Abstract
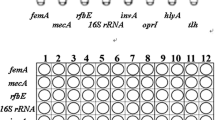
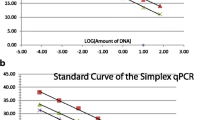
Rapid and sensitive detection techniques for foodborne pathogens are important to the food industry. However, traditional detection methods rely on bacterial culture in combination with biochemical tests, a process that typically takes 4–7 days to complete. In this study, we described a high-flux polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for simultaneous detection of nine targeted genes (rfbE, stx1, stx2, invA, oprI, tlh, trh, tdh, and hlyA) with multiplex strains. The designed primers were highly specific for their respective target gene fragments. As the selected primers follow the principles of similar melting and annealing temperature, all the targeted genes could be detected for one strain with the same PCR program. Combining with 96-well PCR plate, by adding a single different gene to each well in each row, both the ATCC strains (E. coli, Salmonella spp., V. parahaemolyticus, L. monocytogenes, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus) and the clinical strains (E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus) were simultaneously detected to carry their specific and virulence genes. Therefore, using 96-well PCR plate for PCR amplification might be applied to high-flux sequencing of specific and virulence genes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcentire J (2013) Foodborne disease: the global movement of food and people. Infect Dis Clin N Am 27:687–693
Chen DQ, Yang L, Peters BM et al (2019) Complete sequence of a novel multidrug-resistant pseudomonas putida strain carrying two copies of qnrVC6. Microb Drug Resist 25:1–7
Zhao XH, Yu ZX, Xu ZB (2018) Study the features of 57 confirmed CRISPR Loci in 38 strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 9:1591
Wen SX, Feng DH, Lu ZR et al (2018) Microbial infection pattern, pathogenic features and resistance mechanism of carbapenem-resistant Gram negative bacilli during long-term hospitalization. Microb Pathogenesis 117:356–360
Wu Q, Ye Y, Li F et al (2016) Prevalence and genetic characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in drinking water in Guangdong Province of China. LWT Food Sci Technol 69:24–31
Wang F, Jiang L, Yang Q et al (2011) Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of major foodborne pathogens in imported seafood. J Food Prot 74:1451–1461
Chao G, Zhou X, Jiao X et al (2007) Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of foodborne pathogens isolated from food products in China. Foodborne Pathog Dis 4:277–284
Newell DG, Koopmans M, Verhoef L et al (2010) Food-borne diseases—the challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int J Food Microbiol 139(Suppl 1):S3–15
Liu JY, Yang L, Hou YC et al (2018) Transcriptomics study on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm under low concentration of ampicillin. Front Microbiol 9:2413
Miao J, Liang YR, Chen LQ et al (2017) Formation and development of Staphylococcus biofilm: with focus on food safety. J Food Saf 37:e12358
Bao XR, Jia XY, Chen LQ et al (2017) Effect of polymyxin resistance (pmr) on biofilm formation of Cronobacter sakazakii. Microb Pathogenesis 106:16–19
Xu ZB, Liang YR, Lin SQ et al (2016) Crystal violet and XTT assays on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm quantification. Curr Microbiol 73:474–482
Xue J, Zhang W (2013) Understanding China's food safety problem: an analysis of 2387 incidents of acute foodborne illness. Food Control 30:311–317
Liu LY, Xu RR, Li L et al (2018) Correlation and in vitro mechanism of bactericidal activity on E. coli with whey protein isolate during ultrasonic treatment. Microb Pathogenesis 115:154–158
Liu LY, Lu ZR, Li L et al (2018) Physical relation and mechanism of ultrasonic bactericidal activity on pathogenic E. coli with WPI. Microb Pathogenesis 117:73–79
Liu JY, Li L, Zhou LZ et al (2018) Effect of ultrasonic field on the enzyme activities and ion balance of potential pathogen Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Pathogenesis 119:216–220
Jia XY, Hua JJ, Liu L et al (2018) Phenotypic characterization of pathogenic Cronobacter spp. strains. Microb Pathogenesis 121:232–237
Xu ZB, Xu XY, Qi D et al (2017) Effect of aminoglycosides on the pathogenic characteristics of microbiology. Microb Pathogenesis 113:357–364
Xu ZB, Hou YC, Peters BM et al (2016) Chromogenic media for MRSA diagnostics. Mol Biol Rep 43:1205–1212
Zhao X, Lin CW, Wang J et al (2014) Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:297–312
Zhao XH, Li M, Xu ZB (2018) Detection of foodborne pathogens by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Front Microbiol 9:1236
Miao J, Wang WX, Xu WY et al (2018) The fingerprint mapping and genotyping systems application on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb Pathogenesis 125:246–251
Miao J, Chen LQ, Wang JW et al (2017) Current methodologies on genotyping for nosocomial pathogen methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Microb Pathogenesis 107:17–28
Bao XR, Yang L, Chen LQ et al (2017) Analysis on pathogenic and virulent characteristics of the Cronobacter sakazakii strain BAA-894 by whole genome sequencing and its demonstration in basic biology science. Microb Pathogenesis 109:280–286
Bao XR, Yang L, Chen LQ et al (2017) Virulent and pathogenic features on the Cronobacter sakazakii polymyxin resistant pmr mutant strain s-3. Microb Pathogenesis 110:359–364
Lin SQ, Yang L, Chen G et al (2017) Pathogenic features and characteristics of food borne pathogens biofilm: biomass, viability and matrix. Microb Pathogenesis 111:285–291
Xu ZB, Xie JH, Liu JY et al (2017) Whole-genome resequencing of Bacillus cereus and expression of genes functioning in sodium chloride stress. Microb Pathogenesis 104:248–253
Yu GC, Wen WR, Peters BM et al (2016) First report of novel genetic array aacA4-bla(IMP-25)-oxa30-catB3 and identification of novel metallo-beta-lactamase gene bla(IMP25): a Retrospective Study of antibiotic resistance surveillance on Psuedomonas aeruginosa in Guangzhou of South China, 2003–2007. Microb Pathogenesis 95:62–67
Xu ZB, Xie JH, Yang L et al (2018) Complete sequence of pCY-CTX, a plasmid carrying a phage-like region and an ISEcp1-mediated Tn2 element from Enterobacter cloacae. Microb Drug Resist 24:307–313
Desmarchelier PM, Bilge SS, Fegan N et al (1998) A PCR specific for Escherichia coli O157 based on the rfb locus encoding O157 lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol 36:1801–1804
Rahn K, De Grandis SA, Clarke RC et al (1992) Amplification of an invA gene sequence of Salmonella typhimurium by polymerase chain reaction as a specific method of detection of Salmonella. Mol Cell Probes 6:271–279
Matthijs S, Coorevits A, Gebrekidan TT et al (2013) Evaluation of oprI and oprL genes as molecular markers for the genus Pseudomonas and their use in studying the biodiversity of a small Belgian River. Res Microbiol 164:254–261
Rawool DB, Malik SV, Shakuntala I et al (2007) Detection of multiple virulence-associated genes in Listeria monocytogenes isolated from bovine mastitis cases. Int J Food Microbiol 113:201–207
Bej AK, Patterson DP, Brasher CW et al (1999) Detection of total and hemolysin-producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish using multiplex PCR amplification of tl, tdh and trh. J Microbiol Meth 36:215–225
Xu ZB, Li L, Shi L et al (2011) Class 1 integron in staphylococci. Mol Biol Rep 38:5261–5279
Xu Z, Li L, Shirtliff ME et al (2011) Resistance class 1 integron in clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in southern China, 2001–2006. Clin Microbiol Infec 17:714–718
Xu ZB, Li L, Shirtliff ME et al (2010) First report of class 2 integron in clinical Enterococcus faecalis and class 1 integron in Enterococcus faecium in South China. Diagn Micr Infect Dis 68:315–317
Xu ZB, Li L, Shirtliff ME et al (2009) Occurrence and characteristics of Class 1 and 2 integrons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from patients in Southern China. J Clin Microbiol 47:230–234
Xu ZB, Shi L, Alam MJ et al (2008) Integron-bearing methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in South China, 2001–2004. Fems Microbiol Lett 278:223–230
Xu ZB, Li L, Alam MJ et al (2008) First confirmation of integron-bearing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Microbiol 57:264–268
Xu Z, Shi L, Zhang C et al (2007) Nosocomial infection caused by class 1 integron-carrying Staphylococcus aureus in a hospital in South China. Clin Microbiol Infec 13:980–984
Deng Y, Liu JY, Peters BM et al (2015) Antimicrobial resistance investigation on Staphylococcus strains in a local hospital in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2010. Microb Drug Resist 21:102–104
Liu JY, Chen DQ, Peters BM et al (2016) Staphylococcal chromosomal cassettes mec (SCCmec): a mobile genetic element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb Pathogenesis 101:56–67
Miao J, Peters BM, Li L et al (2016) Evaluation of Eric-Pcr for fingerprinting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Basic Clin Pharmacol 118:33–33
Miao J, Chen LQ, Wang JW et al (2017) Evaluation and application of molecular genotyping on nosocomial pathogen-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Guangzhou representative of Southern China. Microb Pathogenesis 107:397–403
Xu ZB, Xie JH, Peters BM et al (2017) Longitudinal surveillance on antibiogram of important Gram-positive pathogens in Southern China, 2001–2015. Microb Pathogenesis 103:80–86
Xie JH, Yang L, Peters BM et al (2017) A 16-year retrospective surveillance report on the pathogenic features and antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from FAHJU in Guangzhou representative of Southern China. Microb Pathogenesis 110:37–41
Xie JH, Peters BM, Li B et al (2017) Clinical features and antimicrobial resistance profiles of important Enterobacteriaceae pathogens in Guangzhou representative of Southern China, 2001–2015. Microb Pathogenesis 107:206–211
Xu ZB, Li L, Chu J et al (2012) Development and application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays on rapid detection of various types of Staphylococci strains. Food Res Int 47:166–173
Wang L, Li Y, Chu J et al (2012) Development and application of a simple loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes strains. Mol Biol Rep 39:445–449
Zhao XH, Wang L, Li YM et al (2011) Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. World J Microb Biot 27:181–184
Xu ZB, Li L, Zhao XH et al (2011) Development and application of a novel multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for rapid detection of various types of staphylococci strains. Afr J Microbiol Res 5:1869–1873
Wang L, Zhao XH, Chu J et al (2011) Application of an improved loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from various seafood samples. Afr J Microbiol Res 5:5765–5771
Zhao XH, Wang L, Chu J et al (2010) Rapid detection of vibrio parahaemolyticus strains and virulent factors by loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays. Food Sci Biotechnol 19:1191–1197
Zhao XH, Wang L, Chu J et al (2010) Development and application of a rapid and simple loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for food-borne salmonella detection. Food Sci Biotechnol 19:1655–1659
Zhao XH, Li YM, Wang L et al (2010) Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection Escherichia coli O157 strains from food samples. Mol Biol Rep 37:2183–2188
Xu ZB, Hou YC, Qin D et al (2016) Evaluation of current methodologies for rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Basic Clin Pharmacol 118:33–33
Ferrario C, Lugli GA, Ossiprandi MC et al (2017) Next generation sequencing-based multigene panel for high throughput detection of food-borne pathogens. Int J Food Microbiol 256:20–29
Liu JY, Zhou R, Li L et al (2017) Viable but non-culturable state and toxin gene expression of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli 0157 under cryopreservation. Res Microbiol 168:188–193
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (no. 2016YFD0400203), YangFan Innovative and Entrepreneurial Research Team Project (No. 2014YT02S029), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD04012021), Guangdong Special Support Program (2016TQ03N682), Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (201710010061), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Dr. Zhenbo Xu, D2191310), Collaborative Grant with AEIC (KEO-2019-0624-001-1), the 111 Project (B17018), and Guangdong Province Key Laboratory for Green Processing of Natural Products and Product Safety (KL-2018-05, KL-2018-14, KL-2018-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Yi Liang was employed by the company Guangdong Zhongqing Font Biochemical Science and Technology Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Qiu, Y., Ye, C. et al. High-flux simultaneous screening of common foodborne pathogens and their virulent factors . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 693–700 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02267-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02267-7