Abstract
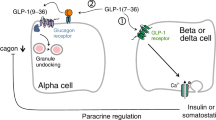
An1 original drug, Glypin, has been developed for the treatment of type-II human diabetes mellitus. Its active pharmaceutical substance is a completely biosynthetic, recombinant, modified, human glucagon-like peptide (rmGlp-1) obtained via culturing of E. coli cells. In addition to the GLP-1 portion, which contains the well-known Ala8Gly substitution, the rmGLP-1 protein has an additional amino acid sequence at the C-terminus that includes the heparin-binding peptide of human HB-EGF. Preclinical testing of Glypin specific activity (with Lixumia as a reference drug) was performed. A commercial preparation of Lixumia served as the main reference drug for comparison with the specific activity of Glypin. During preclinical studies of both medicines, it was shown that Glypin and Lixumia have similar mechanisms, power, and time of action upon subcutaneous and intramuscular introductions, as well as comparable therapeutic effects under long-term use. Based on these data, the subcutaneous injection was selected as the main therapeutic method of Glypin administration; the minimal effective dose for Glypin preclinical study was established as 100 μg/kg body mass, and a single dose for human treatment was defined as 0.75 and 1.5 mg. The intranasal introduction of Glypin was observed to have a statistically reliable positive effect on the cognitive capacities of a mouse with Alzheimer’s disease model. The similarity of the characteristics of Glypin and Lixumia shown in our study make it possible to expect that they will have equal therapeutic efficacy with daily use of a single dose.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Di Cesare, M., Bentham, J., Stevens, G.A., et al., Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants, Lancet, 2016, vol. 387, pp. 1377–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X
Holscher, C., The incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide are neuroprotective in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dementia, 2014, vol. 10, suppl. 1, pp. S47–S54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2013.12.009
Shi, L., Zhang, Z., Li, L., and Holscher, C., A novel dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist alleviates cognitive decline by re-sensitizing insulin signaling in the Alzheimer icv. STZ rat model, Behav. Brain Res., 2017, vol. 327, pp. 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.03.032
Tai, J., Liu, W., Li, Y., et al., Neuroprotective effects of a triple GLP-1/GIP/glucagon receptor agonist in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Brain Res., 2018, vol. 1678, pp. 64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.10.012
Day, J.W., Ottaway, N., Patterson, J.T., et al., A new glucagon and GLP-1 coagonist eliminates obesity in rodents, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2009, vol. 5, pp. 749–757. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.209
Finan, B., Ma, T., Ottaway, N., et al., Unimolecular dual incretins maximize metabolic benefits in rodents, monkeys, and humans, Sci. Transl. Med., 2013, vol. 5, no. 209, p. 209ra151. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3007218
Finan, B., Yang, B., Ottaway, N., et al., A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents, Nat. Med., 2015, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 27–36.
Lau, J., Bloch, P., Schaffer, L., et al., Discovery of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide, J. Med. Chem., 2015, vol. 58, no. 18, pp. 7370–7380. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00726
Painter, N.A., Morello, C.M., Singh, R.F., and M-cBane, S.E., An-evidence-based and practical approach to using BydureonTM in patients with type 2 diabetes, J. Am. Board Fam. Med., 2013, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 203–210. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2013.02.120174
Fonseca, V.A., Alvarado-Ruiz, R., Raccah, D., et al., Efficacy and safety of the once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide in monotherapy: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes (GetGoal-Mono), Diabetes Care, 2012, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1225–1231. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1935
Rosenstock, J., Raccah, D., Koranyi, L., et al., Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide once-daily versus exenatide twice-daily in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 24-week, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (GetGoal-X), Diabetes Care, 2013, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 2945–2951. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-2709
Ostawal, A., Mocevic, E., Kragh, N., and Xu, W., Clinical Effectiveness of liraglutide in type 2 diabetes treatment in the real-world setting: a systematic literature review, Diabetes Ther., 2016, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 411–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-016-0180-0
Jendle, J., Grunberger, G., Blevins, T., et al., Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive review of the dulaglutide clinical data focusing on the AWARD phase 3 clinical trial program, Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev., 2016, vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 776–790. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2810
Rosenstock, J., Reusch, J., Bush, M., et al., Potential of albiglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist, in type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial exploring weekly, biweekly, and monthly dosing, Diabetes Care, 2009, vol. 32, no. 10, pp. 1880–1886. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-0366
Sanchez-Garrido, M.A., Brandt, S.J., Clemmensen, C., et al., GLP-1/glucagon receptor co-agonism for treatment of obesity, Diabetologia, 2017, vol. 60, no. 10, pp. 1851–1861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-017-4354-8
Haslam, D., Weight management in obesity—past and present, Int. J. Clin. Pract., 2016, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 206–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12771
Thompson, S.A., Higashiyama, S., Wood, K., et al., Characterization of sequences within heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor that mediate interaction with heparin, J. Biol. Chem., 1994, vol. 269, no. 4, pp. 2541–2549.
Kozlov, D.G., Sannikova, E.P., Klebanov, F.A., Cheperegin, S.E., Bulushova, N.V., Zalunin, I.A., Gracheva, T.S., Grachev, S.A., Yurin, V.L., Rykalina, N.V., Askerova, E.V., and Yarotskii, S.V., Polypeptide for lowering blood sugar based on human glucagon-like peptide-1, recombinant producer strain, and method for producing this polypeptide, RF Patent no. 2642260, Byull. Izobr., 2018, no. 3.
Kozlov, D.G., Sannikova, E.P., and Cheperegin, S.E., Temperature-sensitive mutant intein for insoluble expression of the target protein precursor, RF Patent no. 2619217, Byull. Izobr., 2017, no. 14.
Khorovskaya, L.A., Chernichuk, O.V., and Lobachevskaya, T.V., Evaluation of the glucose measurement quality using the Accu-Chek Active diagnostic device near the patient, Effekt.Farmakoter., 2014, vol. 20, pp. 20–26.
Yang, X., Li, Y., Wang, Y., et al., Analogue in V-shaped conformation by terminal polylysine modifications, Mol. Pharmaceut., 2014, vol. 11, no. 11, pp. 4092–4099. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp5002685
Rerup, C. and Tarding, F., Streptozotocin- and alloxan-diabetes in mice, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 1969, vol. 7, pp. 89–96.
Thorend, B. and Waeber, G., Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the control of insulin secretion in the normal state and in NIDDM, Diabetes, 1993, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 1219–1225.
Ma, X., Guang, Y., and Hua, X., Glucagon-like peptide 1-potentiated insulin secretion and proliferation of pancreatic beta-cells, J. Diabetes, 2014, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 304–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12161
Morris, R., Development of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat, J. Neurosci. Methods, 1984, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 47–60.
Aleksandrova, I.Yu., Kuvichkin, B.B., Kashparov, I.A., et al., Increased level of beta-amyloid in the brain of bulbectomized mice, Biochemistry, (Moscow), 2004, vol. 69, no.2, pp. 176–180.
Deacon, C.F., Knudsen, L.B., Madsen, K., et al., Dipeptidyl peptidase IV resistant analogues of glucagon-like peptide-1 which have extended metabolic stability and improved biological activity, Diabetologia, 1998, vol. 41, pp. 271–278.
Green, B.D., Gault, V.A., O’Harte, F.P.M., and Flatt, P.R., Structurally modified analogues of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) as future antidiabetic agents, Curr. Pharmaceut. Design., 2004, vol. 10, pp. 3651–3662. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612043382774
Kozlov, D.G., Cheperegin, S.E., Sannikova, E.P., Gubaidullin, I.I., Klebanov, F.A., Chestukhina, G.G., Bulushova, N.V., Ryabichenko, V.V., Zalunin, I.A., Kotlova, E.K., Konstantinova, G.E., Pokrovskii, V.S., and Yarotskii, S.V., Fusion protein based on Wolinella succinogenes L-asparaginase, Escherichia coli strain– producer of the fusion protein (variants), and the method for producing the fusion protein exhibiting antitumor activity, RF Patent Nno. 2562166, Byull. Izobr., 2015, no. 25.
Sannikova, E.P., Bulushova, N.V., Cheperegin, S.E., et al., The modified heparin-binding L-asparaginase of Wolinella succinogenes,Mol. Biotechnol., 2016, vol. 58, nos. 8–9, pp. 528–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-016-9950-1
Schwarze, S.R., Ho, A., Vocero-Akbani, A., and Dowdy, S.F., In vivo transduction: delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse, Science, 1999, vol. 285, pp. 1569–1572.
Zou, L.L., Ma, J.L., Wang, T., et al., Cell-penetrating peptide-mediated therapeutic molecule delivery into the central nervous system, Curr. Neuropharmacol., 2013, vol. 11, pp. 197–208. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X11311020006
Zhang, D., Wang, J., and Xu, D., Cell-penetrating peptides as noninvasive transmembrane vectors for the development of novel multifunctional drug-delivery systems, J. Control. Release, 2016, vol. 229, pp. 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.03.020
Ma, C., Gao, M., Liu, W., et al., Intein-mediated expression and purification of an analog of glucagon-like peptide-1 in Escherichia coli,Protein Peptide Lett., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 1245–1250. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986610792231582
Gao, M., Tong, Y., Tian, H., et al., Recombinant production of mGLP-1 by coupling of refolding and intein-mediated self-cleavage (CRIS), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 96, pp. 1283–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4163-4
Jiang, A., Jin, W., Zhao, F., et al., Split Ssp DnaB mini-intein-mediated production of recombinant human glucagon-like peptide-1/7-36, Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 2015, vol. 62, no. 3, pp. 309–315. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1274
Doyle, M.E. and Egan, J.M., Mechanisms of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pancreas, Pharmacol. Ther., 2007, vol. 113, no. 3, pp. 546–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.11.007
Thorkildsen, C., Neve, S., Larsen, B.D., et al., Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist ZP10A increases insulin mRNA expression and prevents diabetic progression in db/db mice, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 2003, vol. 307, no. 2, pp. 490–496. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.051987
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (State Contract 14.N08.12.1038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Translated by I. Gordon
Abbreviations: API—active pharmaceutical ingredient; BBB—blood brain barrier; BE animals—bulbectomized animals; DF—drug formulation, DM2—diabetes mellitus type II; GLP-1—human glucagon-like peptide 1; HB peptide—heparin-binding peptide; HEB—hemato-encephalic barrier; OB—olfactory bubble; PBS—phosphate-buffered saline; PO animals—pseudo-operated animals; rmGLP-1—recombinant modified GLP-1; TGT—test for glucose tolerance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sannikova, E.P., Bulushova, N.V., Cheperegin, S.E. et al. Specific Activity of Recombinant Modified Human Glucagon-Like Peptide 1. Appl Biochem Microbiol 55, 722–732 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683819070068
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683819070068