Abstract
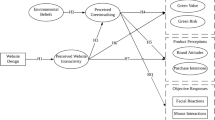
This study introduces a user adoption model for smart TVs and investigates how the components of the coolness concept contribute to user adoption in order to clarify the social diffusion of smart TVs. The results of a confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling of a sample of more than 1100 people indicate that all components of coolness except subcultural appeal lead to users’ intentions to utilize smart TVs based on their positive attitude toward them. The results of this study validate the role of the components of the coolness concept as effective and appropriate motivations for the intention to use. The paper also presents the implications of the results and the accompanying limitations of the study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, I., Khusro, S., Naeem, M.: A review of smart TV: Past, present, and future. In: 2017 International Conference on Open Source Systems & Technologies (ICOSST), pp. 35–41. IEEE (2017, December)
Anderson, J.C., Gerbing, D.W.: Structural equation modeling in practice: a review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 103(3), 411–423 (1988)
Bloch, P.H., Brunel, F.F., Arnold, T.J.: Individual differences in the centrality of visual product aesthetics: concept and measurement. J. Consum. Res. 29(4), 551–565 (2003)
Bodine, K., Gemperle, F.: Effects of functionality on perceived comfort of wearables. In: Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers, p. 57. IEEE Computer Society (2003, October)
Byrne, B.M.: Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming. Routledge, London (2016)
Chan, M., Estève, D., Escriba, C., Campo, E.: A review of smart homes—present state and future challenges. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 91(1), 55–81 (2008)
Colborne, G.: Simple and Usable Web, Mobile, and Interaction Design. New Riders, San Francisco (2017)
Davcik, N.S.: The use and misuse of structural equation modeling in management research: a review and critique. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 11(1), 47–81 (2014)
Davis, F.D.: Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 13(3), 319–340 (1989)
Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R.: User acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of two theoretical models. Manag. Sci. 35(8), 982–1003 (1989)
Digital Times: Smart TV in China and Korea (2017). Retrieved from http://www.dt.co.kr/contents.html?article_no=2017033002100832816001
Filieri, R., Chen, W., Lal Dey, B.: The importance of enhancing, maintaining and saving face in smartphone repurchase intentions of Chinese early adopters: an exploratory study. Inf. Technol. People 30(3), 629–652 (2017)
Franke, N., Schreier, M.: Product uniqueness as a driver of customer utility in mass customization. Mark. Lett. 19(2), 93–107 (2008)
Gerbing, D.W., Hamilton, J.G.: Viability of exploratory factor analysis as a precursor to confirmatory factor analysis. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 3(1), 62–72 (1996)
Hassenzahl, M., Tractinsky, N.: User experience—a research agenda. Behav. Inf. Technol. 25(2), 91–97 (2006)
Holbert, R.L., Stephenson, M.T.: Structural equation modeling in the communication sciences, 1995–2000. Hum. Commun. Res. 28(4), 531–551 (2002)
Im, S., Bhat, S., Lee, Y.: Consumer perceptions of product creativity, coolness, value and attitude. J. Bus. Res. 68(1), 166–172 (2015)
Keil, F.C.: Concepts, Kinds, and Cognitive Development. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Kettanurak, V.N., Ramamurthy, K., Haseman, W.D.: User attitude as a mediator of learning performance improvement in an interactive multimedia environment: an empirical investigation of the degree of interactivity and learning styles. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 54(4), 541–583 (2001)
Kim, K.J.: Round or square? How screen shape affects utilitarian and hedonic motivations for smartwatch adoption. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 19(12), 733–739 (2016)
Kim, K.J., Shin, D.H.: An acceptance model for smart watches: implications for the adoption of future wearable technology. Internet Res. 25(4), 527–541 (2015)
Kim, K.J., Shin, D.H., Park, E.: Can coolness predict technology adoption? Effects of perceived coolness on user acceptance of smartphones with curved screens. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 18(9), 528–533 (2015)
Kim, M., Park, J.: Demand forecasting and strategies for the successfully deployment of the smart TV in Korea. In: 2011 13th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), pp. 1475–1478. IEEE (2011, February)
Kim, S.Y., Lee, S.H., Hwang, H.S.: A study of the factors affecting user acceptance of smart TVs. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 14(4), 1652–1662 (2013)
Kim, K.J., Sundar, S.S.: Does screen size matter for smartphones? Utilitarian and hedonic effects of screen size on smartphone adoption. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 17(7), 466–473 (2014)
Kline, R.B.: Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. Guilford Publications, New York (2015)
Korunka, C., Hoonakker, P.: The Impact of ICT on Quality of Working Life. Springer, Dordrecht (2014)
Kwon, S.J., Park, E., Kim, K.J.: What drives successful social networking services? A comparative analysis of user acceptance of Facebook and Twitter. Soc. Sci. J. 51(4), 534–544 (2014)
Leron, U., Hazzan, O.: Intuitive vs analytical thinking: four perspectives. Educ. Stud. Math. 71(3), 263–278 (2009)
Lin, C., Ha, L.: Subculture, critical mass, and technology use. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 50(3), 72–80 (2010)
Mitomo, H., Fuke, H., Bohlin, E. (eds.): The Smart Revolution Towards the Sustainable Digital Society: Beyond the Era of Convergence. Edward Elgar Publishing, Cheltenham (2015)
Park, E., Baek, S., Ohm, J., Chang, H.J.: Determinants of player acceptance of mobile social network games: an application of extended technology acceptance model. Telemat. Inform. 31(1), 3–15 (2014)
Park, E., Cho, Y., Han, J., Kwon, S.J.: Comprehensive approaches to user acceptance of Internet of Things in a smart home environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 4(6), 2342–2350 (2017)
Park, E., Kim, K.J.: User acceptance of long-term evolution (LTE) services: an application of extended technology acceptance model. Program 47(2), 188–205 (2013)
Park, E., Kim, K.J.: An integrated adoption model of mobile cloud services: exploration of key determinants and extension of technology acceptance model. Telemat. Inform. 31(3), 376–385 (2014)
Park, E., Kim, S., Kim, Y., Kwon, S.J.: Smart home services as the next mainstream of the ICT industry: determinants of the adoption of smart home services. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 17(1), 175–190 (2018)
Park, E., Ohm, J.: Factors influencing users’ employment of mobile map services. Telematics Inform. 31(2), 253–265 (2014)
Park, J.H., Kim, M.K.: Factors influencing the low usage of smart TV services by the terminal buyers in Korea. Telematics Inform. 33(4), 1130–1140 (2016)
Rahman, K.: “Wow! It’s cool”: the meaning of coolness in marketing. Mark. Intell. Plan. 31(6), 620–638 (2013)
Scaife, M., Rogers, Y.: External cognition: how do graphical representations work? Int. J. Hum Comput Stud. 45(2), 185–213 (1996)
Shang, R.A., Chen, Y.C., Shen, L.: Extrinsic versus intrinsic motivations for consumers to shop on-line. Inf. Manag. 42(3), 401–413 (2005)
Shin, D.H., Hwang, Y., Choo, H.: Smart TV: are they really smart in interacting with people? Understanding the interactivity of Korean Smart TV. Behav. Inf. Technol. 32(2), 156–172 (2013)
Sundar, S.S., Kim, J.: Interactivity and persuasion: influencing attitudes with information and involvement. J. Interact. Advert. 5(2), 5–18 (2005)
Sundar, S.S., Tamul, D.J., Wu, M.: Capturing “cool”: measures for assessing coolness of technological products. Int. J. Hum Comput Stud. 72(2), 169–180 (2014)
Tractinsky, N., Cokhavi, A., Kirschenbaum, M., Sharfi, T.: Evaluating the consistency of immediate aesthetic perceptions of web pages. Int. J. Hum Comput Stud. 64(11), 1071–1083 (2006)
Tractinsky, N., Shoval-Katz, A., Ikar, D.: What is beautiful is usable. Interact. Comput. 13(2), 127–145 (2000)
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M.G., Davis, G.B., Davis, F.D.: User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Q. 27(3), 425–478 (2003)
Woodson, W.E., Tillman, B., Tillman, P.: Human Factors Design Handbook: Information and Guidelines for the Design of Systems, Facilities, Equipment, and Products for Human Use. McGraw-Hill, New York (1992)
Yu, E., Hong, A., Hwang, J.: A socio-technical analysis of factors affecting the adoption of smart TV in Korea. Comput. Hum. Behav. 61, 89–102 (2016)
Zhou, T.: Understanding online community user participation: a social influence perspective. Internet Res. 21(1), 67–81 (2011)
Zhou, K.Z., Nakamoto, K.: How do enhanced and unique features affect new product preference? The moderating role of product familiarity. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 35(1), 53–62 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the National Program for Excellence in SW supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information and communications Technology Promotion) (2015-0-00914) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korean government (NRF-2017R1C1B5017437).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, E. Understanding the social adoption of smart TVs: the key role of product coolness. Univ Access Inf Soc 19, 595–602 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-019-00652-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-019-00652-3