Abstract
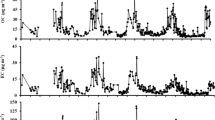
Haze-fog conditions over northern India are associated with visibility degradation and severe attenuation of solar radiation by airborne particles with various chemical compositions. PM2.5 samples have been collected in Delhi, India from December 2011 to November 2012 and analyzed for carbonaceous and inorganic species. PM10 measurements were made simultaneously such that PM10–2.5 could be estimated by difference. This study analyzes the temporal variation of PM2.5 and carbonaceous particles (CP), focusing on identification of the primary and secondary aerosol emissions, estimations of light extinction coefficient (bext) and the contributions by the major PM2.5 chemical components. The annual mean concentrations of PM2.5, organic carbon (OC), elemental carbon (EC) and PM10–2.5 were found to be 153.6 ± 59.8, 33.5 ± 15.9, 6.9 ± 3.9 and 91.1 ± 99.9 μg m−3, respectively. Total CP, secondary organic aerosols and major anions (e.g., SO4 2− and NO3 −) maximize during the post-monsoon and winter due to fossil fuel combustion and biomass burning. PM10–2.5 is more abundant during the pre-monsoon and post-monsoon. The OC/EC varies from 2.45 to 9.26 (mean of 5.18 ± 1.47), indicating the influence of multiple combustion sources. The bext exhibits highest values (910 ± 280 and 1221 ± 371 Mm−1) in post-monsoon and winter and lowest in monsoon (363 ± 110 and 457 ± 133 Mm−1) as estimated via the original and revised IMPROVE algorithms, respectively. Organic matter (OM =1.6 × OC) accounts for ~39 % and ~48 % of the bext, followed by (NH4)2SO4 (~21 % and ~24 %) and EC (~13 % and ~10 %), according to the original and revised algorithms, respectively. The bext estimates via the two IMPROVE versions are highly correlated (R2 = 0.95, root mean square error = 38 % and mean bias error = 28 %) and are strongly related to visibility impairment (r = −0.72), mostly associated with anthropogenic rather than natural PM contributions. Therefore, reduction of CP and precursor gas emissions represents an urgent opportunity for air quality improvement across Delhi.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae, M., Gelencsér, A.: Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos Chem Phys. 6, 3131–3148 (2006)
Badarinath, K.V.S., Kharol, S.K., Krishna Prasad, V., Reddi, E.U.B., Kambezidis, H.D., Kaskaoutis, D.G.: Influence of natural and anthropogenic activities on UV index variations–a study over tropical urban region using ground based observations and satellite data. J Atmos Chem. 59, 219–236 (2008)
Behera, S.N., Sharma, M.: Investigating the potential role of ammonia in ion chemistry of fine particulate matter formation for an urban environment. Sci Total Environ. 408, 3569–3575 (2010a)
Behera, S.N., Sharma, M.: Reconstructing primary and secondary components of PM2.5 compositions for an urban atmosphere. Aer SciTechn. 44, 983–992 (2010b)
Birch, M.E., Cary, R.A.: Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposures to particulate diesel exhaust. Aerosp Sci Technol. 25, 221–241 (1986)
Bisht, D.S., Dumka, U.C., Kaskaoutis, D.G., Pipal, A.S., Srivastava, A.K., Soni, V.K., Attri, S.D., Sateesh, M., Tiwari, S.: Carbonaceous aerosols and pollutants over Delhi urban environment: temporal evolution, source apportionment and radiative forcing. Sci Total Environ. 521–522, 431–445 (2015)
Bond, T.C., Bhardwaj, E., Dong, R., Jogani, R., Jung, S., Roden, C., Streets, D.G., Trautmann, N.M.: Historical emissions of black and organic carbon aerosol from energy related combustion, 1850–2000. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. 21, GB2018 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006GB002840
Bond, T.C., Doherty, S.J., Fahey, D.W., Forster, P.M., Berntsen, T., DeAngelo, B.J., Flanner, M.G., Ghan, S., Karcher, B., Koch, D., Kinne, S., Kondo, Y., Quinn, P.K., Sarofim, M.C., Schultz, M.G., Schulz, M., Venkataraman, C., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Bellouin, N., Guttikunda, S.K., Hopke, P.K., Jacobson, M.Z., Kaiser, J.W., Klimont, Z., Lohmann, U., Schwarz, J.P., Shindell, D., Storelvmo, T., Warren, S.G., Zender, C.S.: Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J Geophys Res. 118, 5380–5552 (2013)
Bougiatioti, A., Zarmpas, P., Koulouri, E., Antoniou, M., Theodosi, C., Kouvarakis, G., Saarikoski, S., Mäkelä, T., Hillamo, R., Mihalopoulos, N.: Organic, elemental and water-soluble organic carbon in size segregated aerosols, in the marine boundary layer of the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Environ. 64, 251–262 (2013)
Cao, J., Wang, Q.-Y., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Tie, X.-X., Shen, Z.-X., Wang, P., An, Z.-S.: Impacts of aerosol compositions on visibility impairment in Xi’an. China. Atmos. Environ. 59, 559–566, (2012).
Castro, L.M., Pio, C.A., Harrison, R.M., Smith, D.J.T.: Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos Environ. 33, 2771–2781 (1999)
Chen, Y., Zhi, G., Feng, Y., Fu, J., Feng, J., Sheng, G., Simoneit, B.R.T.: Measurements of emission factors for primary carbonaceous particles from residential raw-coal combustion in China. Geophys Res Lett. 33, (2006). doi:10.1029/2006GL026966
Chen, X., Lai, S., Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., Chen, D., Zheng, J., Zhong, L., Lee, S.-C., Chen, B.: Reconstructed light extinction coefficients of fine particulate matter in rural Guangzhou. Southern China Aer Air Qual Res. 16, 1981–1990 (2016)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Chen, L.-W.A., Arnott, W.P., Moosmüller, H., Fung, K.K.: Equivalence of elemental carbon by thermal/optical reflectance and transmittance with different temperature protocols. Environ Sci Technol. 38, 4414–4422 (2004)
Decesari, S., Facchini, M.C., Fuzzi, S., Tagliavini, E.: Characterization of water-soluble organic compounds in atmospheric aerosol: a new approach. J Geophys Res. 105, 1481–1489 (2000)
Dey, S., Girolamo, L.D., Van Donkelaar, A., Tripathi, S.N., Gupta, T., Mohan, M.: Variability of outdoor fine particulate (PM2.5) concentration in the Indian Subcontinent: A remote sensing approach. Remote Sens Environ. 127, 153–161 (2012)
Draxler, R.R., Rolph, G.D., HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Website (http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php). NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD (2016)
Dumka, U.C., Kaskaoutis, D.G., Srivastava, M.K., Devara, P.C.S.: Scattering and absorption properties of near-surface aerosol over Gangetic–Himalayan region: the role of boundary-layer dynamics and long-range transport. Atmos Chem Phys. 15, 1555–1572 (2015)
Feng, Y., Chen, Y., Guo, H., Zhi, G., Xiong, S., Li, J., Sheng, G., Fu, J.: Characteristics of organic carbon in PM2.5 samples in Shanghai, China. Atmos Res. 92, 434–442 (2009)
Foyo-Moreno, I., Alados, I., Antón, M., Fernández-Gálvez, J., Cazorla, A., Alados-Arboledas, L.: Estimating aerosol characteristics from solar irradiance measurements at an urban location in southeastern Spain. J Geophys Res. 119, 1845–1859 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JD020599
Ganguly, D., Rasch, P.J., Wang, H., Yoon, J.-H.: Climate response of the south Asian monsoon system to anthropogenic aerosols. J Geophys Res. 117, D13209 (2012). doi:10.1029/2012JD017508
Gautam, R., Hsu, N.C., Kafatos, M., Tsay, S.–.C.: Influences of winter haze on fog/low cloud over the Indo-Gangetic plains. J Geophys Res. 112, D05207 (2007). doi:10.1029/2005JD007036
Guinot, B., Cachier, H., Oikonomou, K.: Geochemical perspectives from a new aerosol chemical mass closure. Atmos Chem Phys. 7, 1657–1670 (2007)
Guttikunda, S.K., Calori, G.: A GIS based emissions inventory at 1 km × 1 km spatial resolution for air pollution analysis in Delhi. India Atmos Environ. 67, 101–111 (2013)
Hoyle, C.R., Boy, M., Donahue, N.M., Fry, J.L., Glasius, M., Guenther, A., et al.: A review of the anthropogenic influence on biogenic secondary organic aerosol. Atmos Chem Phys. 11, 321–343 (2011)
Huang, L.-K., Wang, G.-Z., Wang, K.: Physicochemical characteristics and long-range transportation of atmospheric particulates during a dust storm episode in Harbin. China Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue/China Environ Sci. 34, 1920–1926 (2014)
Hÿvarinen, A.-P., Raatikainen, T., Komppula, M., Mielonen, T., Sundström, A.-M., Brus, D., Panwar, T.S., Hooda, R.K., Sharma, V.P., de Leeuw, G., Lihavainen, H.: Effect of the summer monsoon on aerosols at two measurement stations in northern India – part 2: physical and optical properties. Atmos Chem Phys. 11, 8283–8294 (2011)
IMPROVE: “Spatial and Seasonal Patterns and Temporal Variability of Haze and Its Constituents in the United States,” Report V, ISSN 0737–5352-87, available from http://vista.cira.colostate.edu/improve/publications/reports/2011/PDF/IMPROVE_V_FullReport.pdf (2011)
Jimenez, J.L., Canagaratna, M.R., Donahue, N.M., Prevot, A.S.H., et al.: 2009. Evolution of organic aerosols in the atmosphere. Science. 326, 1525–1529 (2009)
Kamani, H., Ashrafi, S.D., Isazadeh, S., Jaafari, J., Hoseini, M., Mostafapour, F.K., Bazrafshan, E., Nazmara, S., Mahvi, A.H.: Heavy metal contamination in street dusts with various land uses in Zahedan. Iran Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 94(3), 382–386 (2015)
Kaskaoutis, D.G., Sinha, P.R., Vinoj, V., Kosmopoulos, P.G., Tripathi, S.N., Misra, A., Sharma, M., Singh, R.P.: Aerosol properties and radiative forcing over Kanpur during severe aerosol loading conditions. Atmos Environ. 79, 7–19 (2013)
Kaskaoutis, D.G., Kumar, S., Sharma, D., Singh, R.P., Kharol, S.K., Sharma, M., Singh, A.K., Singh, S., Singh, A., Singh, D.: Effects of crop residue burning on aerosol properties, plume characteristics and long-range transport over northern India. J Geophys Res. 119, 5424–5444 (2014). doi:10.1002/2013JD021357
Khalil, S.A., Shaffie, A.M.: Attenuation of the solar energy by aerosol particles: a review and case study. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 54, 363–375 (2016)
Komppula, M., Mielonen, T., Arola, A., Korhonen, K., Lihavainen, H., Hyvarinen, A.-P., Baars, H., Engelmann, R., Althausen, D., Ansmann, A., Müller, D., Panwar, T.S., Hooda, R.K., Sharma, V.P., Kerminen, V.-M., Lehtinen, K.E.J., Viisanen, Y.: One year of Raman-lidar measurements in Gual Pahari EUCAARI site close to New Delhi in India: seasonal characteristics of the aerosol vertical structure. Atmos Chem Phys. 12, 4513–4524 (2012)
Kumar, A., Sarin, M.M., Srinivas, B.: Aerosol iron solubility over bay of Bengal: role of anthropogenic sources and chemical processing. Mar Chem. 121, 167–175 (2010)
Kumar, R., Naja, M., Satheesh, S.K., Ojha, N., Joshi, H., Sarangi, T., Pant, P., Dumka, U.C., Hegde, P., Venkataramani, S.: Influences of the springtime northern Indian biomass burning over the central Himalayas. J Geophys Res. 116, D19302 (2011). doi:10.1029/2010JD015509
Li, H., Feng, J., Sheng, G., Lü, S., Fu, J., Peng, P., Ren, M.: The PCDD/F and PBDD/F pollution in the ambient atmosphere of shanghai. China Chemosphere. 70, 576–583 (2008)
Lodhi, N.K., Beegum, S.N., Singh, S., Kumar, K.: Aerosol climatology at Delhi in the western indo-Gangetic plain: microphysics, long-term trends, and source strengths. J Geophys Res. 118, 1361–1375 (2013). doi:10.1002/jgrd.50165
Lu, Z., Zhang, Q., Streets, D.G.: Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos Chem Phys. 11, 9839–9864 (2011)
Malm, W.C., Day, D.E.: Estimates of aerosol species scattering characteristics as a function of relative humidity. Atmos Environ. 35, 2845–2860 (2001)
Mantas, E., Remoundaki, E., Halari, I., Kassomenos, P., Theodosi, C., Hatzikioseyian, A., Mihalopoulos, N.: Mass closure and source apportionment of PM2.5 by Positive Matrix Factorization analysis in urban Mediterranean environment. Atmos Environ. 94, 154–163 (2014)
Misra, A., Tripathi, S.N., Kaul, D., Welton, E.: Study of MPLNET derived aerosol climatology over Kanpur, India, and validation of CALIPSO level 2 version 3 backscatter and extinction products. J Atmos Ocean Technol. 29, 1285–1294 (2012)
Nair, V.S., Solmon, F., Giorgi, F., et al.: Simulation of south Asian aerosols for regional climate studies. J Geophys Res. 117, D04209 (2012). doi:10.1029/2011JD016711
Novakov, T., Menon, S., Kirchstetter, T.W., Koch, D., Hansen, J.E.: Aerosol organic carbon to black carbon ratios: analysis of published data and implications for climate forcing. J Geophys Res. 110, D21205 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005JD005977
Panda, S., Sharma, S.K., Mhapatra, P.S., Panda, U., Rath, S., Mhapatra, M., Mandal, T.K., Das, T.: Organic and elemental carbon variation in PM2.5 over megacity Delhi and Bhubaneswar, a semi-urban coastal site in India. Nat Hazards. 80, 1709–1728 (2016)
Pandey, P., Khan, A.H., Verma, A.K., Singh, K.A., Mathur, N., Kisku, G.C., Barman, S.C.: Seasonal Trends of PM2.5 and PM10 in Ambient Air and Their Correlation in Ambient Air of Lucknow City, India. Bull Environ ContamToxicol. 88(2), 265–270 (2012)
Paraskevopoulou, D., Liakakou, E., Gerasopoulos, E., Theodosi, C., Mihalopoulos, N.: Long-term characterization of organic and elemental carbon in the PM2.5 fraction: the case of Athens, Greece. Atmos Chem Phys. 14, 13313–13325 (2014). doi:10.5194/acp-14-13313-2014
Pateraki, S., Asimakopoulos, D.N., Bougiatioti, A., Maggos, T., Vasilakos, C., Mihalopoulos, N.: Assessment of PM2.5 and PM1 chemical profile in a multiple-impacted Mediterranean urban area: origin, sources and meteorological dependence. Sci Total Environ. 479–480, 210–220 (2014)
Pio, C., Cerqueira, M., Harrison, R.M., Nunes, T., Mirante, F., Alves, C., Oliveira, C., de la Campa A, S., Artíñano, B., Matos, M.: OC/EC ratio observations in Europe: Re-thinking the approach for apportionment between primary and secondary organic carbon. Atmos Environ. 45, 6121–6132 (2011)
Pipal, A.S., Kulshrestha, A., Taneja, A.: Characterization and morphological analysis of airborne PM2.5 and PM10 in Agra located in North Central part of India. Atmos Environ. 45, 3621–3630 (2011)
Pitchford, M.L., Malm, W.C., Schichtel, B.A., Kumar, N.K., Lowenthal, D.H., Hand, J.L.: Revised algorithm for estimating light extinction from IMPROVE particle speciation data. J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 57, 1326–1336 (2007)
Putaud, J.-P., Van Dingenen, R., Alastuey, A., Bauer, H., Birmili, W., et al.: A European aerosol phenomenology - 3: physical and chemical characteristics of particulate matter from 60 rural, urban, and kerbside sites across Europe. Atmos Environ. 44, 1308–1320 (2010)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M.: Day-night variability of EC, OC, WSOC and inorganic ions in urban environment of Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications to secondary aerosol formation. Atmos Environ. 45, 460–468 (2011)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M.: Atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols from indo-Gangetic plain and central Himalaya: impact of anthropogenic sources. J Environ Manag. 148, 153–163 (2015)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M., Hegde, P.: Atmospheric abundances of primary and secondary carbonaceous species at two high-altitude sites in India: sources and temporal variability. Atmos Environ. 4, 6785–6796 (2008)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M., Tripathi, S.N.: A 1 year record of carbonaceous aerosols from an urban site in the indo-Gangetic plain: characterization, sources, and temporal variability. J Geophys Res. 11, D24313 (2010a). doi:10.1029/2010JD014188
Ram, K., M.M., S., Hegde, P.: Long-term record of aerosol optical properties and chemical composition from a high-altitude site (Manora Peak) in Central Himalaya. Atmos Chem Phys. 10, 11791–11803 (2010b)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M., Tripathi, S.N.: Temporal trends in atmospheric PM2.5, PM10, elemental carbon, organic carbon, water-soluble organic carbon, and optical properties: Impact of biomass burning emissions in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 686–695 (2012)
Rastogi, N., Singh, A., Singh, D., Sarin, M.M.: Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 at a source region of biomassburning emissions: Evidence for secondary aerosol formation. Environ Pollut. 184, 563–569 (2014)
Reddington, C.L., Butt, E.W., Ridley, D.A., Artaxo, P., Morgan, W.T., Coe, H., Spracklen, D.V.: Air quality and human health improvements from reductions in deforestation-related fire in Brazil. Nat Geosci. 8, 768–773 (2015). doi:10.1038/NGEO2535
Rengarajan, R., Sarin, M.M., Sudheer, A.K.: Carbonaceous and inorganic species in atmospheric aerosols during wintertime over urban and high-altitude sites in North India. J Geophys Res. 112, D21307 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JD008150
Robinson, A.L., Donahue, N.M., Shrivastava, M.K., Weitkamp, E.A., Sage, A.M., Grieshop, A.P., Lane, T.E., Pierce, J.R., Pandis, S.N.: Rethinking organic aerosols: Semivolatile emissions and photochemical aging. Science. 315, 1259–1262 (2007)
Saxena, M., Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Singh, S., Saud, T.: Source apportionment of particulates by receptor models over bay of Bengal during ICARB campaign. Atmos Poll Res. 5, 729–740 (2014)
Sharma, M., Maloo, S.: Assessment of ambient air PM10 and PM2.5 and characterization of PM10 in the city of Kanpur, India. Atmos Environ. 39, 6015–6026 (2005)
Sharma, S.K., Mandal, T.K., Saxena, M., Rashmi, R., Sharma, A., Datta, A., Saud, T.: Variation of OC, EC, WSIC and trace metals of PM10 in Delhi. India J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys. 113, 10–22 (2014)
Sharma, S.K., Sharma, A., Saxena, M., Choudhary, N., Masiwal, R., Mandal, T.K., Sharma, C.: Chemical characterization and source apportionment of aerosol at an urban area of Central Delhi. India Atmos Pollut Res. 7, 110–121 (2016)
Shen, G., Xue, M., Yuan, S., Zhang, J., Zhao, Q., Li, B., Wu, H.: Ding, a: chemical compositions and reconstructed light extinction coefficients of particulate matter in a mega-city in the western Yangtze River Delta. China Atmos Environ. 83, 14–20 (2014)
Singh, A., Rajput, P., Sharma, D., Sarin, M.M., Singh, D.: Black carbon and elemental carbon from postharvest agricultural-waste burning emissions in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Adv Meteorol. ID 179301 (2014). doi:10.1155/2014/179301
Smith, D.J.T., Harrison, R.M., Luhana, L., Pio, C.A., Castro, L.M., Tariq, M.N., Harat, S., Quraishi, T.: Concentration of particulate airborne poly-aromatic hydrocarbons and metals collected in Lahore. Pakistan Atmos Environ. 30, 4031–4040 (2007)
Srinivas, B., Sarin, M.M.: PM2.5, EC and OC in atmospheric outflow from the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Temporal variability and aerosol organic carbon-to-organic mass conversion factor. Sci Total Environ. 487, 196–205 (2014)
Srivastava, A.K., Singh, S., Tiwari, S., Kanawade, V.P., Bisht, D.S.: Variationbetween near-surface and columnar aerosol characteristics during winters andsummers at a station in the Indo-Gangetic Basin. J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys. 77, 57–66 (2012)
Streets, D.G., Bond, T.C., Lee, T., Jang, C.: On the future of carbonaceous aerosol emissions. J Geophys Res. 109, D24212 (2004). doi:10.1029/2004JD004902
Tao, J., Zhang, L., Ho, K., Zheng, R., Lin, Z., Zhang, Z., Lin, M., Cao, J., Liu, S., Wang, G.: Impact of PM2.5 chemical compositions on aerosol light scattering in Guangzhoue the largest megacity in South China. Atmos Res. 135–136, 48–58 (2014)
Taylor, S.R., McLennan, S.M.: The continental crust: its composition and evolution, p. 312p. Blackwell Scientific Publication, Carlton (1985)
Tiwari, S., Srivastava, A.K., Bisht, D.S., Bano, T., Singh, S., Behura, S., Srivastava, M.K., Chate, D.M., Padmanabhamurty, B.: Black Carbon and Chemical characteristics of PM10 and PM2.5 at an urban site of North India. Intern J Atmos Chem. 62, 3193–3209 (2009)
Tiwari, S., Chate, D.M., Srivastava, M.K., Safai, P.D., Srivastava, A.K., Bisht, D.S., Padmanabhamurty, B.: Statistical evaluation of PM10 and distribution of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 in ambient air due to extreme fireworks episodes (Diwali festivals) in megacity Delhi. Nat Hazards. 61, 521–531 (2012)
Tiwari, S., Srivastava, A.K., Bisht, D.S., Safai, P.D.: Assessment of carbonaceousaerosol over Delhi in the Indo-Gangetic Basin: characterization, sources andtemporal variability. Nat Hazards. 65, 1745–1764 (2013a)
Tiwari, S., Srivastava, A.K., Bisht, D.S., Parmita, P., Srivastava, M.K., Attri, S.D.: Diurnal and seasonal variations of black carbon and PM2.5 over New Delhi, India: Influence of meteorology. Atmos Res. 125–126, 50–62 (2013b)
Tiwari, S., Bisht, D.S., Srivastava, A.K., Pipal, A.S., Taneja, A., Srivastava, M.K., Attri, S.D.: Variability in atmospheric particulates and meteorological effects on its mass concentrations over Delhi. India Atmos Res. 145-146, 45–56 (2014)
Tiwari, S., Pipal, A.S., Hopke, P.K., Bisht, D.S., Srivastava, A.K., Tiwari, S., Saxena, P.N., Khan, A.H., Pervez, S.: Study of the carbonaceous aerosol and morphological analysis of fine particles along with their mixing state in Delhi, India: a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 22, 10744 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4272-6
Tiwari, S., Dumka, U.C., Kaskaoutis, D.G., Ram, K., Panicker, A.S., Srivastava, M.K., Tiwari, S., Attri, S.D., Soni, V.K., Pandey, A.K.: Aerosol chemical characterization and role of carbonaceous aerosol on radiative effect over Varanasi in central Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos Environ. 125, 437–449 (2016)
Turpin, B.J., Huntzicker, J.J.: Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantification of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos Environ. 23, 3527–3544 (1995)
Vadrevu, K.P., Ellicott, E., Giglio, L., Badarinath, K.V.S., Vermote, E., Justice, C., Lau, W.K.M.: Vegetation fires in the Himalayan region—aerosol load, black carbon emissions and smoke plume heights. Atmos Environ. 47, 241–251 (2012)
Valenzuela, A., Olmo, F.J., Lyamani, H., Antón, M., Titos, G., Cazorla, A., Alados-Arboledas, L.: Aerosol scattering and absorption Angström exponents as indicators of dust and dust-free days over Granada (Spain). Atmos Res. 154, 1–13 (2015)
Venkataraman, C., Habib, G., Eiguren Fernandez, A., Miguel, A.H., Friedlander, S.K.: Residential biofuels in South Asia: carbonaceous aerosol emissions and climate impacts. Science. 307, 1454–1456 (2005)
Viana, M., Maenhaut, W., Ten Brink, H.M., Chi, X., Weijers, E., Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Mikuska., P., Vecera, Z.: Comparative analysis of organic and elemental carbon concentrations in carbonaceous aerosols in three European cities. Atmos Environ. 41, 5972–5983 (2007)
Wang, B., Shi, G.: Long-term trends of atmospheric absorbing and scattering optical depths over China region estimated from the routine observation data of surface solar irradiances. J Geophys Res. 115, D00K28 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JD013239
Wang, X., Ding, X., Fu, X., He, Q., Wang, S., Bernard, F., Zhao, X., Wu, D.: Aerosol scattering coefficients and major chemical compositions of fine particles observed at a rural site in the central Pearl River Delta. South China J Environ Sci. 24, 72–77 (2012)
Wang, L., Salazar, G.A., Gong, W., Peng, S., Zou, L., Lin, A.: An improved method for estimating the Ångstrom turbidity coefficient β in Central China during 1961-2010. Energy. 81, 67–73 (2015)
Zhang, F., Chen, J., Qiu, T., Yin, L., Chen, X., Yu, J.: Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 during a Typical Haze Episode in Xiamen, China. Atmos Clim Sci. 3, 427–439 (2013a)
Zhang, G., Bi, X., Chan, L., Wang, X., Sheng, G., Fu, J.: Size-segregated chemical characteristics of aerosol during haze in an urban area of the Pearl River Delta region. China Urban Clim. 4, 74–84 (2013b)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director, IITM Pune and Ministry of Earth Science, Government of India for their constant encouragement and support of the research work. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for the provision of the HYSPLIT transport and dispersion model and/or READY website (http://www.ready.noaa.gov) used in this study. UCD and DGK greatly appreciate the fruitful communications and comments provided by Prof. Nikos Mihalopoulos. Authors would like to thanks the editor in Chief Prof. E. Atlas and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions which helped us to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumka, U., Tiwari, S., Kaskaoutis, D. et al. Assessment of PM2.5 chemical compositions in Delhi: primary vs secondary emissions and contribution to light extinction coefficient and visibility degradation. J Atmos Chem 74, 423–450 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9350-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9350-8