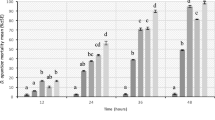
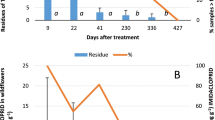
Abstract
Chrysoperla externa and Coleomegilla quadrifasciata are important biological control agents in peach orchards. However, orchard management with these predatory insects is viable only by using selective agrochemicals. The objective of this study is to evaluate the toxicity of nine agrochemicals used in peach orchards in larval and adult stages of the C. externa and C. quadrifasciata in laboratory conditions. The bioassays followed the methodologies proposed by the International Organization for Biological and Integrated Control (IOBC). Larvae and adults of C. externa and C. quadrifasciata were exposed to the dry residues of these products. Lethal and sublethal effects were evaluated in bioassays with the larval and adult stages of both predators. The agrochemicals were classified according to the IOBC guidelines. The insecticide chlorantraniliprole was harmless (class 1) to the larval stage of C. externa and C. quadrifasciata. Azadirachtin, copper 25% + calcium 10%, and deltamethrin were harmless to the adult stage of both insect species. The organophosphates fenitrothion and malathion were harmful (class 4) to both species in the larval and adult stages and should not be used in peach orchards. Therefore, this study demonstrates the importance of toxicity and the lethal and sublethal effects of these agrochemicals to better determine their compatibility with IPM in peach production.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott CE (1945) The toxic gases of lime-sulfur. J Econ Entomol 38:618–620
Abbes K, Biondi A, Kurtulus A, Ricupero M, Russo A, Siscaro G, Chermiti B, Zappalà L (2015) Combined non-target effects of insecticide and high temperature on the Parasitoid Bracon nigricans. PLoS ONE 10(9):e0138411. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138411
Araujo ES, Paiva LR, Alves SG, Bevacqua D, Nava DE, Lavigne C, García FR (2019) Phenological asynchrony between the fruit fly Anastrepha fraterculus and early maturing peach cultivars could contribute to pesticide use reduction. Spanish J Agric Res 17(1):e1001. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2019171-13294
Azod F, Shahidi-Noghabi S, Mahdian K, Smagghe G (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of spirotetramat and abamectin on predatory beetles (Menochilus sexmaculatus) via prey (Agonoscena pistaciae) exposure, important for integrated pest management in pistachio orchards. Belg J Zool 146(2):113–122
Bacci L, Crespo AL, Galvan TL, Pereira EJ, Picanço MC, Silva GA, Chediak M (2007) Toxicity of insecticides to the sweetpotato whitefly (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) and its natural enemies. Pest Manag Sci 63:699–706. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1393
Benamú MA, Schneider MI, Gonzalez A, Sánchez NE (2013) Short and long-term effects of three neurotoxic insecticides on the orb-web spider Alpaida veniliae (Araneae, Araneidae): implications for IPM programs. Ecotoxicology 22(7):1155–1164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1102-9
Bengochea P, Saelices R, Amor F, Adán A, Budia F, Estal P, Viñuela E, Medina P (2014) Non-target effects of kaolin and coppers applied on olive trees for the predatory lacewing Chrysoperla carnea. Biocontrol Sci Technol 24(6):625–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583157.2014.884212
Bernabò P, Gadfio M, Bellamoli F, Viero G, Lencioni V (2017) DNA damage and translational response during detoxification from copper exposure in a wild population of Chironomus riparius. Chemosphere 173:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.052
Biondi A, Desneux N, Sicaro G, Zappalà L (2012) Using organic-certified rather than synthetic pesticides may not be safer for biological control agents: selectivity and side effects of 14 pesticides on the predator Orius laevigatus. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.082
Biondi A, Zappalà L, Stark JD, Desneux N (2013) Do biopesticides affect the demographic traits of a parasitoid wasp and its biocontrol services through sublethal effects? Plos One 8(9):e76548. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076548
Botton M, Scoz PL, Arioli CJ (2002) IPM on peaches in Brazil: actual situation and future trends. Acta Hortic. 592:655–658. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2002.592.90
Botton M, Kulcheski F, Colletta VD, Ariolli CJ, Pastori PL (2005) Avaliação do uso do feromônio de confundimento no controle de Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) em pomares de pessegueiro. Idésia 23:43–50
Brattsten LB, Holyoke Jr CW, Leeper JR, Raffa KF (1986) Insecticide resistance: challenge to pest management and basic research. Science 231:1255–1260. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.231.4743.1255
Brooks SJA (1994) Taxonomic review of the common green lacewing genus Chrysoperla (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Bull Br Nat Hist Ent 63(2):137–210
Bueno AF, Carvalho GA, Santos AC, Sosa-Gómez DR, Silva DM (2017) Pesticide selectivity to natural enemies: challenges and constraints for research and field recommendation. Cienc Rural 47(6):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20160829
Cabrera P, Cormier D, Lucas E (2018) Sublethal effects of two reduced-risk insecticides: when the invasive ladybeetle is drastically affected, whereas the indigenous not. J Pest Sci 91(3):1153–1164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-0978-9
Carvalho GA, Parra JRP, Baptista GC (2001) Seletividade de alguns produtos fitossanitários a duas linhagens de Trichogramma pretiosum Riley, 1879 (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Ciênc Agrotec 25(3):583–591
Carvalho CF, Souza B (2000) Métodos de criação e produção de crisopídeos. In: Bueno VHP (ed) Controle biológico de pragas: produção massal e controle de qualidade. UFLA, Lavras, p 91–109
Castilhos RV, Grützmacher AD, Nava DE, Zotti MJ, Siqueira PRB (2011) Seletividade de agrotóxicos utilizados em pomares de pêssego a adultos do predador Chrysoperla externa (Hagen,1861) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Rev Bras Frutic 3(1):73–80. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-29452011005000042
Castro AA, Corrêa AS, Legaspi JC, Guedes RNC, Serrão JE, Zanuncio JC (2013) Survival and behavior of the insecticide-exposed predators Podisus nigrispinus and Supputius cincticeps (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Chemosphere 3(6):1043–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.075
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) Sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.52.110405.091440
Di N, Hladun KR, Zhang K, Liu TX, Trumble JT (2016) Laboratory bioassays on the impact of cadmium, copper and lead on the development and survival of honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) larvae and foragers. Chemosphere 152:530–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.033
Duarte F, Calvo MV, Borges A, Scaton IB (2015) Geostatistics and geographic information systems to study the spatial distribution of Grapholita molesta (Busck) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in peach fields. Neotrop Entomol 44:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-015-0288-3
Fernandes FL, Bacci L, Fernandes MS (2010) Impact and selectivity of insecticides to predators and parasitoids. EntomoBrasilis 3(1):1–10
Fortes JF (2002) Tratamento de inverno para o cultivo do pessegueiro. Embrapa Clima Temperado, Pelotas
Garzón A, Medina P, Amor F, Vinuela E, Budia F (2015) Toxicity and sublethal effects of six insecticides to last instar larvae and adults of the biocontrol agents Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) and Adalia bipunctata (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemosphere 132:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.016
Gessler C, Pertot I, Perazzolli M (2011) Plasmopara viticola: a review of knowledge ondowny mildew of grapevine and effective disease management. Phytopathol Mediterr 50:3–44. https://doi.org/10.14601/Phytopathol_Mediterr-9360
Guedes RNC, Smagghe G, Stark JD, Desneux N (2016) Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu Rev Entomol 61:3.1–3.20. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-010715-023646
Hafsi A, Abbes K, Harbi A, Duyck PF, Chermiti B (2016) Attract-and-kill systems efficiency against Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae) and effects on non-target insects in peach orchards. J Appl Entomol 140:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/jen.12259
Hannig GT, Ziedfe M, Marçon PG (2009) Feeding cessation effects of chlorantraniliprole, a new anthranilic diamide insecticide, in comparison with several insecticides in distinct chemical classes andmode-of-action groups. Pest Manag Sci 65:969–974. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1781
Hassan SA (1988) Guideline for testing the side effect of pesticides on the egg parasite Trichogramma cacoeciae. Bulletin SROP 11:3–18
IRAC, Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (2018). The Irac classification: an interactive mode of action (MoA) tool. Disponível em: http://www.irac-online.org/modes-of-action/. Accessed 05 Dec 2018
Jam NA, Saber M (2018) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on the functional response of the aphid parasitoid, Lysiphlebus fabarum. Entomol Gen 38(2):173–190. https://doi.org/10.1127/entomologia/2018/0734
Lixa AT, Campos JM, Resende ALS, Silva JC, Almeida MMTB, Aguiar-Menezes EL (2010) Diversidade de coccinellidae (Coleoptera) em plantas aromáticas (Apiaceae) como sítios de sobrevivência e reprodução em sistema agroecológico. Neotrop Entomol 39:354–359. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2010000300007
Lo PL (2004) Toxicity of pesticides to Halmus chalybeus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and the effect of three fungicides on their densities in a citrus orchard. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 32(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671.2004.9514281
Madbouni MAZ, Samih MA, Qureshi JA, Biondi A, Namvar P (2017) Compatibility of insecticides and fungicides with the zoophytophagous mirid predator Nesidiocoris tenuis. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0187439. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187439
Marco MP, Pascual N, Bellés X, Camps F, Messeguer A (1990) Ecdysteroid depletion by azadirachtin in Tenebrio molitor pupae. Pest Biochem Physiol 38(1):60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-3575(90)90149-V
MAPA, Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento (2018) Sistema de Agrotóxicos Fitossanitários. http://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons. Accessed 24 Nov
MAPA, Ministério da Agricultura Pecuária e Abastecimento (1999) Normas para a produção de produtos orgânicos vegetais e animais. Instrução Normativa n° 7 de 17 de maio de 1999, Brasília, Brasil
Milléo J, Meira WV (2012) Morfologia dos Coccinellini (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Depositados na Coleção Entomológica dos Campos Gerais do Paraná, Ponta Grossa, Paraná. EntomoBrasilis 5(2):146–163. https://doi.org/10.12741/ebrasilis.v5i2.231
Nava DE, Botton M, Arioli CJ, Garcia MS, Grützmacher AD (2014) Insetos e ácaros praga. In: Raseira MCB, Pereira JFM, Carvalho FLC (eds) Pessegueiro. Embrapa, Brasília, p 433–486
Nörnberg SD, Grützmacher AD, Nava DE, Valgas RA, Ozelame AL (2016) Residual effects of pesticides in peach orchards on the maize weevil Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Rev Bras Frutic 38(3):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-29452016017
NORMAS, Normas técnicas específicas para a Produção Integrada de Pêssego (2003) Grade de Agroquímicos, Instrução Normativa/ SARC nº 016 - 1º de dezembro de 2003. Disponível em: http://www.inmetro.gov.br/credenciamento/pessego/GradeAgroquimicos.pdf. Accessed 11 Nov 2018
Oliveira RL, Gontijo PC, Sâmia RR, Carvalho GA (2019) Long-term effects of chlorantraniliprole reduced risk insecticide applied as seed treatment on lady beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemosphere 219:678–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.058
Oliveira NC, Wilcken CF, Matos CAO (2004) Ciclo biológico e predação de três espécies de coccinelídeos (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) sobre o pulgão-gigante-do-pinus Cinara atlantica (Wilson) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Rev Bras Entomol 48(4):529–533. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0085-56262004000400016
Pasini RA, Grützmacher AD, Pazini JB, De Armas FS, Bueno FA, Pires SN (2018) Side effects of inseticides used in wheat crop on eggs and pupae of Chrysoperla externa and Eriopis connexa. Phytoparasitica 46:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-018-0639-9
Parra JRP (1997) Técnicas de criação de Anagasta kuehniella, hospedeiro alternativo para produção de Trichogramma. In: Parra JRP, Zucchi RA (eds) Trichogramma e o controle biológico aplicado. FEALQ, Piracicaba, p 121–150
Passos LC, Soares MA, Collares LJ, Malagoli I, Desneux N, Carvalho GA (2018) Lethal, sublethal and transgenerational effects of insecticides on Macrolophus basicornis, predator of Tuta absoluta. Entomol Gen 38(2):127–143. https://doi.org/10.1127/entomologia/2018/0744
Pérez-Aguilar DA, Soares MA, Passos LC, Martínez AM, Pineda S, Carvalho GA (2018) Lethal and sublethal effects of insecticides on Engytatus varians (Heteroptera: Miridae), a predator of Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Ecotoxicology 27:719–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1954-0
Prabhaker N, Castle SJ, Naranjo SE, Toscano NC, Morse JG (2017) Compatibility of two systemic neonicotinoids, imidacloprid and thiamethoxam, with various natural enemies of agricultural pests. J Econ Entomol 104(3):773–781. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC10362
Püntener W (1981) Manual for field trials in plant protection. Ciba-Geigy, Suiça, Basle
Rashidi F, Nouri-Ganbalani G, Imani S (2018) Sublethal effects of some insecticides on functional response of Habrobracon hebetor (Hymneoptera: Braconidae) when reared on two lepidopteran hosts. J Econ Entomol 111(3):1104–1111. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toy069
Rimoldi F, Fogel NM, Ronco AE, Schneider MI (2017) Comparative susceptibility of two Neotropical predators, Eriopis connexa and Chrysoperla externa, to acetamiprid and pyriproxyfen: short and long-term effects after egg exposure. Polluto Environ 231(1):1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.06.014
Rodrigues ARS, Spindola AF, Torres JB, Siqueira HAA, Colares F (2013) Response of different populations of seven lady beetle species to lambda-cyhalothrin with record of resistance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 96:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.06.014
Rugno GR, Zanardi OZ, Parra JRP, Yamamoto PT (2018) Lethal and sublethal toxicity of insecticides to the lacewing Ceraeochrysa Cubana. Neotrop Entomol. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-018-0626-3
Sciarretta A, Tabilio MR, Lampazzi E, Ceccaroli C, Colacci M, Trematerra P (2018) Analysis of the Mediterranean fruit fly [Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann)] spatio-temporal distribution in relation to sex and female mating status for precision IPM. PLoS ONE 13(4):e0195097. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1204939
Schmuck R, Candolfi MP, Kleiner R, Mead-Briggs M, Moll M, Kemmeter F, Jans D, Waltersdorfer A, Wilhelmy HA (2000) Laboratory test system for assessing effects of plant protection products on the plant dwelling insect Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). In: Candolfi MP, Blumel S, Forster R, Bakker FM, Grimm C, Hassan SA, Heimbach U, Mead-Briggs MA, Reber B, Schmuck R, Vogt H (eds) Guidelines to evaluate side-effects of plant protection products to non-target arthropods. IOBC/ WPRS, Reinheim, p 45–56
Silva BKDA, Godoy MSD, Lima AGD, Oliveira AKSD, Pastori PL (2017) Toxicity of insecticides used in muskmelon on first-instar larvae of Chrysoperla genanigra Freitas (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Revista Caatinga 30(3):662–669. https://doi.org/10.1590/1983-21252017v30n314rc
Silva DM, Bueno AF, Andrade K, Stecca CS, Neves MOJ, Moscardi F (2016) Selectivity of organic compounds to the egg parasitoid Telenomus remus Nixon (Hymenoptera: Plastygastridae). Semina Ciênc Agrár 37(1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0359.2016v37n1p55
Silva DM, Bueno AF (2014) Toxicity of organic supplies for the egg parasitoid Telenomus podisi. Cienc Rural 44(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-84782014000100003
Silva RB, Zanuncio JC, Serrão JE, Lima ER, Figueiredo MLC, Cruz I (2009) Suitability of different artificial diets for development and survival of stages of the predaceous ladybird beetle Eriopis connexa. Phytoparasitica 37:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-008-0015-2
Sterk G, Hassan SA, Baillod M, Bakker F, Bigler F, Blümel S, Bogenschutz H, Boller E, Bromand B, Brun J, Calis JNM, Coremans-Pelseneer J, Duso C, Garrido A, Grove A, Heimbach U, Hokkanen H, Jacas J, Lewis G, Moreth L, Polgar L, Roversti L, Samsoe-Peterson L, Sauphanor B, Schaub L, Stäubli A, Tuset JJ, Vainio A, Van de Veire M, Viggiani G, Vinuela E, Vogt H (1999) Results of the seventh joint pesticide testing programme carried out by the IOBC/WPRS-working group ‘Pesticides and beneficial Organisms’. BioControl 44(1):99–117. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009959009802
Symondson WOC, Sunderland KD, Greenstone MH (2002) Can generalist predators be effective biocontrol agents? Annu Rev Entomol 47:561–94. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145240
Torres AF, Carvalho GA, Santa-Cecília LVC, Moscardini VF (2013) Selectivity of seven insecticides against pupae and adults of Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Rev Colomb Entomol 39(1):34–39
Tuelher ES, Venzon M, Guedes RNC, Pallini A (2014) Toxicity of organic-coffee-approved products to the southern red mite Oligonychus ilicis and to its predator Iphiseiodes zuluagai. Crop Protection 55:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2013.09.011
Varikou K, Garantonakis N, Birouraki A (2019) Exposure of Bombus terrestris L. to three different active ingredients and two application methods for olive pest control. Entomol Gen 39(1):53–60. https://doi.org/10.1127/entomologia/2019/0706
Venzon M, Diez-Rodríguez GI, Ferraz CS, Lemos F, Nava DE, Pallin A (2016) Manejo agroecológico das pragas das fruteiras. Informe Agropecuário 37(293):94–103
Vogelweith F, Thiéry D (2018) Assessing the non-targeted effect of copper on the leaf arthropods communities in a vineyard. Biol Control 127:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2018.08.011
Vogt H, Bidfer F, Brown K, Candolfi MP, Kemmeter F, Kühner C, Moll M, Travis A, Ufer A, Viñuela E, Wladburger M, Waltersdorfer A (2000) Laboratory method to test effects of plant protection products on larvae of Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). In: Candolfi MP, Blumel S, Forster R, Bakker FM, Grimm C, Hassan SA, Heimbach U, Mead-Briggs MA, Reber B, Schmuck R, Vogt H (eds) Guidelines to evaluate side-effects of plant protection products to non-target arthropods. IOBC/ WPRS, Reinheim, p 27–44
Vogt H, Rumpf S, Wetzel C, Hassan SA (1992) A field method for testing effects of pesticides on the green lacewing Chrysoperla carnea Steph. IOBC/WPRS Bull 15:176–182
Yang XF, Fan F, Wang C, Wei GS (2016) Where does Grapholita molesta (Busck)(Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) overwinter in adjacent peach, pear and apple orchards? Bull Entomol Res 106(1):135–140. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485315000887
Zappalà L, Siscaro G, Biondi A, Mollá O, González-Cabrera J, Urbaneja A (2012) Efficacy of sulphur on Tuta absoluta and its side effects on the predator Nesidiocoris tenuis. J Appl Ent 136:401–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0418.2011.01662.x
Zanuncio JC, Mourão SA, Martínez LC, Wilcken CF, Ramalho FS, Plata-Rueda A, Soares MA, Serrão JE (2016) Toxic effects of the neem oil (Azadirachta indica) formulation on the stink bug predator, Podisus nigrispinus (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Sci Rep 6:30261. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30261
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Brazilian Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) – Financial code 001.
Author contributions
FSA, ADG and DEN conceived research. FSA, MR and RAP kept insects rearing. FSA, MR, RAP and JBP conducted experiments. FSA analyzed data. FSA, MR and RAP wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The authors agree with the publication of the manuscript in this form.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Armas, F.S., Dionei Grutzmacher, A., Edson Nava, D. et al. Non-target toxicity of nine agrochemicals toward larvae and adults of two generalist predators active in peach orchards. Ecotoxicology 29, 327–339 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02177-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02177-5