Abstract
Background
Plexiform neurofibromas (PN) are the most frequent tumors associated with Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1). PN can cause significant complications, including pain, functional impairment, and disfigurement. There is no efficient medical treatment and, surgical resection of large PN is frequently infeasible. Selumetinib (AZD6244/ARRY-142886) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase enzyme (MEK1/2) inhibitor and works by targeting the MAPK pathway. It is an investigational treatment option for inoperable symptomatic PN associated with NF-1. Herein, we describe a single institutional experience with selumetinib for inoperable PN in NF-1.
Methods
Case series study of demographics, clinical, baseline characteristics, treatment effect, and follow-up of consecutive genetically confirmed NF1 patients with inoperable PN associated with significant or potential significant morbidity treated with selumetinib (April 2018 to April 2019).
Results
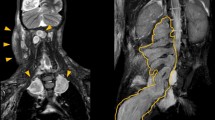
Nineteen patients were treated with selumetinib. Predominant target locations were head and neck (31.6%, 6/19), chest (26.3%, 5/19) and pelvis (21%, 4/19) and the most important comorbidities were disfigurement (47.4%, 9/19) and pain (26.3%, 5/19). The mean follow-up time was 223 days (range 35–420 days). All but one had sustained clinical improvement, mainly in the first 60–90 days of treatment. In one patient, the treatment was suspended after 168 days (lack of clear benefit and left ventricular ejection fraction drop). There were no adverse effects leading to treatment suspension.
Conclusions
In the first observational study of selumetinib for NF-1 associated PN we showed that the drug was associated with clinical and radiological improvement. Our study also confirms the safety described in the clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huson SM, Harper PS, Compston DA (1988) Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. A clinical and population study in south-east Wales. Brain 111(Pt 6):1355–1381
Hirbe AC, Gutmann DH (2014) Neurofi bromatosis type 1: a multidisciplinary approach to care. Lancet Neurol 13:835–843
Andrea Gross BCW, Wolters P, Baldwin A, Dombi E, Fisher MJ, Weiss B, Kim AR, Blakeley J, Whitcomb P, Holmblad M, Maritin S, Roderick MC, Paul SM, Therrien J, Heisey K, Doyle A, Malc (2018) Neuro-Oncology. Neuro-Oncol 1:i143–i144
Evans DGR, Baser ME, McGaughran J, Sharif S, Howard E, Moran A (2002) Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in neurofibromatosis 1. J Med Genet 39(5):311–314
Dombi E et al (2007) NF1 plexiform neurofibroma growth rate by volumetric MRI Relationship to age and body weight. Neurology 68:643–648
Dombi E et al (2016) Activity of selumetinib in neurofibromatosis type 1-related plexiform neurofibromas. N Engl J Med 375(26):2550–2560
Eisenhauer EA (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 45(2):228–247
Passos J, Nzwalo H, Azevedo M, Tavares M, Nunes S (2019) Dramatic improvement of a massive plexiform neurofibroma after administration of selumetinib. Pediatr Neurol 19(11):30928–30932
Dombi E et al (2013) Recommendations for imaging tumor response in neurofibromatosis clinical trials. Neurology 81(21 Suppl 1):S33–40
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the patients and their relatives for their collaboration and AstraZeneca for providing selumetinib under the "early access drug program."
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espírito Santo, V., Passos, J., Nzwalo, H. et al. Selumetinib for plexiform neurofibromas in neurofibromatosis type 1: a single-institution experience. J Neurooncol 147, 459–463 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03443-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03443-6