Abstract
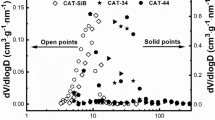
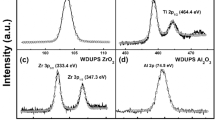
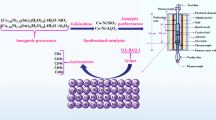
A series of well-defined and uniform pore-structure (WDUPS) TiO2/SiO2 supports with various percentages of rutile TiO2 was developed. Then Fe was introduced into the as-prepared WDUPS supports by incipient wetness impregnation to obtain WDUPS Fe/TiO2/SiO2 catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch (FT) synthesis. Due to a similar surface OH density in the supports and the same pore structure and Fe loading, the catalytic performance of WDUPS catalysts dominated by percentages of rutile TiO2. Based on the catalytic performance for FT synthesis and the characterization of the H2 temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR) and the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), the results suggested that rutile TiO2 acted as a structure promoter in titania-supported iron catalysts and led to an increase in the catalytic activity during FT synthesis. The C5+ selectivity had an increase as the percentage of the rutile phase increased, which was also probably because of rutile TiO2 as a structure promoter for enhancing chain growth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou W, Cheng K, Kang JC, Zhou C, Subramanian V, Zhang QH, Wang Y (2019) New horizon in C1 chemistry: breaking the selectivity limitation in transformation of syngas and hydrogenation of CO2 into hydrocarbon chemicals and fuels. Chem Soc Rev 48(12):3193–3228
Kang SH, Bae JW, Sai Prasad PS, Park SJ, Woo K-J, Jun K-W (2009) Effect of preparation method of Fe-based Fischer–Tropsch catalyst on their light olefin production. Catal Lett 130(3):630–636
Zhang QH, Kang JC, Wang Y (2010) Development of novel catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: tuning the product selectivity. ChemCatChem 2(9):1030–1058
Liu Y, Li Z, Zhang Y (2016) Selectively forming light olefins via macroporous iron-based Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. React Kinet Mech Cat 119(2):457–468
Cheng K, Virginie M, Ordomsky VV, Cordier C, Chernavskii PA, Ivantsov MI, Paul S, Wang Y, Khodakov AY (2015) Pore size effects in high-temperature Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over supported iron catalysts. J Catal 328:139–150
Ghofran Pakdel M, Atashi H, Zohdi-Fasaei H, Mirzaei AA (2019) Effect of temperature on deactivation models of alumina supported iron catalyst during Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Petrol Sci Technol 37(5):500–505
Boellaard E, van der Kraan AM, Geus JW (1996) Behaviour of a cyanide-derived Fe/Al2O3 catalyst during Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Appl Catal A 147(1):229–245
Abrokwah RY, Rahman MM, Deshmane VG, Kuila D (2019) Effect of titania support on Fischer–Tropsch synthesis using cobalt, iron, and ruthenium catalysts in silicon-microchannel microreactor. Mol Catal 478:110566
Rao PM, Viswanathan B, Viswanath RP (1995) Strong metal support interaction state in the Fe/TiO2 system—an XPS study. J Mater Sci 30(19):4980–4985
Al-Dossary M, Fierro JLG, Spivey JJ (2015) Cu-promoted Fe2O3/MgO-based Fischer–Tropsch catalysts of biomass-derived syngas. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(3):911–921
Shen JY, Guang B, Tu M, Chen Y (1996) Preparation and characterization of Fe/MgO catalysts obtained from hydrotalcite-like compounds. Catal Today 30(1):77–82
Torres Galvis HM, Bitter JH, Davidian T, Ruitenbeek M, Dugulan AI, de Jong KP (2012) Iron particle size effects for direct production of lower olefins from synthesis gas. J Am Chem Soc 134(39):16207–16215
Chen XQ, Deng DH, Pan XL, Bao XH (2015) Iron catalyst encapsulated in carbon nanotubes for CO hydrogenation to light olefins. Chinese J Catal 36(9):1631–1637
Cho JM, Han GY, Jeong HK, Roh HS, Bae JW (2018) Effects of ordered mesoporous bimodal structures of Fe/KIT-6 for CO hydrogenation activity to hydrocarbons. Chem Eng J 354:197–207
da Silva JF, Bragança LFFPG, da Silva MIP (2018) Catalytic performance of KL zeolite-supported iron and cobalt catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. React Kinet Mech Cat 124(2):563–574
Jongsomjit B, Wongsalee T, Praserthdam P (2005) Characteristics and catalytic properties of Co/TiO2 for various rutile:anatase ratios. Catal Commun 6(11):705–710
Klabunde KJ, Li YX, Tan BJ (1991) Solvated metal atom dispersed catalysts. Chem Mater 3(1):30–39
Chen AC, Chen SL, Hua DR, Zhou Z, Wang ZG, Wu J, Zhang JH (2013) Diffusion of heavy oil in well-defined and uniform pore-structure catalyst under hydrodemetallization reaction conditions. Chem Eng J 231:420–426
Xie YC, Xu XP, Zhao BY, Tang YC, Wu GB (1992) Studies on the dispersion states of Fe2O3 on γ-Al2O3 by means of Mössbauer spectroscopy and XRD. Catal Lett 13(3):239–245
Mahyar A, Amani-Ghadim AR (2011) Influence of solvent type on the characteristics and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by the sol-gel method. Micro Nano Lett 6(4):244–248
John AK, Palaty S (2018) Influence of solvent and pH on the synthesis of visible light active titanium dioxide nano particles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 87(2):391–399
Xu Y, Zheng W, Liu W (1999) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of supported TiO2: dispersing effect of SiO2. J Photoch and Photobio A 122(1):57–60
Takeuchi M, Martra G, Coluccia S, Anpo M (2005) Investigations of the structure of H2O clusters adsorbed on TiO2 surfaces by near-infrared absorption spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 109(15):7387–7391
Liu P, Duan WL, Liang WZ, Li X (2009) Thermokinetic studies of the groups on TiO2 surface. Surf Interface Anal 41(5):394–398
Wu CY, Tu KJ, Deng JP, Lo YS, Wu CH (2017) Markedly enhanced surface hydroxyl groups of TiO2 nanoparticles with superior water-dispersibility for photocatalysis. Materials 10(5):566
Mueller R, Kammler HK, Wegner K, Pratsinis SE (2003) OH surface density of SiO2 and TiO2 by thermogravimetric analysis. Langmuir 19(1):160–165
Shimura K, Miyazawa T, Hanaoka T, Hirata S (2013) Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over TiO2 supported cobalt catalyst: Effect of TiO2 crystal phase and metal ion loading. Appl Catal A 460–461:8–14
Rout TK, Bandyopadhyay N, Narayan R, Rani N, Sengupta DK (2008) Performance of titania–silica composite coating on interstitial-free steel sheet. Scripta Mater 58(6):473–476
Wang HY, Huang SY, Wang J, Zhao Q, Wang YF, Wang Y, Ma XB (2019) Effect of Ca promoter on the structure and catalytic behavior of FeK/Al2O3 catalyst in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. ChemCatChem 11(14):3220–3226
Tian ZP, Wang CG, Si Z, Ma LL, Chen LG, Liu QY, Zhang Q, Huang HY (2017) Fischer-Tropsch synthesis to light olefins over iron-based catalysts supported on KMnO4 modified activated carbon by a facile method. Appl Catal A 541:50–59
Sun B, Qiao MH, Fan KN, Ulrich J, Tao F (2011) Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over molecular sieve supported catalysts. ChemCatChem 3(3):542–550
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2018J05014, No. 2019J01265) and Science Foundation of the Education Department of Fujian Province (No. JT180085) for our funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Xx., Zhang, Qh., Zhang, Gc. et al. Intrinsic effect of crystalline phases in TiO2 on the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over well-defined and uniform pore-structure Fe/TiO2/SiO2 catalysts. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 129, 743–753 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01748-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01748-1