Abstract
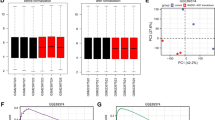
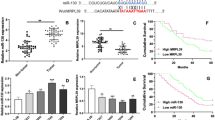
Ovarian cancer has the highest mortality in gynecologic malignancies. LncRNA BLACAT1 serves crucial functions in various cancers, but its role in ovarian cancer has not been investigated. In this article, our team explored the role and the potential regulatory mechanism of BLACAT1 in ovarian cancer. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that BLACAT1 was aberrantly up-regulated in ovarian cancer tissues compared with normal tissues. In vitro, BLACAT1 knockdown induced cell cycle arrest and inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells using flow cytometry, MTT and EdU assays, wound healing assay and transwell assay, respectively. Luciferase assay verified the binding relationship between microRNA-519d-3p and lncRNA BLACAT1, and BLACAT1 negatively regulated the expression of miR-519d-3p. We also found that miR-519d-3p overexpression could inhibit ovarian cancer cells proliferation, migration and invasion. Further, Western blot demonstrated that the expression of RPS15A and nuclear β-catenin expression was markedly reduced by BLACAT1 knockdown, and cytoplasmic β-catenin level was not obviously affected. In vivo, BLACAT1 knockdown inhibited the tumor growth, and immunohistochemistry showed that ki67 expression was decreased by BLACAT1 suppression. Inhibition of BLACAT1 was sufficient to down-regulate the expression of RPS15A and nuclear β-catenin but did not cause an obvious change in cytoplasmic β-catenin expression. Taken together, BLACAT1 knockdown inhibited the progression of ovarian cancer by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via regulating miR-519d-3p. Our work provided a proper understanding of the critical roles of BLACAT1 in ovarian cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2014) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359–386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Morice P (2019) Mucinous ovarian carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380:1256–1266. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1813254
Hennessy BT, Coleman RL (2009) Ovarian cancer. Lancet 374:1371–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61338-6
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC et al (2016) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:271–289. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21349
Yang G, Lu X, Yuan L (2014) LncRNA: a link between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.08.012
Gong J, Xu X, Zhang X, Zhou Y (2019) LncRNA MIR4435-2HG is a potential early diagnostic marker for ovarian carcinoma. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 51:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmz085
Yan H, Li H, Silva MA et al (2019) LncRNA FLVCR1-AS1 mediates miR-513 / YAP1 signaling to promote cell progression, migration, invasion and EMT process in ovarian cancer. Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:1–13
He W, Cai Q, Sun F et al (2013) Linc-UBC1 physically associates with polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) and acts as a negative prognostic factor for lymph node metastasis and survival in bladder cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:1528–1537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.010
Chen X, Dai M, Zhu H et al (2017) Evaluation on the diagnostic and prognostic values of long non-coding RNA BLACAT1 in common types of human cancer. Mol Cancer 16:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0728-2
Hu X, Liu Y, Du Y et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA BLACAT1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by miR-150-5p/CCR2. Cell Biosci 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-019-0274-2
Wang CH, Li YH, Tian HL et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA BLACAT1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer through activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:3002–3009
Huang FX, Chen HJ, Zheng FX et al (2019) LncRNA BLACAT1 is involved in chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating autophagy. Int J Oncol 54:339–347. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4614
Wu X, Zheng Y, Han B, Dong X (2018) Long noncoding RNA BLACAT1 modulates ABCB1 to promote oxaliplatin resistance of gastric cancer via sponging miR-361. Biomed Pharmacother 99:832–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.130
Su J, Zhang E, Han L et al (2017) Long noncoding RNA BLACAT1 indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and affects cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of p15. Cell Death Dis 8:e2665–e2669. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.83
Dong Z, Wang Y (2019) LncRNA BLACAT1 accelerates the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells through regulating STAT3. Pathol Res Pract 215:571–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.01.017
Carlo M, Croce MD (2009) Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 10:704–714. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2634.Causes
Catto JWF, Alcaraz A, Bjartell AS et al (2011) MicroRNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer: a systematic review. Eur Urol 59:671–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.01.044
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN et al (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37:495–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1536
Yue H, Tang B, Zhao Y et al (2017) MIR-519d suppresses the gastric cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Twist1 and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res 9:3654–3664
Yan CQ, Lu YH, Tang SM, Fan WX (2018) MiR-519d inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation, cycle and invasion via targeting NRBP1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:2985–2990. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201805_15054
Ding J, Huang F, Wu G et al (2015) MiR-519d-3p suppresses invasion and migration of trophoblast cells via targeting MMP-2. PLoS ONE 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120321
Liang J, Liu Y, Zhang L et al (2019) Overexpression of microRNA-519d-3p suppressed the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting ribosomal protein S15A-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Chem Biol Interact 304:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.02.026
Guo P, Wang Y, Dai C et al (2018) Ribosomal protein S15a promotes tumor angiogenesis via enhancing Wnt/β-catenin-induced FGF18 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 37:1220–1236. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0017-y
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Joannie Lortet-Tieulent AJ (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2009) Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2521
Lu W, Zhang H, Niu Y et al (2017) Long non-coding RNA linc00673 regulated non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-150-5p. Mol Cancer 16:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0685-9
Chen X, Zeng K, Xu M et al (2018) SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis. Cell Death Dis 9:982. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0962-6
Pang Y, Mao H, Shen L et al (2014) MiR-519d represses ovarian cancer cell proliferation and enhances cisplatin-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro by targeting XIAP. Onco Targets Ther 7:587–597. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S60289
Hou R, Jiang L, Yang Z et al (2016) Rab14 is overexpressed in ovarian cancers and promotes ovarian cancer proliferation through Wnt pathway. Tumor Biol 37:16005–16013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5420-4
Liu H, Shi H, Fan Q, Sun X (2016) Cyclin Y regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via Wnt signaling pathway. Tumor Biol 37:10161–10175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4818-3
Shang S, Hua F, Hu ZW (2017) The regulation of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 8:33972–33989. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15687
Gatcliffe TA, Monk BJ, Planutis K (2008) Wnt signaling in ovarian tumorigenesis. Int J Gynecol Cancer 18:954–962. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2014.371
Funding
This study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: TS; Methodology: HY; Formal analysis and investigation: HY, YQ, XW and JG; Writing original draft preparation: HY; Writing-review and editing: TS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have read this manuscript and authorized the submission for publication. All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were approved by the Ethics Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (Reference Number: 2019PS641K) and in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All procedures performed in this study involving animals were in conformity with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Ethical Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (Reference Number: 2019PS670K).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Qi, Y., Wang, Xl. et al. Down-regulation of lncRNA BLACAT1 inhibits ovarian cancer progression by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via regulating miR-519d-3p. Mol Cell Biochem 467, 95–105 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03704-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03704-y