bandwidth power amplifier for frequency-selective insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip. 2014;14(21):4183–7.
Huang C-T, Weng C-H, Jen C-P. Three-dimensional cellular focusing utilizing a combination of insulator-based and metallic dielectrophoresis. Biomicrofluidics. 2011;5(4):044101.
Pommer MS, Zhang Y, Keerthi N, Chen D, Thomson JA, Meinhart CD, et al. Dielectrophoretic separation of platelets from diluted whole blood in microfluidic channels. Electrophoresis. 2008;29(6):1213–8.
Zhao, K., Larasati, B.P. Duncker, D. Li. Continuous cell characterization and separation by microfluidic alternating current dielectrophoresis. Anal Chem 2019;91(9):6304–6314.
Piacentini N, Mernier G, Tornay R, Renaud P. Separation of platelets from other blood cells in continuous-flow by dielectrophoresis field-flow-fractionation. Biomicrofluidics. 2011;5(3):034122–034122-8.
Sun M, Agarwal P, Zhao S, Zhao Y, Lu X, He X. Continuous on-chip cell separation based on conductivity-induced dielectrophoresis with 3D self-assembled ionic liquid electrodes. Anal Chem. 2016;88(16):8264–71.
Zhang J, Yuan D, Zhao Q, Yan S, Tang S-Y, Tan SH, et al. Tunable particle separation in a hybrid dielectrophoresis (DEP)-inertial microfluidic device. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;267:14–25.
Rohani A, Moore JH, Kashatus JA, Sesaki H, Kashatus DF, Swami NS. Label-free quantification of intracellular mitochondrial dynamics using dielectrophoresis. Anal Chem. 2017;89(11):5757–64.
Su Y-H, Warren CA, Guerrant RL, Swami NS. Dielectrophoretic monitoring and interstrain separation of intact Clostridium difficile based on their S(surface)-layers. Anal Chem. 2014;86(21):10855–63.
Cottet J, Fabregue O, Berger C, Buret F, Renaud P, Frénéa-Robin M. MyDEP: a new computational tool for dielectric modeling of particles and cells. Biophys J. 2019;116(1):12–8.
Wang L, Flanagan LA, Jeon NL, Monuki E, Lee AP. Dielectrophoresis switching with vertical sidewall electrodes for microfluidic flow cytometry. Lab Chip. 2007;7(9):1114–20.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jennifer Guler (PI of the Malaria Lab, University of Virginia) and graduate student Audrey Brown for providing the RBC samples used in this work.
Funding
Funding from NIH grants 1R21AI130902-01 and R01 CA200755, Advanced Regenerative Medicine Institute’s BioFab, USA, Subcontract T0163, and University of Virginia’s 3C program are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors and all authors approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The reported studies on blood samples have been approved by the University of Virginia Institutional Review Board for Health Sciences Research (IRB-HSR protocol #21081) and have been performed in accordance with ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Bioanalytics and Higher Order Electrokinetics with guest editors Mark A. Hayes and Federica Caselli.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 659 kb)
(MP4 2681 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres-Castro, K., Honrado, C., Varhue, W.B. et al. High-throughput dynamical analysis of dielectrophoretic frequency dispersion of single cells based on deflected flow streamlines. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 3847–3857 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02467-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02467-1