Abstract
Purpose
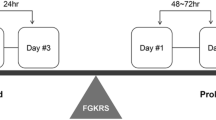
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is typically considered for patients who cannot undergo surgical resection for large (> 10 cm3) brain metastases (BMs). Staged SRS requires adaptive planning during each stage of the irradiation period for improved tumor control and reduced radiation damage. However, there has been no study on the tumor reduction rates of this method. We evaluated the outcomes of two-stage SRS across multiple primary cancer types.
Methods
We analyzed 178 patients with 182 large BMs initially treated with two-stage SRS. The primary cancers included breast (BC), non-small cell lung (NSCLC), and gastrointestinal tract cancers (GIC). We analyzed the overall survival (OS), neurological death, systemic death (SD), tumor progression (TP), tumor recurrence (TR), radiation necrosis (RN), and the tumor reduction rate during both stages.
Results
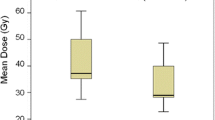
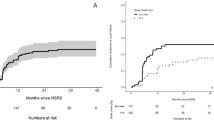
The median survival time after the first Gamma Knife surgery (GKS) procedure was 6.6 months. Compared with patients with BC and NSCLC, patients with GIC had shorter OS and a higher incidence of SD. Compared with patients with NSCLC and GIC, patients with BC had significantly higher tumor reduction rates in both sessions. TP rates were similar among primary cancer types. There was no association of the tumor reduction rate with tumor control. The overall cumulative incidence of RN was 4.2%; further, the RN rates were similar among primary cancer types.
Conclusions
Two-stage SRS should be considered for BC and NSCLC if surgical resection is not indicated. For BMs from GIC, staged SRS should be carefully considered and adapted to each unique case given its lower tumor reduction rate and shorter OS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehta MP, Tsao MN, Whelan TJ, Morris DE, Hayman JA, Flickinger JC, Mills M, Rogers CL, Souhami L (2005) The American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based review of the role of radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.05.023
Navarria P, Pessina F, Cozzi L, Ascolese AM, De Rose F, Fogliata A, Franzese C, Franceschini D, Tozzi A, D'Agostino G, Comito T, Iftode C, Maggi G, Reggiori G, Bello L, Scorsetti M (2016) Hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone using volumetric modulated arc therapy for patients with single, large brain metastases unsuitable for surgical resection. Radiat Oncol 11:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-016-0653-3
Murai T, Ogino H, Manabe Y, Iwabuchi M, Okumura T, Matsushita Y, Tsuji Y, Suzuki H, Shibamoto Y (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using CyberKnife for the treatment of large brain metastases: a dose escalation study. Clin Oncol 26:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2013.11.027
Han JH, Kim DG, Chung HT, Paek SH, Park CK, Jung HW (2012) Radiosurgery for large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.06.1965
Arvold ND, Lee EQ, Mehta MP, Margolin K, Alexander BM, Lin NU, Anders CK, Soffietti R, Camidge DR, Vogelbaum MA, Dunn IF, Wen PY (2016) Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro-oncology 18:1043–1065. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now127
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.30.1655
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, Markesbery WR, Macdonald JS, Young B (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199002223220802
Ewend MG, Elbabaa S, Carey LA (2005) Current treatment paradigms for the management of patients with brain metastases. Neurosurgery 57:S66–77; discussion S61–64. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000182739.84734.6e
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Nagano O, Sato Y, Yamamoto M, Ono J, Saeki N, Miyakawa A, Hirai T (2012) Analysis of 2000 cases treated with Gamma Knife surgery: validating eligibility criteria for a prospective multi-institutional study of stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of patients with 1–10 brain metastases (JLGK0901) in Japan. J Radiosurg SBRT 2:19–27
Shiau CY, Sneed PK, Shu HK, Lamborn KR, McDermott MW, Chang S, Nowak P, Petti PL, Smith V, Verhey LJ, Ho M, Park E, Wara WM, Gutin PH, Larson DA (1997) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: relationship of dose and pattern of enhancement to local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(96)00497-x
Linskey ME, Andrews DW, Asher AL, Burri SH, Kondziolka D, Robinson PD, Ammirati M, Cobbs CS, Gaspar LE, Loeffler JS, McDermott M, Mehta MP, Mikkelsen T, Olson JJ, Paleologos NA, Patchell RA, Ryken TC, Kalkanis SN (2010) The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 96:45–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0073-4
Ellis TL, Neal MT, Chan MD (2012) The role of surgery, radiosurgery and whole brain radiation therapy in the management of patients with metastatic brain tumors. Int J Surg Oncol 2012:952345. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/952345
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16250-8
Bowden G, Kano H, Caparosa E, Park SH, Niranjan A, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2015) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for the management of cerebral metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. J Neurosurg 122:766–772. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.jns141111
Devoid HM, McTyre ER, Page BR, Metheny-Barlow L, Ruiz J, Chan MD (2016) Recent advances in radiosurgical management of brain metastases. Front Biosci 8:203–214. https://doi.org/10.2741/s458
Serizawa T, Saeki N, Higuchi Y, Ono J, Iuchi T, Nagano O, Yamaura A (2005) Gamma Knife surgery for brain metastases: indications for and limitations of a local treatment protocol. Acta Neurochir 147:721–726; discussion 726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0540-4
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Kirkwood JM, Agarwala S, Lunsford LD (1998) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma: factors affecting local disease control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(98)00272-7
Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Ono J, Sato M, Iwadate Y, Saeki N (2009) Three-staged stereotactic radiotherapy without whole brain irradiation for large metastatic brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:1543–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.10.035
Yomo S, Hayashi M, Nicholson C (2012) A prospective pilot study of two-session Gamma Knife surgery for large metastatic brain tumors. J Neurooncol 109:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0882-8
Yomo S, Hayashi M (2014) A minimally invasive treatment option for large metastatic brain tumors: long-term results of two-session Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiation Oncology 9:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717x-9-132
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Yamamoto T, Iizuka H, Nishikawa T, Ito H, Kato N (2017) Multisession Gamma Knife surgery for large brain metastases. J Neurooncol 131:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2317-4
Angelov L, Mohammadi AM, Bennett EE, Abbassy M, Elson P, Chao ST, Montgomery JS, Habboub G, Vogelbaum MA, Suh JH, Murphy ES, Ahluwalia MS, Nagel SJ, Barnett GH (2018) Impact of 2-staged stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases ≥ 2 cm. J Neurosurg 129:366–382. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.3.jns162532
Dohm AE, Hughes R, Wheless W, Lecompte M, Lanier C, Ruiz J, Watabe K, Xing F, Su J, Cramer C, Laxton A, Tatter S, Chan MD (2018) Surgical resection and postoperative radiosurgery versus staged radiosurgery for large brain metastases. J Neurooncol 140:749–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03008-8
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Yamamoto M, Matsunaga S, Nagano O, Sato Y, Aoyagi K, Yomo S, Koiso T, Hasegawa T, Nakazaki K, Moriki A, Kondoh T, Nagatomo Y, Okamoto H, Kohda Y, Kawai H, Shidoh S, Shibazaki T, Onoue S, Kenai H, Inoue A, Mori H (2018) Comparison of treatment results between 3- and 2-stage Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large brain metastases: a retrospective multi-institutional study. J Neurosurg 131:227–237. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.4.jns172596
Yamamoto M, Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Kawabe T, Nagano O, Sato Y, Koiso T, Watanabe S, Aiyama H, Kasuya H (2018) Three-stage Gamma Knife treatment for metastatic brain tumors larger than 10 cm3: a 2-institute study including re-analyses of earlier results using competing risk analysis. J Neurosurg 129:77–85. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.7.gks181392
Serizawa T, Yamamoto M, Higuchi Y, Sato Y, Shuto T, Akabane A, Jokura H, Yomo S, Nagano O, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K (2019) Local tumor progression treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery: differences between patients with 2–4 versus 5–10 brain metastases based on an update of a multi-institutional prospective observational study (JLGK0901). J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.1.jns183085
Chernov M, Hayashi M, Izawa M, Ochiai T, Usukura M, Abe K, Ono Y, Muragaki Y, Kubo O, Hori T, Takakura K (2005) Differentiation of the radiation-induced necrosis and tumor recurrence after Gamma Knife radiosurgery for brain metastases: importance of multi-voxel proton MRS. Minim Invasive Neurosurg MIN 48:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-870952
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Lobato-Polo J, Zorro O, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2010) T1/T2 matching to differentiate tumor growth from radiation effects after stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 66:486–491; discussion 491–482. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000360391.35749.a5
Minamimoto R, Saginoya T, Kondo C, Tomura N, Ito K, Matsuo Y, Matsunaga S, Shuto T, Akabane A, Miyata Y, Sakai S, Kubota K (2015) Differentiation of brain tumor recurrence from post-radiotherapy necrosis with 11C-methionine PET: visual assessment versus quantitative assessment. PLoS ONE 10:e0132515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132515
Serizawa T, Saeki N, Higuchi Y, Ono J, Matsuda S, Sato M, Yanagisawa M, Iuchi T, Nagano O, Yamaura A (2005) Diagnostic value of thallium-201 chloride single-photon emission computerized tomography in differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation injury after Gamma Knife surgery for metastatic brain tumors. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):266–271. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.s_supplement.0266
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Aoyagi K, Ono J, Saeki N, Iwadate Y, Hirai T, Takemoto S, Shibamoto Y (2017) Robustness of the neurological prognostic score in brain metastasis patients treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 127:1000–1006. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.jns16528
Nieder C, Andratschke NH, Geinitz H, Grosu AL (2012) Diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment score is valid in patients with brain metastases treated in routine clinical practice in two European countries. Med Sci Monit 18:450–455. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.883213
Meyners T, Heisterkamp C, Kueter JD, Veninga T, Stalpers LJ, Schild SE, Rades D (2010) Prognostic factors for outcomes after whole-brain irradiation of brain metastases from relatively radioresistant tumors: a retrospective analysis. BMC Cancer 10:582. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-582
Brown PD, Brown CA, Pollock BE, Gorman DA, Foote RL (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with "radioresistant" brain metastases. Neurosurgery 62(Suppl 2):790–801. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000316283.45242.e1
Ahmed KA, Scott JG, Arrington JA, Naghavi AO, Grass GD, Perez BA, Caudell JJ, Berglund AE, Welsh EA, Eschrich SA, Dilling TJ, Torres-Roca JF (2018) Radiosensitivity of lung metastases by primary histology and implications for stereotactic body radiation therapy using the genomically adjusted radiation dose. J Thorac Oncol 13:1121–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.04.027
Kocher M, Treuer H, Voges J, Hoevels M, Sturm V, Muller RP (2000) Computer simulation of cytotoxic and vascular effects of radiosurgery in solid and necrotic brain metastases. Radiother Oncol 54:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8140(99)00168-1
Kubo K, Kenjo M, Doi Y, Nakao M, Miura H, Ozawa S, Nagata Y (2019) MRI appearance change during stereotactic radiotherapy for large brain metastases and importance of treatment plan modification during treatment period. Jpn J Radiol 37: 850-859. doi:10.1007/s11604-019-00886-4.
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Onimaru R, Kagei K, Ikeda J, Ishii N, Sawamura Y, Miyasaka K (2003) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone without whole-brain irradiation for patients with solitary and oligo brain metastasis using noninvasive fixation of the skull. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00014-2
Jeong WJ, Park JH, Lee EJ, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Cho YH (2015) Efficacy and Safety of Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Large Brain Metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58:217–224. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.217
Yomo S, Serizawa T, Yamamoto M, Higuchi Y, Sato Y, Shuto T, Akabane A, Jokura H, Kawagishi J, Aoyama H (2019) The impact of EGFR-TKI use on clinical outcomes of lung adenocarcinoma patients with brain metastases after Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a propensity score-matched analysis based on extended JLGK0901 dataset (JLGK0901-EGFR-TKI). J Neurooncol 145:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03282-0
Funding
This study received no financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Daisuke Ito, Kyoko Aoyagi, Osamu Nagano, Yoshinori Higuchi, and Toru Serizawa. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Daisuke Ito and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants
The institutional review board of Chiba Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center IRB (IRB Number: #456) approved this retrospective study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, D., Aoyagi, K., Nagano, O. et al. Comparison of two-stage Gamma Knife radiosurgery outcomes for large brain metastases among primary cancers. J Neurooncol 147, 237–246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03421-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03421-y