Abstract
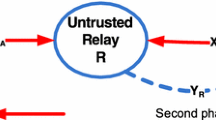
By considering an adversary jammer in a communication network, we investigate the secrecy performance of a cooperative wireless network comprised of a source, a destination and an untrusted amplify-and-forward relay. We assume that either the source or the destination, as well as the jammer are equipped with large-scale multiple antennas systems, while the rest are equipped with a single-antenna. To prevent the untrusted relay from intercepting the source message, the destination sends an intended jamming noise to the relay, which is referred to as destination-assisted cooperative jamming. On the other hand, the role of the jammer is to disturb the communication by transmitting jamming signals toward the untrusted relay. Given this system model, novel closed-form expressions are extracted for the ergodic secrecy rate (ESR) with Rayleigh fading channels. We further evaluate the ESR at high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and then determine the high SNR slope and power offset of the ESR to get some insights into the network. Next, with the aim of maximizing the instantaneous secrecy rate, we derive new closed-form solutions for the optimal power allocation (OPA). Numerical examples depict that the presented OPA considerably improves the system secrecy rate compared to the equal power allocation (EPA) which reveals the priority of our optimized network. We also illustrate that by increasing the number of jammer antennas, the ESR performance of both the OPA and EPA is reduced. The results state that unlike the EPA technique, increasing the number of source antennas enhances the ESR of the proposed OPA technique which reveals the priority of our OPA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukherjee, A., Fakoorian, S. A. A., Huang, J., & Swindlehurst, A. L. (2014). Principles of physical-layer security in multiuser wireless networks: A survey. IEEE Communication on Surveys and Tutorials, 16(3), 3062–3080.
Yang, N., Wang, L., Geraci, G., Elkashlan, M., Yuan, J., & Renzo, M. D. (2015). Safeguarding 5G wireless communication networks using physical layer security. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(4), 20–27.
Rodriguez, L. J., Tran, N. H., Duong, T. Q., Ngoc, T. L.-, Elkashlan, M., & Shetty, S. (2015). Physical layer security in wireless cooperative relay networks: State of the art and beyond. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(12), 32–39.
Kapetanovic, D., Zheng, G., & Rusek, F. (2015). Physical layer security for massive MIMO: An overview on passive eavesdropping and active attacks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(6), 21–27.
Wu, Y., Schober, R., Ng, D. W. K., Xiao, C., & Caire, G. (2016). Secure massive MIMO transmission with an active eavesdropper. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 62(7), 3880–3900.
Mukherjee, A., & Swindlehurst, A. L. (2011). A full-duplex active eavesdropper in MIMO wiretap channels: Construction and countermeasures. In Proceedings of Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA (pp. 265–269).
Zhou, X., Maham, B., & Hjorungnes, A. (2012). Pilot contamination for active eavesdropping. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(3), 903–907.
Rusek, F., Persson, D., Lau, B. K., Larsson, E. G., Marzetta, T. L., Edfors, O., et al. (2013). Scaling up MIMO: Opportunities and challenges with very large arrays. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 30(1), 40–46.
Larsson, E. G., Tufvesson, F., Edfors, O., & Marzetta, T. L. (2014). Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(2), 186–195.
He, X., & Yener, A. (Dec. 2008). Two-hop secure communication using an untrusted relay: A case for cooperative jamming. In Proceedings of IEEE Globecom, New Orleans, LA (pp. 1–5).
Khandaker, M. R. A., & Wong, K.-K. (2015). Masked beamforming in the presence of energy-harvesting eavesdroppers. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 10(1), 40–54.
Krikidis, I., Thompson, J. S., & McLaughlin, S. (2009). Relay selection for secure cooperative networks with jamming. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(10), 5003–5011.
Wang, L., Cai, Y., Zou, Y., Yang, W., & Hanzo, L. (2016). Joint relay and jammer selection improves the physical layer security in the face of CSI feedback delays. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(8), 6259–6274.
Wang, C., Wang, H.-M., & Xia, X.-G. (2015). Hybrid opportunistic relaying and jamming with power allocation for secure cooperative networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(2), 589–605.
Huang, J., Mukherjee, A., & Swindlehurst, A. L. (2013). Secure communication via an untrusted non-regenerative relay in fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(10), 2536–2550.
Sun, L., Zhang, T., Li, Y., & Niu, H. (2012). Performance study of two-hop amplify-and-forward systems with untrustworthy relay nodes. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(8), 3801–3807.
Wang, L., Elkashlan, M., Huang, J., Tran, N. H., & Duong, T. Q. (2014). Secure transmission with optimal power allocation in untrusted relay networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 3(3), 289–292.
Kuhestani, A., & Mohammadi, A. (2016). Destination-based cooperative jamming in untrusted amplify-and-forward relay networks: Resource allocation and performance study. IET Communications, 10(1), 1–23.
Kuhestani, A., Mohammadi, A., & Mohammadi, M. (2018). Joint relay selection and power allocation in large-scale MIMO systems with untrusted relays and passive eavesdroppers. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 13(2), 341–355.
Kuhestani, A., Mohammadi, A., Wong, K.-K., Yeoh, P. L., Moradikia, M., & Khandaker, M. R. (2018). Optimal power allocation by imperfect hardware analysis in untrusted relaying networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 17(7), 4302–4314.
Atapattu, S., Ross, N., Jing, Y., & Premaratne, M. (2019). Source-based jamming for physical-layer security on untrusted full-duplex relay. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(5), 842–846.
Kuhestani, A., Mohammadi, A., & Yeoh, P. L. (2018). Security-reliability trade-off in cyber-physical cooperative systems with non-ideal untrusted relaying. In 2018 IEEE 4th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Singapore, 2018 (pp. 552–557).
Kuhestani, A., Yeoh, P. L., & Mohammadi, A. (2017). Optimal power allocation and secrecy sum rate in two-way untrusted relaying. In 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore (pp. 1–6).
Do, T. T., Ngo, H. Q., Duong, T. Q., Oechtering, T. J., & Skoglund, M. (2017). Massive MIMO pilot retransmission strategies for robustification against jamming. IEEE Communications Letters, 6(1), 58–61.
Amariucai, G. T., & Wei, S. (2012). Half-duplex active eavesdropping in fast fading channels: A block-Markov Wyner secrecy encoding scheme. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 58(7), 4660–4677.
Karlsson, M., & Larsson, E. G. (Nov. 2014). Massive MIMO as a cyber-weapon. In Proceedings of Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA (pp. 661–665).
Nguyen, N., Ngo, H. Q., Duong, T. Q., Tuan, H. D., & da Costa, D. B. (2017). Full-duplex cyber-weapon with massive arrays. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 65(12), 5544–5558.
El Shafie, A., Tourki, K., Ding, Z., & Al-Dhahir, N. (2017). Probabilistic jamming/eavesdropping attacks to confuse a buffer-aided transmitter receiver pair. IEEE Communications Letters, 21(7), 549–1552.
Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., Li, M., Yan, Q., & Leung, V. C. M. (2016). Physical layer security issues in interference- alignment-based wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 54(8), 162–168.
Zhao, N., Cao, Y., Yu, F. R., Chen, Y., Jin, M., & Leung, V. C. M. (2018). Artificial noise assisted secure interference networks with wireless power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(2), 1087–1098.
Guo, J., Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., Liu, X., & Leung, V. C. M. (2017). Exploiting adversarial jamming signals for energy harvesting in interference networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(2), 1267–1280.
Chen, J., Chen, H., Zhang, H., & Zhao, F. (2016). Spectral-energy efficiency tradeoff in relay-aided massive MIMO cellular networks with pilot contamination. IEEE Access, 4, 5234–5242.
Gradshteyn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (2007). Table of integrals, series, and products (7th ed.). New York: Academic.
Zhou, X., Niyato, D., & Hjrungnes, A. (2011). Optimizing training-based transmission against smart jamming. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(6), 2644–2655.
Moon, J., Wong, T. F., & Shea, J. M. (2006). Pilot-assisted and blind joint data detection and channel estimation in partial-time jamming. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 54(11), 2092–2102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saedi, H., Mohammadi, A. & Kuhestani, A. Characterization of untrusted relaying networks in the presence of an adversary jammer. Wireless Netw 26, 2113–2124 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02049-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02049-9