Abstract
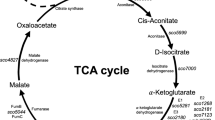
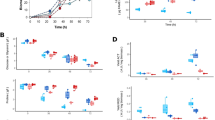
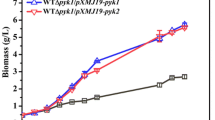
The phosphoenolpyruvate-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node is a major branch within the central carbon metabolism and acts as a connection point between glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the TCA cycle. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, malic enzymes, and pyruvate kinase, among others, are enzymes included in this node. We determined the mRNA levels and specific activity profiles of some of these genes and enzymes in Streptomyces coelicolor M-145. The results obtained in the presence of glucose demonstrated that all genes studied of the phosphoenolpyruvate-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node were expressed, although at different levels, with 10- to 100-fold differences. SCO3127 (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene) and SCO5261 (NADP+-dependent malic enzyme gene) showed the highest expression in the rapid growth phase, and the mRNA levels corresponding to SCO5896 (phosphoenolpyruvate-utilizing enzyme gene), and SCO0546 (pyruvate carboxylase gene) increased 5- to 10-fold towards the stationary phase. In casamino acids, in general mRNA levels of S. coelicolor were lower than in glucose, however, results showed greater mRNA expression of SCO4979 (PEP carboxykinase), SCO0208 (pyruvate phosphate dikinase gene), and SCO5261 (NADP+-dependent malic enzyme). These results suggest that PEP carboxylase (SCO3127) is an important enzyme during glucose catabolism and oxaloacetate replenishment. On the other hand, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, pyruvate phosphate dikinase, and NADP+-malic enzyme could have an important role in gluconeogenesis in S. coelicolor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeño-Tárraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O'Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bramwell H, Nimmo HG, Hunter IS, Coggins JR (1993) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): purification of the enzyme, cloning of the ppc gene and over-expression of the protein in a streptomycete. Biochem J 293(Pt 1):131–136
Brewster NK, Val DL, Walker ME, Wallace JC (1994) Regulation of pyruvate carboxylase isozyme (PYC1, PYC2) gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae during fermentative and nonfermentative growth. Arch Biochem Biophys 311:62–71
Bustin SA (2004) Data analysis and interpretation. In: Tsigelny IF (ed) A-Z of quantitative PCR. International University Line, La Jolla, pp 451–457
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622
Flores ME, Sánchez S (1985) Nitrogen regulation of erythromycin formation in Streptomyces erythreus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 26:191–194
Goldie H, Medina V (1990) Physical and genetic analysis of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (pckA) locus from Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet 220:191–196
Gourdon P, Baucher MF, Lindley ND, Guyonvarch A (2000) Cloning of the malic enzyme gene from Corynebacterium glutamicum and role of the enzyme in lactate metabolism. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2981–2987
Hiltner JK, Hunter IS, Hoskisson PA (2015) Tailoring specialized metabolite production in streptomyces. Adv Appl Microbiol 91:237–255
Ishigaki Y, Akanuma G, Yoshida M, Horinouchi S, Kosono S, Ohnishi Y (2017) Protein acetylation involved in streptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus. J Proteome 155:63–72
Jeong Y, Kim JN, Kim MW, Bucca G, Cho S, Yoon YJ, Kim BG, Roe JH, Kim SC, Smith CP, Cho BK (2016) The dynamic transcriptional and translational landscape of the model antibiotic producer Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nat Commun 7:11605
Jetten MSM, Sinskey AJ (1993) Characterization of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 111:183–188
Koffas MAG, Jung GY, Aon JC, Stephanopoulos G (2002) Effect of pyruvate carboxylase overexpression on the physiology of <em>Corynebacterium glutamicum</em>. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5422
Lee HJ, Kim H-J, Seo J, Na YA, Lee J, Lee J-Y, Kim P (2013) Estimation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylation mediated by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PCK) in engineered Escherichia coli having high ATP. Enzym Microb Technol 53:13–17
Li S, Wang W, Li X, Fan K, Yang K (2015) Genome-wide identification and characterization of reference genes with different transcript abundances for Streptomyces coelicolor. Sci Rep 5:15840
Liao G, Xie L, Li X, Cheng Z, Xie J (2014) Unexpected extensive lysine acetylation in the trump-card antibiotic producer Streptomyces roseosporus revealed by proteome-wide profiling. J Proteome 106:260–269
Machová I, Snašel J, Zimmermann M, Laubitz D, Plocinski P, Oehlmann W, Singh M, Dostál J, Sauer U, Pichová I (2014) Mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is regulated by redox mechanisms and interaction with thioredoxin. J Biol Chem 289:13066–13078
Menéndez J, Gancedo C (1998) Regulatory regions in the promoters of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PYC1 and PYC2 genes encoding isoenzymes of pyruvate carboxylase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 164:345–352
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Novotna J, Vohradsky J, Berndt P, Gramajo H, Langen H, Li XM, Minas W, Orsaria L, Roeder D, Thompson CJ (2003) Proteomic studies of diauxic lag in the differentiating prokaryote Streptomyces coelicolor reveal a regulatory network of stress-induced proteins and central metabolic enzymes. Mol Microbiol 48:1289–1303
Petersen S, de Graaf AA, Eggeling L, Möllney M, Wiechert W, Sahm H (2000) In vivo quantification of parallel and bidirectional fluxes in the anaplerosis of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biol Chem 275:35932–35941
Petersen S, Mack C, De Graaf AA, Riedel C, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H (2001) Metabolic consequences of altered phosphoenolpyruvatecarboxykinase activity in Corynebacterium glutamicum reveal anaplerotic regulation mechanisms in vivo. Metab Eng 3:344–361
Peters-Wendisch PG, Kreutzer C, Kalinowski J, Pátek M, Sahm H, Eikmanns BJ (1998) Pyruvate carboxylase from Corynebacterium glutamicum: characterization, expression and inactivation of the pyc gene. Microbiology 144:915–927
Rodriguez E, Navone L, Casati P, Gramajo H (2012) Impact of malic enzymes on antibiotic and triacylglycerol production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4571–4579
Sauer U, Eikmanns BJ (2005) The PEP-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node as the switch point for carbon flux distribution in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:765–794
Schilling B, Christensen D, Davis R, Sahu AK, Hu LI, Walker-Peddakotla A, Sorensen DJ, Zemaitaitis B, Gibson BW, Wolfe AJ (2015) Protein acetylation dynamics in response to carbon overflow in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 98:847–863
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Schniete JK, Cruz-Morales P, Selem-Mojica N, Fernández-Martínez LT, Hunter IS, Barona-Gómez F, Hoskisson PA (2018) Expanding primary metabolism helps generate the metabolic robustness to facilitate antibiotic biosynthesis in. MBio 9
Spížek J, Sigler K, Řezanka T, Demain A (2016) Biogenesis of antibiotics-viewing its history and glimpses of the future. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 61:347–358
Takahashi-Íñiguez T, Barrios-Hernández J, Rodríguez-Maldonado M, Flores ME (2018) Tricarboxylic acid cycle without malate dehydrogenase in Streptomyces coelicolor M-145. Arch Microbiol
Taylor BL, Routman S, Utter MF (1975) The control of the synthesis of pyruvate carboxylase in Pseudomonas citronellolis. Evience from double labeling studies. J Biol Chem 250:2376–2382
Thomas L, Hodgson DA, Wentzel A, Nieselt K, Ellingsen TE, Moore J, Morrissey ER, Legaie R, Wohlleben W, Rodríguez-García A, Martín JF, Burroughs NJ, Wellington EMH, Smith MCM (2012) Metabolic switches and adaptations deduced from the proteomes of Streptomyces coelicolor wild type and phoP mutant grown in batch culture. Mol Cell Proteomics 11:M111.013797
Valle F, Muñoz E, Ponce E, Flores N, Bolivar F (1996) Basic and applied aspects of metabolic diversity: the phosphoenolpyruvate node. J Ind Microbiol 17:458–462
Van Keulen GS, Dijkhuizen J, Lubbert (2011) Central carbon metabolic pathways in Streptomyces. In: P D (ed) Streptomyces: molecular biology and biotechnology. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, pp 105–124
Wada M, Sawada K, Ogura K, Shimono Y, Hagiwara T, Sugimoto M, Onuki A, Yokota A (2016) Effects of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase desensitization on glutamic acid production in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. J Biosci Bioeng 121:172–177
Weatherburn MW (1967) Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39:971–974
Yang C, Hua Q, Baba T, Mori H, Shimizu K (2003) Analysis of Escherichia coli anaplerotic metabolism and its regulation mechanisms from the metabolic responses to altered dilution rates and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase knockout. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:129–144
Acknowledgments
We thank Omar Rangel y Martha Cariño for technical support. This work was supported by Grant PAPIIT IN214116 (DGAPA-UNAM) and by CONACyT through scholarship 450646 (RLR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llamas-Ramírez, R., Takahashi-Iñiguez, T. & Flores, M.E. The phosphoenolpyruvate-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node genes and enzymes in Streptomyces coelicolor M-145. Int Microbiol 23, 429–439 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00116-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00116-x