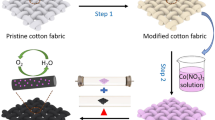
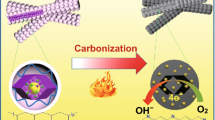
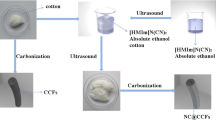
Abstract
Exploring self-supported electrodes with effective oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and durability is of great significance for the future development of metal-air batteries and fuel cells. However, there remain serious challenges in identifying suitable materials and developing sustainable fabrication processes to achieve highly efficient, durable and low-cost self-supported air cathodes. In this work, we report a facile and environmentally friendly method to fabricate electrocatalytic carbon electrodes from commercial cotton fabrics with excellent ORR activity. The iron and nitrogen co-doped carbon fabrics possess outstanding ORR catalytic performance comparable with that of Pt/C, with an onset potential of 0.92 V (vs. RHE) and an electron transfer number close to 4. The experimental results have shown that our carbonisation process can give a high specific surface area (1769 m2/g) with a hierarchical porous structure. Doping leads to the formation of Fe-Nχ species with excellent catalytic activity and durability. Finally, both fundamental understanding of liquid Zn-air battery with well-ground catalysts powders from carbon fabric and practical application of self-supported carbon fabric electrode in solid-state Zn-air battery exhibit promising performance. Our results strongly suggest that natural cellulose fabrics can be a promising material for fabricating highly active, durable and affordable air cathodes for many renewable energy devices such as metal-air batteries and fuel cells.

Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Katsounaros, S. Cherevko, A.R. Zeradjanin, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, Oxygen electrochemistry as a cornerstone for sustainable energy conversion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53(1), 102–121 (2014)
R. Jasinski, A new fuel cell cathode catalyst. Nature 201(4925), 1212 (1964)
Y. Jiao, Y. Zheng, M. Jaroniec, S.Z. Qiao, Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen-and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(8), 2060–2086 (2015)
F. Cheng, J. Chen, Metal–air batteries: From oxygen reduction electrochemistry to cathode catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(6), 2172–2192 (2012)
C.R. Raj, A. Samanta, S.H. Noh, S. Mondal, T. Okajima, T. Ohsaka, Emerging new generation electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(29), 11156–11178 (2016)
C.W. Bezerra, L. Zhang, K. Lee, H. Liu, A.L. Marques, E.P. Marques, H. Wang, J. Zhang, A review of Fe–N/C and Co–N/C catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 53(15), 4937–4951 (2008)
A. Sarapuu, E. Kibena Põldsepp, M. Borghei, K. Tammeveski, Electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction on heteroatom-doped nanocarbons and transition metal–nitrogen–carbon catalysts for alkaline membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(3), 776–804 (2018)
W. Gu, L. Hu, J. Li, E. Wang, Recent advancements in transition metal-nitrogen-carbon catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Electroanalysis 30(7), 1217–1228 (2018)
Y.J. Sa, J.H. Kim, S.H. Joo, Recent progress in the identification of active sites in pyrolyzed Fe-N/C catalysts and insights into their role in oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Electrochemical Science Technology 8(3), 169–182 (2017)
X. Zhang, P. Lu, C. Zhang, X. Cui, Y. Xu, H. Qu, J. Shi, Towards understanding ORR activity and electron-transfer pathway of M-Nx/C electro-catalyst in acidic media. J. Catal. 356, 229–236 (2017)
C. Medard, M. Lefevre, J. Dodelet, F. Jaouen, G. Lindbergh, Oxygen reduction by Fe-based catalysts in PEM fuel cell conditions: Activity and selectivity of the catalysts obtained with two Fe precursors and various carbon supports. Electrochim. Acta 51(16), 3202–3213 (2006)
J. Oh, S. Park, D. Jang, Y. Shin, D. Lim, S. Park, Metal-free N-doped carbon blacks as excellent electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. Carbon 145, 481–487 (2019)
K.A. Shah, B.A. Tali, Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by catalytic chemical vapour deposition: A review on carbon sources, catalysts and substrates. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 41, 67–82 (2016)
J. Wang, H. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, H. Zhao, M. Cheng, A. Li, J. Wang, Co-synthesis of atomic Fe and few-layer graphene towards superior ORR electrocatalyst. Energy Storage Materials 12, 1–7 (2018)
D. Geng, Y. Chen, Y. Chen, Y. Li, R. Li, X. Sun, S. Ye, S. Knights, High oxygen-reduction activity and durability of nitrogen-doped graphene. Energy Environ. Sci. 4(3), 760–764 (2011)
X. Lin, X. Wang, L. Li, M. Yan, Y. Tian, Rupturing cotton microfibers into mesoporous nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets as metal-free catalysts for efficient oxygen electroreduction. ACS Sustainable Chemistry Engineering 5(11), 9709–9717 (2017)
J. Liu, D. Zhu, Y. Zheng, A. Vasileff, S.Z. Qiao, Self-supported earth-abundant nanoarrays as efficient and robust electrocatalysts for energy-related reactions. ACS Catal. 8(7), 6707–6732 (2018)
B. Li, S.P. Sasikala, D.H. Kim, J. Bak, I.D. Kim, E. Cho, S.O. Kim, Fe-N4 complex embedded free-standing carbon fabric catalysts for higher performance ORR both in alkaline & acidic media. Nano Energy 56, 524–530 (2019)
C. Song, Z. Zhao, X. Sun, Y. Zhou, Y. Wang, and D.S. Wang, In situ growth of Ag nanodots decorated Cu2O porous nanobelts networks on copper foam for efficient HER electrocatalysis. Small, 1804268 (2019)
F. Zhang, Y. Pei, Y. Ge, H. Chu, S. Craig, P. Dong, J. Cao, P.M. Ajayan, M. Ye, and J. Shen, Controlled synthesis of eutectic NiSe/Ni3Se2 self-supported on Ni foam: An excellent bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Advanced Materials Interfaces 5(8), 1701507 (2018)
D.U. Lee, J.Y. Choi, K. Feng, H.W. Park, and Z. Chen, Advanced extremely durable 3D bifunctional air electrodes for rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 4(6), 1301389 (2014)
J. Gao, Z. Cheng, C. Shao, Y. Zhao, Z. Zhang, L. Qu, A 2D free-standing film-inspired electrocatalyst for highly efficient hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem. A 5(24), 12027–12033 (2017)
L. Wang, J. Zhang, W. Jiang, H. Zhao, H. Liu, Free-standing, flexible β-Ni (OH) 2/electrochemically-exfoliated graphene film electrode for efficient oxygen evolution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 433, 88–93 (2018)
T.Y. Ma, S. Dai, S.Z. Qiao, Self-supported electrocatalysts for advanced energy conversion processes. Mater. Today 19(5), 265–273 (2016)
S. De, A.M. Balu, J.C. van der Waal, R. Luque, Biomass-derived porous carbon materials: Synthesis and catalytic applications. ChemCatChem 7(11), 1608–1629 (2015)
M. Borghei, J. Lehtonen, L. Liu, and O.J. Rojas, Advanced biomass-derived electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 30(24), 1703691 (2018)
Q. Zhou, X. Ye, Z. Wan, C. Jia, A three-dimensional flexible supercapacitor with enhanced performance based on lightweight, conductive graphene-cotton fabric electrode. J. Power Sources 296, 186–196 (2015)
G. Amirthan, A. Udayakumar, V.B. Prasad, M. Balasubramanian, Synthesis and characterization of Si/SiC ceramics prepared using cotton fabric. Ceram. Int. 35(3), 967–973 (2009)
L. Chen, T. Ji, L. Mu, J. Zhu, Cotton fabric derived hierarchically porous carbon and nitrogen doping for sustainable capacitor electrode. Carbon 111, 839–848 (2017)
C. Zhang, S. Bhoyate, M. Hyatt, B.L. Neria, K. Siam, P. Kahol, M. Ghimire, S. Mishra, F. Perez, R.K. Gupta, Nitrogen-doped flexible carbon cloth for durable metal free electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Surface Coatings Technology 347, 407–413 (2018)
L. Ni, G. Chen, X. Liu, J. Han, X. Xiao, N. Zhang, S. Liang, G. Qiu, R. Ma, Self-supported Fe-doped CoP nanowire arrays grown on carbon cloth with enhanced properties in lithium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Energy Materials 2, 406–412 (2019)
A. Hu, J. Long, C. Shu, C. Xu, T. Yang, R. Liang, J. Li, Three-dimensional CoNi2S4 nanorod arrays anchored on carbon textiles as an integrated cathode for high-rate and long-life lithium−oxygen battery. Electrochim. Acta 301, 69–79 (2019)
T.Y. Ma, J. Ran, S. Dai, M. Jaroniec, S.Z. Qiao, Phosphorus-doped graphitic carbon nitrides grown in situ on carbon-fiber paper: Flexible and reversible oxygen electrodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54(15), 4646–4650 (2015)
S. Xie, S. Liu, F. Cheng, X. Lu, Recent advances toward achieving high-performance carbon-fiber materials for supercapacitors. ChemElectroChem 5(4), 571–582 (2018)
W. Xia, A. Mahmood, Z. Liang, R. Zou, S. Guo, Earth-abundant nanomaterials for oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(8), 2650–2676 (2016)
J. Xiao, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Q. Lv, F. Jing, K. Chi, S. Wang, Self-supported biocarbon-fiber electrode decorated with molybdenum carbide nanoparticles for highly active hydrogen-evolution reaction. ACS applied materials interfaces 9(27), 22604–22611 (2017)
J. Pallarés, A. González-Cencerrado, I. Arauzo, Production and characterization of activated carbon from barley straw by physical activation with carbon dioxide and steam. Biomass Bioenergy 115, 64–73 (2018)
S. Chakraborty, Y.J. Colón, R.Q. Snurr, S.T. Nguyen, Hierarchically porous organic polymers: Highly enhanced gas uptake and transport through templated synthesis. Chem. Sci. 6(1), 384–389 (2015)
E.O. Pentsak, E.G. Gordeev, V.P. Ananikov, Noninnocent nature of carbon support in metal/carbon catalysts: Etching/pitting vs nanotube growth under microwave irradiation. ACS Catal. 4(11), 3806–3814 (2014)
Q.M. Ramasse, R. Zan, U. Bangert, D.W. Boukhvalov, Y.-W. Son, K.S. Novoselov, Direct experimental evidence of metal-mediated etching of suspended graphene. ACS Nano 6(5), 4063–4071 (2012)
S.S. Datta, D.R. Strachan, S.M. Khamis, A.T.C. Johnson, Crystallographic etching of few-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 8(7), 1912–1915 (2008)
X. Li, B.Y. Guan, S. Gao, X.W. Lou, A general dual-templating approach to biomass-derived hierarchically porous heteroatom-doped carbon materials for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Energy Environmental Science 12(2), 648–655 (2019)
S. Li, W. Xu, P. Cheng, J. Luo, D. Zhou, J. Li, R. Li, D. Yuan, Bacterial cellulose derived iron and phosphorus co-doped carbon nanofibers as an efficient oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. Synth. Met. 223, 137–144 (2017)
N. Dwivedi, R.J. Yeo, N. Satyanarayana, S. Kundu, S. Tripathy, C. Bhatia, Understanding the role of nitrogen in plasma-assisted surface modification of magnetic recording media with and without ultrathin carbon overcoats. Sci. Rep. 5, 7772 (2015)
M. Wu, Q. Tang, F. Dong, Y. Wang, D. Li, Q. Guo, Y. Liu, and J. Qiao, The design of Fe, N-doped hierarchically porous carbons as highly active and durable electrocatalysts for a Zn–air battery. PCCP 18(28), 18665–18669 (2016)
Z. Zhang, X. Gao, M. Dou, J. Ji, F. Wang, Fe–N x moiety-modified hierarchically porous carbons derived from porphyra for highly effective oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 5(4), 1526–1532 (2017)
M. Sun, D. Davenport, H. Liu, J. Qu, M. Elimelech, J. Li, Highly efficient and sustainable non-precious-metal Fe–N–C electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(6), 2527–2539 (2018)
W.J. Jiang, L. Gu, L. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, L.J. Zhang, J.Q. Wang, J.S. Hu, Z. Wei, L.J. Wan, Understanding the high activity of Fe–N–C electrocatalysts in oxygen reduction: Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles boost the activity of Fe–N x. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(10), 3570–3578 (2016)
L. Liu, G. Zeng, J. Chen, L. Bi, L. Dai, Z. Wen, N-doped porous carbon nanosheets as pH-universal ORR electrocatalyst in various fuel cell devices. Nano Energy 49, 393–402 (2018)
Y.L. Liu, X.Y. Xu, C.X. Shi, X.W. Ye, P.C. Sun, T.H. Chen, Iron–nitrogen co-doped hierarchically mesoporous carbon spheres as highly efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. RSC Adv. 7(15), 8879–8885 (2017)
Q. Liu, Y. Wang, L. Dai, J. Yao, Scalable fabrication of nanoporous carbon fiber films as bifunctional catalytic electrodes for flexible Zn-air batteries. Adv. Mater. 28(15), 3000–3006 (2016)
L. Lin, Q. Zhu, A.W. Xu, Noble-metal-free Fe–N/C catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction under both alkaline and acidic conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(31), 11027–11033 (2014)
M.Q. Wang, W.H. Yang, H.H. Wang, C. Chen, Z.Y. Zhou, S.G. Sun, Pyrolyzed Fe–N–C composite as an efficient non-precious metal catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in acidic medium. ACS Catal. 4(11), 3928–3936 (2014)
G. Wu, C.M. Johnston, N.H. Mack, K. Artyushkova, M. Ferrandon, M. Nelson, J.S. Lezama Pacheco, S.D. Conradson, K.L. More, D.J. Myers, Synthesis–structure–performance correlation for polyaniline–Me–C non-precious metal cathode catalysts for oxygen reduction in fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 21(30), 11392–11405 (2011)
T. Sun, J. Wang, C. Qiu, X. Ling, B. Tian, W. Chen, and C. Su, B, N codoped and defect-rich nanocarbon material as a metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Advanced Science 5(7), 1800036 (2018)
L. Yang, D. Cheng, H. Xu, X. Zeng, X. Wan, J. Shui, Z. Xiang, D. Cao, Unveiling the high-activity origin of single-atom iron catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115(26), 6626–6631 (2018)
F. Meng, H. Zhong, D. Bao, J. Yan, X. Zhang, In situ coupling of strung Co4N and intertwined N–C fibers toward free-standing bifunctional cathode for robust, efficient, and flexible Zn–air batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(32), 10226–10231 (2016)
Q. Wang, Y. Lei, Z. Chen, N. Wu, Y. Wang, B. Wang, Y. Wang, Fe/Fe 3 C@ C nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped graphene–CNTs framework as an efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for robust rechargeable Zn–air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(2), 516–526 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the support from Australian Research Council (ARC) through ARC Centre of Excellence for Electromaterials Science (ACES). Deakin University’s Advanced Characterization Facility is acknowledged for use of the EM instrument and assistance from Dr. Pavel Cizek. This work was performed in part at the Deakin node of the Australian National Fabrication Facility, a company established under the National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy to provide nano and micro-fabrication facilities for Australia’s researchers. The authors also thank the assistance from Mr. Zhiyu Wang and Dr. Si Qin during the stability test of the liquid cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Cao, G., Shao, H. et al. Turning Cotton to Self-Supported Electrocatalytic Carbon Electrode for Highly Efficient Oxygen Reduction. Electrocatalysis 11, 317–328 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-020-00582-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-020-00582-2