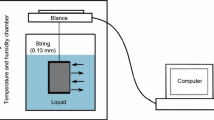
Abstract
This study presents the imbibition characteristics of mudstone extracting water from cement grout. The pore-size distribution characteristics of the weak-cemented mudstone were obtained by some pore characteristic tests. The water distribution and migration of mudstone during imbibition with cement grout of different water-cement (W-C) ratios were tested by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and surface deformation and water (from the cement grout) migration velocity (migration state) for mudstone samples with different initial water content were tested by digital photographic measurement (DPM) tests. The results showed that each T2 spectrum presented an isolated bimodal feature, and the left peak area was much larger than that of the right, indicating that the mudstone is mostly microporous, which confirms the pore characteristics of the mudstone obtained by scanning electron microscope, mercury intrusion porosimetry, and nitrogen adsorption desorption. The average slopes of the curves (signal amplitude and total area of the peak) increased with the increasing W-C ratios of grout, but the W-C ratio of 1 was a critical value for the imbibition capacity of mudstone extracting water from the cement grout. The deformation ranges of mudstone samples were very consistent with the ranges of spontaneous imbibition, and the deformation of the mudstone samples increased with the increasing imbibition time; the values of grout viscosities after the imbibition were all bigger than those of original cement grout. Moreover, the water migration velocities showed a trend of increasing and decreasing with the increase of W-C ratios of grout and the initial water content of mudstone samples at the same imbibition time.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso EE, Romero E, Hoffmann C, García-Escudero E (2005) Expansive bentonite–sand mixtures in cyclic controlled-suction drying and wetting. Eng Geol 81(3):213–226
Andriani G, Walsh N (2003) Fabric, porosity and water permeability of calcarenites from Apulia (SE Italy) used as building and ornamental stone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 62(1):77–84
Aydan Ö. (2003) The moisture migration characteristics of clay-bearing geo-materials and the variations of their physical and mechanical properties with water content. 2nd Asian Conference on Saturated Soils (UNSAT-ASIA 2003), 383-388
Aydan Ö, Ulusay R (2003) Geotechnical and environmental characteristics of man-made underground structures in Cappadocia, Turkey. Eng Geol 69(3/4):245–272
Aydan Ö, Ulusay R (2013) Geomechanical evaluation of derinkuyu antique underground city and its implications in geoengineering. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46:731–754
Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP (1951) The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J Am Chem Soc 73:373–380
Brodowski S, Amelung W, Haumaier L, Abetz C, Zech W (2005) Morphological and chemical properties of black carbon in physical soil fractions as revealed by scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Geoderma 128(1):116–129
Colas E, Mertz JD, Thomachot-Schneider C, Barbin V, Rassineux F (2011) Influence of the clay coating properties on the dilation behavior of sandstones. Appl Clay Sci 52(3):245–252
Dayakar P, Raman K, Venkat RKVB (2012) Study on permeation grouting using cement grout in sandy soil. IOSR J Mech Civil Eng 4(4):5–10
Eynatten HV, Tolosana-Delgado R, Karius V, Kai B, Caracciolo L (2016) Sediment generation in humid mediterranean setting: grain-size and source-rock control on sediment geochemistry and mineralogy (Sila Massif, Calabria). Sediment Geol 336:68–80
Ferro ND, Delmas P, Duwig C, Simonetti G, Morari F (2012) Coupling X-ray microtomography and mercury intrusion porosimetry to quantify aggregate structures of a cambisol under different fertilisation treatments. Soil Tillage Res 119:13–21
Fheed A, Krzyżak A, Świerczewska A (2018) Exploring a carbonate reef reservoir–nuclear magnetic resonance and computed microtomography confronted with narrow channel and fracture porosity. J Appl Geophys 151:343–358
Franzini M, Leoni L, Lezzerini M, Cardelli R (2007) Relationships between mineralogical composition, water absorption and hydric dilatation in the “Macigno” sandstones from Lunigiana (Massa, Tuscany). Eur J Mineral 19(1):113–123
Fu CF, Bloemendal J, Qiang XK, Hill MJ, An ZS (2015) Occurrence of greigite in the Pliocene sediments of Lake Qinghai, China, and its paleoenvironmental and paleomagnetic implications. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 16(5):1293–1306
Gao F, Wang QL, Deng HW, Zhang J, Tian WG, Ke B (2017a) Coupled effects of chemical environments and freeze–thaw cycles on damage characteristics of red sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76(4):1481–1490
Gao ZY, Hu QH, Jiang ZX (2017b) Investigate the spontaneous imbibition characteristics of marine and continental shales and their controlling factors. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs 49(6)
Ge HK, Yang L, Shen YH, Ren K, Meng FB, Ji WM, Wu S (2015) Experimental investigation of shale imbibition capacity and the factors influencing loss of hydraulic fracturing fluids. Pet Sci 12(4):636–650
Hassine MA, Beck K, Brunetaud X, Al-Mukhtar M (2018a) Strain measurements during capillary water infiltration in porous limestones. Constr Build Mater 175:439–447
Hassine MA, Beck K, Brunetaud X, Al-Mukhtar M (2018b) Use of electrical resistance measurement to assess the water saturation profile in porous limestones during capillary imbibition. Constr Build Mater 165:206–217
Hu MQ, Persoff P, Wang JSY (2001) Laboratory measurement of water imbibition into low-permeability welded tuff. J Hydrol 242(1-2):64–78
Hussain R, Mitchell J, Hammond PS, Sederman AJ, Johns ML (2013) Monitoring water transport in sandstone using flow propagators: a quantitative comparison of nuclear magnetic resonance measurement with lattice Boltzmann and pore network simulations. Adv Water Resour 60:64–74
Jin YH, Han LJ, Meng QB, Ma D, Wen SY, Wang S (2018a) Experimental investigation of the mechanical behaviors of grouted crushed coal rocks under uniaxial compression. Geomech Eng 16(3):273–284
Jin YH, Han LJ, Meng QB, Sanda S, Zang HZ, Feng B (2018b) Mechanical properties of grouted crushed coal with different grain size mixtures under triaxial compression. Adv Civil Eng 2018:1–13
Lai FP, Li ZP, Wei Q, Zhang TT, Zhao QH (2016) Experimental investigation of spontaneous imbibition in tight reservoir with nuclear magnetic resonance testing. Energy Fuel 30(11):8932–8940
Li JJ, Hitch M (2016) Characterization of the microstructure of mechanically-activated olivine using X-ray diffraction pattern analysis. Miner Eng 86:24–33
Ma D, Wang JJ, Li ZH (2019) Effect of particle erosion on mining-induced water inrush hazard of karst collapse pillar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(19):19719–19728
Meng MM, Ge HK, Ji WM, Wang XQ (2016a) Research on the auto-removal mechanism of shale aqueous phase trapping using low field nuclear magnetic resonance technique. J Pet Sci Eng 137:63–73
Meng QB, Liu HQ, Wang J, Pang ZX (2016b) Asymmetry characteristics of oil production by spontaneous imbibition from cores with two ends open. Transp Porous Media 113(3):735–751
Mohammed MH, Pusch R, Knutsson S (2015) Study of cement-grout penetration into fractures under static and oscillatory conditions. Tunnel Underground Space Technol Incorp Trenchless Technol Res 45:10–19
Nooruddin HA, Blunt MJ (2016) Analytical and numerical investigations of spontaneous imbibition in porous media. Water Resour Res 52(9):7284–7310
Ouahabi ME, Daoudi L, Fagel N (2014) Mineralogical and geotechnical characterization of clays from northern Morocco for their potential use in the ceramic industry. Clay Miner 49(1):35–51
Paz-Ferreiro J, Vázquez EV (2014) Pore size distribution patterns in tropical soils obtained by mercury intrusion porosimetry: the multifractal approach. Vadose Zone J 13(6):1–12
Pham QT, Vales F, Malinsky L, Nguyen MD, Gharbi H (2007) Effects of desaturation–resaturation on mudstone. Phys Chem Earth A/b/c 32(8-14):646–655
Rahardjo H, Aung KK, Leong EC, Rezaur RB (2004) Characteristics of residual soils in Singapore as formed by weathering. Eng Geol 73(1-2):157–169
Rokhforouz MR, Amiri HA, Akhlaghi (2017) Phase-field simulation of counter-current spontaneous imbibition in a fractured heterogeneous porous medium. Phys Fluids 29(6)
Saric-Coric M, Khayat KH, Tagnit-Hamou A (2003) Performance characteristics of cement grouts made with various combinations of high-range water reducer and cellulose-based viscosity modifier. Cem Concr Res 33(12):1999–2008
Sato A, Aydan Ö (2014) An X-ray CT imaging of water absorption process of soft rocks. Unsaturated Soils: Research and Applications-Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Unsaturated Soils (UNSAT 2014), 675-678
Suits LD, Sheahan TC, Chen LX, Miller GA, Kibbey TCG (2007) Rapid pseudo-static measurement of hysteretic capillary pressure-saturation relationships in unconsolidated porous media. Geotech Test J 30(6):474–483
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87(9-10):1051–1069
Wang Q, Wang SY, Sloan SW, Sheng DC, Pakzad R (2016) Experimental investigation of pressure grouting in sand. Soils Found 56(2):161–173
Wang XZ, Peng XL, Zhang SJ, Du ZW, Zeng FH (2018) Characteristics of oil distributions in forced and spontaneous imbibition of tight oil reservoir. Fuel 224:280–288
Wei X, Hattab M, Fleureau JM, Hu RL (2013) Micro-macro-experimental study of two clayey materials on drying paths. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72(3-4):495–508
Wu K, Ma MY, Hao DX (2012) Study on grouting pressure of splitting grouting based on cylindrical expansion considering large strain. J Dis Prevent Mitigat Eng 378-379:288–291
Wu JH, Yu JC, Wang ZF, Fu XH, Su WW (2018a) Experimental investigation on spontaneous imbibition of water in coal: implications for methane desorption and diffusion. Fuel 231:427–437
Wu JY, Feng MM, Mao XB, Xu JM, Zhang WL, Ni XY, Han GS (2018b) Particle size distribution of aggregate effects on mechanical and structural properties of cemented rockfill: experiments and modeling. Constr Build Mater 193:295–311
Wu JY, Feng MM, Yu BY, Han GS (2018c) The length of pre-existing fissures effects on the mechanical properties of cracked red sandstone and strength design in engineering. Ultrasonics 82(1):188–199
Wyrzykowski M, Kiesewetter R, Kaufmann J, Baumann R, Lura P (2014) Pore structure of mortars with cellulose ether additions-mercury intrusion porosimetry study. Cem Concr Compos 53(10):25–34
Xiao L, Li JR, Mao ZQ, Lu J, Yu HY, Guo HP, Li GR (2018) A method to determine nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) T2 cutoff based on normal distribution simulation in tight sandstone reservoirs. Fuel 225:472–482
Yang L, Ge HK, Shi X, Cheng YF, Zhang KH, Chen H, Shen YH, Zhang JJ, Qu XM (2016) The effect of microstructure and rock mineralogy on water imbibition characteristics in tight reservoirs. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 34:1461–1471
Yang R, Guo XS, Yi JZ, Fang ZX, Hu QH, He S (2017) Spontaneous imbibition of three leading shale formations in the Middle Yangtze Platform, South China. Energy Fuel 31(7):6903–6916
Zhang N, He MC, Liu PY (2012) Water vapor sorption and its mechanical effect on clay-bearing conglomerate selected from China. Eng Geol 141-142:1–8
Zhang ZH, Liu W, Cui Q, Han L, Yao HY (2018) Disintegration characteristics of moderately weathered mudstone in drawdown area of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Arab J Geosci 11(15)
Zheng G, Zhang XS, Diao Y, Lei HY (2016) Experimental study on grouting in underconsolidated soil to control excessive settlement. Nat Hazards 83(3):1683–1701
Funding
This work was supported by Outstanding Innovation Scholarship for Doctoral Candidate of CUMT (2019YCBS009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Han, L., Xu, C. et al. Experimental study of the spontaneous imbibition characteristics of mudstone extracting water from cement grout. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79, 1333–1347 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01663-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01663-3