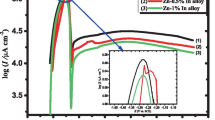
Abstract
Ultrafine spherical zinc powder prepared by direct-current arc plasma evaporation increased the capacity and life of zinc-air batteries. To decelerate the corrosion of the ultrafine zinc powder and improve the charge–discharge performance of the zinc-air batteries, we added different amounts of ultrafine bismuth powder to a zinc electrode. The hydrogen evolution rate of the Zn-Bi electrode and the properties of zinc-air batteries were investigated by hydrogen evolution experiments and electrochemical performance tests. The corrosion inhibition mechanism of the newly added bismuth powder on the zinc electrode was studied via x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results show that when the amount of the ultrafine bismuth powder was 1.5 wt.% of the zinc powder, the anticorrosion efficiency of the Zn-Bi electrode was the highest, reaching 53.8%. After the battery assembly, the Zn-Bi electrode reached a capacity retention rate of 84.6% and had a 21.7% higher specific capacity than that of a blank zinc electrode (419 mA h g−1 versus 344.3 mA h g−1) after 60 cycles. The ultrafine bismuth powder improved the nucleation efficiency, reduced the corrosion current, increased the polarization resistance threefold, and inhibited the formation of dendrites and corrosion, thereby increasing the battery specific capacity and cycle efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Suren and S. Kheawhom, J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, 846 (2016).
M.N. Masri and A.A. Mohamad, J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, 715 (2013).
X.Y. Wen, X.W. Lu, K.X. Xiang, L. Xiao, H.Y. Liao, W.H. Chen, W. Zhou, and H. Chen, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 544, 711 (2019).
M. Schmid and M. Willert-Porada, Electrochim. Acta 260, 246 (2018).
E. Davari and D.G. Ivey, J. Appl. Electrochem. 47, 815 (2017).
K. Lopez, G. Park, H.J. Sun, J.C. An, S. Eom, and J. Shim, J. Appl. Electrochem. 45, 313 (2015).
Z. Li, J.J. Huang, Z.Z. Zhang, F.X. Zhao, and Y. Wu, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 6 (2018).
A. Nakata, H. Murayama, K. Fukuda, T. Yamane, H. Arai, T. Hirai, Y. Uchimoto, J. Yamaki, and Z. Ogumi, Electrochim. Acta 166, 82 (2015).
M. Hilder, B. Winther-Jensen, and N.B. Clark, Electrochim. Acta 69, 308 (2012).
H.Y. Liao, H. Chen, F.L. Zhou, Z.Z. Zhang, and H. Chen, J. Power Sources 435, 226748 (2019).
Y. He, K.X. Xiang, Y.F. Wang, W. Zhou, Y.R. Zhu, L. Xiao, W.H. Chen, X.H. Chen, H. Chen, H. Cheng, and Z.G. Lu, Carbon 154, 330 (2019).
D. Schroeder, N.N. Borker, M. Koenig, and U. Krewer, J. Appl. Electrochem. 45, 427 (2015).
M. Pino, C. Cuadrado, J. Chacon, P. Rodriguez, E. Fatas, and P. Ocon, J. Appl. Electrochem. 44, 1371 (2014).
W.G. Gan, D.B. Zhou, J. Zhao, and L. Zhou, J. Appl. Electrochem. 45, 913 (2015).
H. Kim, E. Kim, S. Kim, and H. Shin, J. Appl. Electrochem. 45, 335 (2015).
K. Miyazaki, A. Nakata, Y. Lee, T. Fukutsuka, and T. Abe, J. Appl. Electrochem. 46, 1067 (2016).
J.L. Ortiz-Aparicio, Y. Meas, G. Trejo, R. Ortega, T.W. Chapman, and E. Chainet, J. Appl. Electrochem. 43, 289 (2013).
C. Mele and B. Bozzini, J. Appl. Electrochem. 45, 43 (2015).
Y. Xiao, J.C. Shi, F.X. Zhao, Z.Z. Zhang, and W. He, J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, A47 (2018).
C. Zhang, J.M. Wang, L. Zhang, J.Q. Zhang, and C.N. Cao, J. Appl. Electrochem. 31, 1049 (2001).
S.M. Lee, Y.J. Kim, S.W. Eom, N.S. Choi, K.W. Kim, and S.B. Cho, J. Power Sources 227, 177 (2013).
J.L. Pan, Y.H. Wen, J. Cheng, J.Q. Pan, Z.L. Bai, and Y.S. Yang, J. Appl. Electrochem. 43, 541 (2013).
Y. He, K.X. Xiang, W. Zhou, Y.R. Zhu, X.H. Chen, and H. Chen, Chem. Eng. J. 353, 666 (2018).
D.V. Malakhov, CALPHAD: Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 24, 1 (2000).
Y. Kurata, J. Nucl. Mater. 448, 239 (2014).
X.J. Wang, Q.S. Zhu, B. Liu, N. Liu, and F.J. Wang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 2297 (2014).
S. Das, A. Ramakrishnan, M. Rudra, K.H. Chen, T.P. Sinha, D.K. Misra, and R.C. Mallik, J. Electron. Mater. 48, 3631 (2019).
C.F. Shi, K.X. Xiang, Y.R. Zhu, X.H. Chen, W. Zhou, and H. Chen, Electrochim. Acta 246, 1088 (2017).
J.Y. Xia, M.T. Tang, C. Chen, S.M. Jin, and Y.M. Chen, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22, 2289 (2012).
N. Junker, M. Schneider, and A. Michaelis, Mater. Corros. 68, 1389 (2017).
F. Rosalbino, R. Carlini, G. Zanicchi, and G. Scavino, J. Alloy. Compd. 567, 26 (2013).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Jiangsu University Advantage Discipline Construction Project (Jiangsu Gov. Office issued 2018-10), the Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (TAPP, PPZY2015B128) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Da, Y., Zhao, F., Shi, J. et al. Effects of Ultrafine Bismuth Powder on the Properties of Zinc Electrodes in Zinc-Air Batteries. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 2479–2490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-07978-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-07978-2