Abstract
Purpose
Acute vertebrobasilar occlusion (VBO) has a grave clinical course; however, thrombectomy in VBO patients has rarely been reported. We retrospectively evaluated the clinical and radiological outcomes of thrombectomy in VBO patients.
Methods
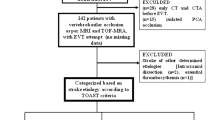
From March 2010 to December 2017, 38 patients with 40 acute VBOs underwent thrombectomy at our hospital. Thrombectomy was performed using catheter aspiration (n = 11, 26.8%) or a stent retriever (n = 29, 70.7%).
Results
Good clinical outcomes (3-month modified Rankin scale (mRS) of 2 or lower) were achieved in 9 cases (22.5%), and successful recanalization (thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) grade of 2b or 3) was achieved in 35 cases (87.5%). Good clinical outcomes were significantly related to aetiologies other than atherosclerosis (p = 0.020) and lower National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores on admission (p = 0.025). The clinical and radiological outcomes did not differ significantly between catheter aspiration and stent retriever thrombectomy (p = 1.000 and p = 0.603, respectively); however, stent retriever thrombectomy had a shorter procedure time than catheter aspiration (59.7 ± 31.2 vs. 84.5 ± 35.1 min, p = 0.037).
Conclusion
In our series, good clinical outcomes were associated with a lower NIHSS score on admission and stroke aetiologies other than atherosclerosis. The two thrombectomy modalities showed similar clinical and radiological outcomes. However, stent retrievers seemed to allow more rapid recanalization than catheter aspiration in VBO.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fahed R, Di Maria F, Rosso C et al (2017) A leap forward in the endovascular management of acute basilar artery occlusion since the appearance of stent retrievers: a single-center comparative study. J Neurosurg 126:1578–1584
Yang H, Ma N, Zhang S, Huo X, Gao F, Sun X, Mo D, Miao Z (2018) Endovascular revascularisation of acute tandem vertebrobasilar artery occlusion: seven case series with literature reviews. Stroke Vasc Neurol 3:17–21
Uno J, Kameda K, Otsuji R, Ren N, Nagaoka S, Maeda K, Ikai Y, Gi H (2017) Mechanical thrombectomy for acute basilar artery occlusion in early therapeutic time window. Cerebrovasc Dis 44:217–224
Mak CH-K, Ho JW-K, Chan K-Y et al (2016) Intra-arterial revascularization therapy for basilar artery occlusion—a systematic review and analysis. Neurosurg Rev 39:575–580
Long J, Qin H, Zhang H (2017) Evaluation of recanalisation treatment on posterior circulation ischemic stroke by Solitaire device—a multicenter retrospective study. Neurol Neurochir Pol 51:208–213
Luo G, Mo D, Tong X, Liebeskind DS, Song L, Ma N, Gao F, Sun X, Zhang X, Wang B, Jia B, Fernandez-Escobar A, Miao Z (2018) Factors associated with 90-day outcomes of patients with acute posterior circulation stroke treated by mechanical thrombectomy. World Neurosurg 109:e318–e328
van Houwelingen RC, Luijckx G-J, Mazuri A et al (2016) Safety and outcome of intra-arterial treatment for basilar artery occlusion. JAMA Neurol 73:1225
Qureshi AI, Caplan LR (2014) Intracranial atherosclerosis. Lancet 383:984–998
Banerjee C, Chimowitz MI (2017) Stroke caused by atherosclerosis of the major intracranial arteries. Circ Res 120:502–513
Kim SJ, Ryoo S, Bang OY, Chung CS, Lee KH, Kim GM (2010) Perfusion-weighted MRI as a predictor of clinical outcomes following medullary infarctions. Cerebrovasc Dis 29:382–388
Kistler JP, Furie KL (2000) Carotid endarterectomy revisited. N Engl J Med 342:1743–1745
Labropoulos N, Nandivada P, Bekelis K (2011) Stroke of the posterior cerebral circulation. Int Angiol 30:105–114
Kang D-H, Kim Y-W, Hwang Y-H et al (2014) Instant reocclusion following mechanical thrombectomy of in situ thromboocclusion and the role of low-dose intra-arterial tirofiban. Cerebrovasc Dis 37:350–355
Mordasini P, Brekenfeld C, Byrne JV et al (2013) Technical feasibility and application of mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire FR revascularization device in acute basilar artery occlusion. Am J Neuroradiol 34:159–163
Tian C, Cao X, Wang J (2017) Recanalisation therapy in patients with acute ischaemic stroke caused by large artery occlusion: choice of therapeutic strategy according to underlying aetiological mechanism? Stroke Vasc Neurol 2:244–250
Fromm A, Waje-Andreassen U, Thomassen L et al (2011) Comparison between ischemic stroke patients <50 years and ≥50 years admitted to a single centre: the Bergen stroke study. Stroke Res Treat 20:183256
Niu J, Ding Y, Zhai T et al (2019) The efficacy and safety of tirofiban for patients with acute ischemic stroke: a protocol for systematic review and a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 98:e14673
Yu T, Lin Y, Jin A, Zhang P, Zhou X, Fang M, Liu X (2018) Safety and efficiency of low dose intra-arterial tirofiban in mechanical thrombectomy during acute ischemic stroke. Curr Neurovasc Res 15:145–150
Xianxian Z, Chengsong Y, Qiang M et al (2017) The efficiency analysis of thrombolytic rt-PA combined with intravascular interventional therapy in patients with acute basilar artery occlusion. Int J Biol Sci 13:57–64
Young FB, Weir CJ, Lees KR (2005) Comparison of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale with disability outcome measures in acute stroke trials. Stroke 36:2187–2192
Gory B, Mazighi M, Labreuche J, Blanc R, Piotin M, Turjman F, Lapergue B, ETIS (Endovascular Treatment in Ischemic Stroke) Investigators (2018) Predictors for mortality after mechanical thrombectomy of acute basilar artery occlusion. Cerebrovasc Dis 45:61–67
Linfante I, Llinas RH, Schlaug G et al (2001) Diffusion-weighted imaging and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale in the acute phase of posterior-circulation stroke. Arch Neurol 58:621–628
Tsao JW, Hemphill JC, Johnston SC et al (2005) Initial Glasgow Coma Scale score predicts outcome following thrombolysis for posterior circulation stroke. Arch Neurol 62:1126
Neuberger U, Kickingereder P, Schönenberger S, Schieber S, Ringleb PA, Bendszus M, Pfaff J, Möhlenbruch MA (2019) Risk factors of intracranial hemorrhage after mechanical thrombectomy of anterior circulation ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 61:461–469
Kwon J-H, Shin SH, Weon YC et al (2011) Intra-arterial adjuvant tirofiban after unsuccessful intra-arterial thrombolysis of acute ischemic stroke: preliminary experience in 16 patients. Neuroradiology 53:779–785
Son S, Choi DS, Oh MK, Hong J, Kim SK, Kang H, Park KJ, Choi NC, Kwon OY, Lim BH (2016) Comparison of Solitaire thrombectomy and Penumbra suction thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke caused by basilar artery occlusion. J Neurointerv Surg 8:13–18
Li W, Lin L, Zhang M et al (2016) Safety and preliminary efficacy of early tirofiban treatment after alteplase in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke 47:2649–2651
Kim BJ, Kim JS (2014) Ischemic stroke subtype classification: an asian viewpoint. J Stroke 16:8–17
Kang DH, Yoon W, Baek BH et al (2019) Front-line thrombectomy for acute large-vessel occlusion with underlying severe intracranial stenosis: stent retriever versus contact aspiration. J Neurosurg 29:1–7
Funding
This study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.H., Kim, S.H., Lee, H. et al. Thrombectomy in acute vertebrobasilar occlusion: a single-centre experience. Neuroradiology 62, 723–731 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02376-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02376-1