Abstract
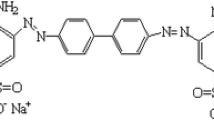
In this paper, a Co3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanoparticle-nylon-6 (CSMN6) was synthesized for the first time and used for the elimination of Congo red dye from wastewater samples. The morphology and the structure of the prepared CSMN6 were studied completely and its adsorption behavior vs. Congo red dye has been investigated. The sorption performance was evaluated using batch studies at room temperature, at varying operating conditions such as solution pH, sorbent dosage, initial dye concentration and contact time. It has been found that the Elovich kinetics model and Langmuir isotherm can describe this process adequately and a maximum adsorption rate of 138.9 mg g−1 is obtained which may be illustrated by homogeneous physical and chemical adsorption of Congo red on the surface of the adsorbent. Through this process of adsorption with the adsorbent dose of 1.4 g l−1, more than 86% of the Congo red dye from a solution with the concentration of 50 mg L−1 was eliminated. The saturation magnetization of CSMN6 was 7.8 emu g−1 and shows paramagnetic properties and could be isolated from the environment using an exterior magnet. The higher temperature was more suitable for the elimination of the Congo red dye. Also, intraparticle rate constant computed for Congo red was 4.87 mg g−1 min−1/2 that indicates higher tendency of CSMN6 to remove Congo red from aqueous solutions. The used CSMN6 can be recovered simply by using ethanol and utilized again for eliminating Congo red dye from contaminated water. In these reusing processes, a high yield of 76% may be obtained up to 5 recovery cycles. These results demonstrate that CSMN6 is a considerable candidate for water treatment processes with high effective and repeatable performance.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Yang, Y. Li, H. Gao, C. Wang, X. Zhang, H. Zhou, One-step fabrication of chitosan-Fe (OH) 3 beads for efficient adsorption of anionic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 117, 30–41 (2018)
W. Dong, Y. Lu, W. Wang, L. Zong, Y. Zhu, Y. Kang, A. Wang, A new route to fabricate high-efficient porous silicate adsorbents by simultaneous inorganic-organic functionalization of low-grade palygorskite clay for removal of Congo red. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 277, 267–276 (2019)
M. Jourvand, G. Shams Khorramabadi, Y. Omidi Khaniabadi, H. Godini, H. Nourmoradi, Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using modified clay. J. Basic Res. Med. Sci. 2, 32–41 (2015)
S. Chawla, H. Uppal, M. Yadav, N. Bahadur, N. Singh, Zinc peroxide nanomaterial as an adsorbent for removal of congo red dye from water. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 135, 68–74 (2017)
R. Rahimi, H. Kerdari, M. Rabbani, M. Shafiee, Synthesis, characterization and adsorbing properties of hollow Zn-Fe2O4 nanospheres on the removal of congo red from aqueous solution. Desalination 280, 412–418 (2011)
K. Rani, A. Naik, R.S. Chaurasiya, K. Raghavarao, Removal of toxic congo red dye from water employing low-cost coconut residual fiber. Water Sci. Technol. 75, 2225–2236 (2017)
G.A. Kloster, M.A. Mosiewicki, N.E. Marcovich, Chitosan/iron oxide nanocomposite films: Effect of the composition and preparation methods on the adsorption of congo red. Carbohyd. Polym. 221, 186–194 (2019)
A. Seidmohammadi, G. Asgari, M. Leili, A. Dargahi, A. Mobarakian, Effectiveness of quercus branti activated carbon in removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Arch. Hyg. Sci. 4, 217–225 (2015)
Y. Bao, M. Qin, Y. Yu, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Facile fabrication of porous NiCo2O4 nanosheets with high adsorption performance toward Congo red. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 124, 289–295 (2019)
S. Madan, R. Shaw, S. Tiwari, S.K. Tiwari, Adsorption dynamics of Congo red dye removal using ZnO functionalized high silica zeolitic particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 487, 907–917 (2019)
X. Quan, Z. Sun, H. Meng, Y. Han, J. Wu, J. Xu, Y. Xu, X. Zhang, Polyethyleneimine (PEI) incorporated Cu-BTC composites: extended applications in ultra-high efficient removal of congo red. J. Solid State Chem. 270, 231–241 (2019)
H. Hu, J. Liu, Z. Xu, L. Zhang, B. Cheng, W. Ho, Hierarchical porous Ni/Co-LDH hollow dodecahedron with excellent adsorption property for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 478, 981–990 (2019)
S. Rahpeima, V. Javanbakht, J. Esmaili, Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon/maghemite/starch magnetic bionanocomposite and its application for permanganate removal from aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 28, 195–211 (2018)
H. Wang, Y. Lin, Y. Li, A. Dolgormaa, H. Fang, L. Guo, J. Huang, J. Yang, A novel magnetic Cd(II) ion-imprinted polymer as a selective sorbent for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 29, 1874–1885 (2019)
M. Adibmehr, H. Faghihian, Magnetized activated carbon prepared by oak shell biowaste and modified with nickel hexacyanoferrate for selective removal of cesium. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 29, 1941–1955 (2019)
S. Krishna Lakkaboyana, S. Khantong, N.K. Asmel, A. Yuzir, W.Z. Wan Yaacob, Synthesis of copper oxide nanowires-activated carbon (AC@CuO-NWs) and applied for removal methylene blue from aqueous solution: kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 29, 1658–1668 (2019)
V. Suba, G. Rathika, E. Ranjith Kumar, M. Saravanabhavan, V. Nayak Badavath, K.S. Thangamani, Enhanced adsorption and antimicrobial activity of fabricated apocynaceae leaf waste activated carbon by cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for textile effluent treatment. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 29, 550–563 (2019)
Z. Cheng, Z. Gao, W. Ma, Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 particles modified sawdust as the adsorbent to remove strontium ions. Chem. Eng. J. 209, 451–457 (2012)
T. Etemadinia, B. Barikbin, A. Allahresani, Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions using ZnFe2O4/SiO2/Tragacanth gum magnetic nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent. Surf. Interface 14, 117–126 (2019)
R. Ravi, S. Iqbal, A. Ghosal, S. Ahmad, Novel mesoporous trimetallic strontium magnesium ferrite (Sr0.3Mg0.7Fe2O4) nanocubes: a selective and recoverable magnetic nanoadsorbent for Congo red. J. Alloys Compd. 791, 336–347 (2019)
Q. Wang, A. Tang, L. Zhong, X. Wen, P. Yan, J. Wang, Amino-modified γ-Fe2O3/sepiolite composite with rod-like morphology for magnetic separation removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 339, 872–881 (2018)
J. Liu, N. Wang, H. Zhang, J. Baeyens, Adsorption of Congo red dye on FexCo3-xO4 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 238, 473–483 (2019)
J.K. Sahoo, S.K. Paikra, M. Mishra, H. Sahoo, Amine functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, antibacterial activity and rapid removal of Congo red dye. J. Mol. Liq. 282, 428–440 (2019)
L. You, C. Huang, F. Lu, A. Wang, X. Liu, Q. Zhang, Facile synthesis of high performance porous magnetic chitosan polyethylenimine polymer composite for Congo red removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 107, 1620–1628 (2018)
E. Saksornchai, J. Kavinchan, S. Thongtem, T. Thongtem, Simple wet-chemical synthesis of superparamagnetic CTAB-modified magnetite nanoparticles using as an adsorbent for anionic Congo red dye treatment. Mater. Lett. 213, 138–142 (2017)
W. Huang, J. Xu, D. Lu, J. Deng, G. Shi, T. Zhou, Rational design of magnetic infinite coordination polymer core-shell nanoparticles as recyclable adsorbents for selective removal of anionic dyes from colored wastewater. Appl. Surf. Sci. 462, 453–465 (2018)
G. Pandey, S. Singh, G. Hitkari, Synthesis and characterization of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP)-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles by chemical co-precipitation method and removal of Congo red dye by adsorption process. Int. Nano Lett. 8, 111–121 (2018)
N. Belachew, G. Bekele, Synergy of magnetite intercalated bentonite for enhanced adsorption of congo red dye. Silicon (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00152-2
H. Song, S. You, X. Jia, A facile in situ reduction method for the preparation of magnetic Ni/MoS2 nanocomposites and their adsorption behaviors of Congo red. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 27, 10841–10848 (2016)
F. Zhang, X. Tang, J. Lan, Y. Huang, Successive removal of Pb2+ and Congo red by magnetic phosphate nanocomposites from aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 658, 1139–1149 (2018)
Y. Zhang, L. Bai, W. Zhou, R. Lu, H. Gao, S. Zhang, Superior adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2 core-shell microspheres for removal of congo red from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 219, 88–94 (2016)
Q. Yang, H. Song, Y. Li, Z. Pan, M. Dong, F. Chen, Z. Chen, Flower-like core-shell Fe3O4@MnO2 microspheres: synthesis and selective removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 234, 18–23 (2017)
A.M. El-Toni, M.A. Habila, J. Puzon Labis, Z.A. Alothman, M. Alhoshan, A.A. Elzatahry, F. Zhang, Design, synthesis and applications of core–shell, hollow core, and nanorattle multifunctional nanostructures. Nanoscale 8, 2510–2531 (2016)
X. Wu, Z. Han, X. Zheng, S. Yao, X. Yang, T. Zhai, Core-shell structured Co3O4@NiCo2O4 electrodes grown on flexible carbon fibers with superior electrochemical properties. Nano Energy 31, 410–417 (2017)
N. Joshi, L.F. da Silva, H.S. Jadhav, F.M. Shimizu, P.H. Suman, J.-C. Meko, M. Ornaghi Orlandi, J. GilSeo, V.R. Mastelaro, O.N. Oliveira Jr., Yolk-shelled ZnCo2O4 microspheres: surface properties and gas sensing application. Sens Actuators B 257, 906–915 (2018)
P. Jiang, Q. Wang, J. Dai, W. Li, Z. Wei, Fabrication of NiO@Co3O4 core/shell nanofibres for high-performance supercapacitors. Mater. Lett. 188, 69–72 (2017)
S. Kandula, P. Jeevanandam, A facile synthetic approach for SiO2@Co3O4 core–shell nanorattles with enhanced peroxidase-like activity. RSC Adv. 5, 5295–5306 (2015)
J. Zhou, C. Tang, B. Cheng, J. Yu, M. Jaroniec, Rattle-type carbon-alumina core-shell spheres: synthesis and application for adsorption of organic dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 2174–2179 (2012)
T. Li, C. Yang, X. Rao, F. Xiao, J. Wang, X. Su, Synthesis of magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@NiO nanostructures for styrene epoxidation and adsorption application. Ceram. Int. 41, 2214–2220 (2015)
A. Belalia, A. Zehhaf, A. Benyoucef, Preparation of hybrid material Based of PANI with SiO2 and Its Adsorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solution. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 60, 816–824 (2018)
W.-C. Chien, Y.-Y. Yu, P.-K. Chen, H.-H. Yu, Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of poly(acrylic)/SiO2–TiO2 core–shell nanoparticle hybrid thin films. Thin Solid Films 519, 5274–5279 (2011)
S.Z. Mohammadi, A. Seyedi, Preconcentration of cadmium and copper ions on magnetic core–shell nanoparticles for determination by flame atomic absorption. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 98, 705–713 (2015)
N.M. Mahmoodi, Synthesis of core–shell magnetic adsorbent nanoparticle and selectivity analysis for binary system dye removal. J. Indust. Eng. Chem. 20, 2050–2058 (2014)
T. Hu, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, T. Tang, H. Xiao, W. Chen, M. Zhao, J. Jia, H. Zhu, Facile synthesis of PdO-doped Co3O4 nanoparticles as an efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B 243, 175–182 (2019)
A. Din, K. Akhtar, KhS Karimov, N. Fatima, A.M. Asiri, M.I. Khan, S. Bahadar Khan, Fe2O3-Co3O4 nanocomposites based humidity and temperature sensors. J. Mol. Liq. 237, 266–271 (2017)
Q. Xu, X. Yin, S. Wu, M. Wang, Z. Wen, Z. Gu, Determination of phthalate esters in water samples using Nylon 6 nanofibers mat-based solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography. Microchim. Acta 168, 267–275 (2010)
E.M. Reyes-Gallardo, R. Lucena, S. Cardenas, M. Valcarcel, Dispersive solid phase extraction of bisphenol A from milk using magnetic nylon 6 composite and its final determination by HPLC-UV. Microchem. J. 124, 751–756 (2016)
J. Han, S. Meng, Y. Dong, J. Hu, W. Gao, Capturing hormones and bisphenol A from water via sustained hydrogen bond driven sorption in polyamide microfiltration membranes. Water Res. 47, 197–208 (2013)
Z. Mehrani, H. Ebrahimzadeh, E. Moradi, Poly m-aminophenol/nylon 6/graphene oxide electrospun nanofiber as an efficient sorbent for thin film microextraction of phthalate esters in water and milk solutions preserved in baby bottle. J. Chromatogr. A 1600, 87–94 (2019)
P. Amirifard, M.A. Taher, M. Naghizadeh, Preconcentration of Pd ion in novel modified magnetic graphene oxide nanoparticles in different samples and its determination by ETAAS. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manage. 10, 140–147 (2018)
A. Moslemizadeh, S. Khezerloo-ye Aghdam, K. Shahbazi, H. Khezerloo-ye Aghdam, F. Alboghobeish, Assessment of swelling inhibitive effect of CTAB adsorption on montmorillonite in aqueous phase. Appl. Clay Sci. 127, 111–122 (2016)
G.D. Cunha, B.T. dos Santos, J.R. Alves, I.A. Silva, D.R. de Souza Cruz, L.P. Romão, Applications of magnetic hybrid adsorbent derived from waste biomass for the removal of metal ions and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Environ. Manag. 213, 236–246 (2018)
S.Z. Mohammadi, M.A. Karimi, N. Mofidinasab, Rapid preconcentration of palladium and rhodium using magnetic graphene oxide/silicon dioxide nanocomposite prior to FAAS determination. Anal. Methods 11, 454–461 (2019)
Q. Yang, R. Lu, S. Ren, H. Zhou, Q. Wu, Y. Zhen, Z. Chen, S. Fang, Magnetic beads embedded in poly (sodium-p-styrenesulfonate) and ZIF-67: Removal of nitrophenol from water. J. Solid State Chem. 265, 200–207 (2018)
C. Qi, L. Zhang, G. Xu, Z. Sun, A. Zhao, D. Jia, Co@Co3O4 nanoparticle embedded nitrogen-doped carbon architectures as efficient bicatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 427, 319–327 (2018)
A.B. Salunkhe, V.M. Khot, N.D. Thorat, M.R. Phadatare, C.I. Sathish, D.S. Dhawale, S.H. Pawar, Polyvinyl alcohol functionalized cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 264, 598–604 (2013)
S. Jana, S.S. Pradhan, T. Tripathy, Poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) grafted hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel: a useful Congo red dye remover. J. Polym. Environ. 26, 273–2747 (2018)
R.K. Gautam, P.K. Gautam, S. Banerjee, S. Soni, S.K. Singh, M.C. Chattopadhyaya, Removal of Ni(II) by magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 204, 60–69 (2015)
S.Z. Mohammadi, M.A. Karimi, D. Afzali, F. Mansouri, Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions using activated carbon from Sea-buckthorn stones by chemical activation. Desalination 262, 86–93 (2010)
H.M.F. Freundlich, Uber die adsorption in lasugen. J. Phys. Chem. 57, 385–470 (1906)
S.Z. Mohammadi, H. Hamidian, Z. Moeinadini, High surface area-activated carbon from Glycyrrhiza glabra residue by ZnCl2 activation for removal of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from water samples. J. Indust. Eng Chem 20, 4112–4118 (2014)
M.J. Temkin, V. Pyzhev, Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Phys. Chim. USSR 12, 217–222 (1940)
D. Pradhan, L.B. Sukla, B.B. Mishra, N. Devi, Biosorption for removal of hexavalent chromium using microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J. Clean. Product. 209, 617–629 (2019)
S.Z. Mohammadi, M.A. Karimi, S.N. Yazdy, T. Shamspur, H. Hamidian, Removal of Pb(II) ions and Malachite green dye from wastewater by activated carbon produced Lemon peel. Quim. Nova 37, 804–809 (2014)
R. Krishnamoorthy, B. Govindan, F. Banat, V. Sagadevan, M. Purushothaman, P.L. Show, Date pits activated carbon for divalent lead ions removal. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 128, 88–97 (2019)
N.S. Mirbagheri, S. Sabbaghi, A natural kaolin/γ-Fe2O3 composite as an efficient nano-adsorbent for removal of phenol from aqueous solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 259, 134–141 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The current study was conducted thanks to the support of Payame Noor University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, S.Z., Safari, Z. & Madady, N. Synthesis of Co3O4@SiO2 Core/Shell–Nylon 6 Magnetic Nanocomposite as an Adsorbent for Removal of Congo Red from Wastewater. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 3199–3212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01485-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01485-x