Abstract
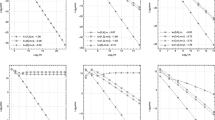
The weak Galerkin form of the finite element method, requiring only C0 basis function, is applied to the biharmonic equation. The computational procedure is thoroughly considered. Local orthogonal bases on triangulations are constructed using various sets of interpolation points with the Gram-Schmidt or Levenberg-Marquardt methods. Comparison and high-precision computations are carried out, and convergence rates are provided up to degree 11 for L2, 10 for H1, and 9 for H2, suggesting that the algorithm is useful for a variety of computations.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R.A., Fournier, J.J.F.: Sobolev Spaces. Pure and Applied Mathematics (Amsterdam), 2nd edn., vol. 140. Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam (2003)
Arad, M., Yakhot, A., Ben-Dor, G.: A highly accurate numerical solution of a biharmonic equation. Numer. Methods Partial Differential Equations 13(4), 375–391 (1997)
Berrut, J.-P., Trefethen, L.N.: Barycentric Lagrange interpolation. SIAM Rev. 46(3), 501–517 (electronic) (2004)
Burkardt, J.: The finite element basis for simplices in arbitrary dimensions (2011)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. Classics in Applied Mathematics, vol. 40, pp. xxviii+ 530. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), Philadelphia. Reprint of the 1978 original [North-Holland, Amsterdam; MR0520174 (58 #25001)] (2002)
Domínguez, V., Sayas, F.-J.: Algorithm 884: a simple Matlab implementation of the Argyris element. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 35(2), Art. 16, 11 (2009)
Dunavant, D.A.: High degree efficient symmetrical Gaussian quadrature rules for the triangle. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 21(6), 1129–1148 (1985)
Durán, A.J., Van Assche, W.: Orthogonal matrix polynomials and higher-order recurrence relations. Linear Algebra Appl. 219, 261–280 (1995)
Farouki, R.T., Goodman, T.N.T., Sauer, T.: Construction of orthogonal bases for polynomials in Bernstein form on triangular and simplex domains. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 20(4), 209–230 (2003)
Gautschi, W.: Orthogonal Polynomials: Computation and Approximation. Numerical Mathematics and Scientific Computation. Oxford University Press, New York (2004). Oxford Science Publications
Guan, Q., Gunzburger, M., Zhao, W.: Weak-Galerkin finite element methods for a second-order elliptic variational inequality. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 337, 677–688 (2018)
Hesthaven, J.S.: From electrostatics to almost optimal nodal sets for polynomial interpolation in a simplex. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35(2), 655–676 (1998)
Lyness, J.N., Jespersen, D.: Moderate degree symmetric quadrature rules for the triangle. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 15, 19–32 (1975)
Monk, P.: A mixed finite element method for the biharmonic equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 24(4), 737–749 (1987)
Moré, J.J.: The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm: implementation and theory. In: Watson, G.A. (ed.) Numerical Analysis: Proceedings of the Biennial Conference Held at Dundee, June 28–July 1, 1977, pp 105–116. Springer, Berlin (1978)
Mozolevski, I., Süli, E.: A priori error analysis for the hp-version of the discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for the biharmonic equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 3(4), 596–607 (2003)
Mu, L., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Ye, X.: A weak Galerkin mixed finite element method for biharmonic equations. In: Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations: Theory, Algorithms, and their Applications. Springer Proc. Math. Stat., vol. 45, pp 247–277. Springer, New York (2013)
Mu, L., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Ye, X.: A computational study of the weak Galerkin method for second-order elliptic equations. Numer. Algorithms 63(4), 753–777 (2013)
Mu, L., Wang, J., Ye, X.: Weak Galerkin finite element methods for the biharmonic equation on polytopal meshes. Numer. Methods Partial Differential Equations 30(3), 1003–1029 (2014)
Wang, C., Wang, J.: An efficient numerical scheme for the biharmonic equation by weak Galerkin finite element methods on polygonal or polyhedral meshes. Comput. Math. Appl. 68(12, part B), 2314–2330 (2014)
Wang, C., Wang, J.: A hybridized weak Galerkin finite element method for the biharmonic equation. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 12(2), 302–317 (2015)
Wang, J., Ye, X.: A weak Galerkin finite element method for second-order elliptic problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 241, 103–115 (2013)
Wang, C., Wang, J.: Weak Galerkin finite element methods for elliptic PDEs. Scientia Sinica Mathematica 45(7), 1061–1092 (2015)
Zhang, S.: On the full C1 − Qk finite element spaces on rectangles and cuboids. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2(6), 701–721 (2010)
Funding
John Burkardt was supported in part by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research grant FA9550-15-1-0001. Max Gunzburger was supported in part by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research grant FA9550-15-1-0001. Wenju Zhao was supported in part by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research grant FA9550-15-1-0001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burkardt, J., Gunzburger, M. & Zhao, W. High-precision computation of the weak Galerkin methods for the fourth-order problem. Numer Algor 84, 181–205 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-019-00751-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-019-00751-5