Abstract
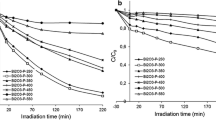
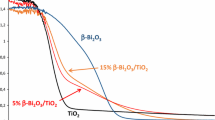
The morphology of a series of Bi–B co-doped titanium oxide photocatalysts and its optical properties were characterized. The results suggested that boron and bismuth as co-dopants were incorporated into the framework of titanium matrix. For the B and Bi-doped TiO2 samples, surface area decreased while the Bi content increased. Based on the photoluminescence spectra, a decrease in recombination rate of photogenerated carriers was observed with the increasing amount from 0.5 to 3 mol% of Bi in Bi–B–TiO2 composites. The most active photocatalyst in 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) photodegradation was 3 mol% of Bi in Bi–B–TiO2. The effects of operating parameters: pH, drug concentration and natural organic matter presence (NOM) in the effluent from wastewater treatment plant, were investigated. The highest efficiency of 5-FU photodegradation was observed at neutral pH for the drug concentration equal to 1 mg/L and photocatalyst of 0.05 g/L. While in distilled water solutions, the catalyst showed good removal efficiency of the drug, the process was totally inhibited by NOM in the complex matrix which was the treated sewage, what could be connected with the internal filter and scavenging effect. Based on the identification of organic and inorganic by-products of the photooxidation, the pathway of 5-FU degradation was proposed. The mineralization was poor (5–7%) in the case of both 3Bi–B–TiO2 and pure TiO2 for the drug of 50 mg/L, but photocatalytic oxidation of drug led to non-toxic products toward Lemma minor.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsin B, Roberts MW (1993) Formation of an oxy-chloride overlayer at a Bi(0001) surface. Spectrosc Lett 27(1):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/00387019408002513
Aguilar CA, Montalvo C, Zermeño BB, Cerón RM, Cerón JG, Anguebes F, Ramírez MA (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of acetaminophen, tergitol and nonylphenol with catalysts TiO2/Ag under UV and Vis light. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(2):843–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1707-x
Bagwasi S, Tian B, Zhang J, Nasir M (2013) Synthesis, characterization and application of bismuth and boron Co-doped TiO2: a visible light active photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 217:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.080
Besse J-P, Latour J-F, Garric J (2012) Anticancer drugs in surface waters: what can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ Int 39:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.10.002
Bukkitgar SD, Shetti NP (2016) Electrochemical behavior of anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil at carbon paste electrode and its analytical application. J Anal Sci Technol 7:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-015-0080-3
Fabiańska A, Białk-Bielińska A, Stepnowski P, Stolte S, Siedlecka EM (2014) Electrochemical degradation of sulfonamides at BDD electrode: kinetics, reaction pathway and eco-toxicity evaluation. J Hazard Mater 280:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.050
Fiszka Borzyszkowska A, Pieczyńska A, Ofiarska A, Nikiforow K, Stepnowski P, Siedlecka EM (2016) Bi–B–TiO2-based photocatalytic decomposition of cytostatic drugs under simulated sunlight treatments. Sep Purif Technol 169:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.012
Galenda A, Crociani L, El Habra N, Favaro M, Natile MM, Rossetto G (2014) Effect of reaction conditions on methyl red degradation mediated by boron and nitrogen doped TiO2. Appl Surf Sci 314:919–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.06.175
Ghafuria Y, Yunesian M, Nabizadeh R, Mesdaghinia A, Dehghani MH, Alimohammadi M (2018) Environmental risk assessment of platinum cytotoxic drugs: a focus on toxicity characterization of hospital effluents. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15(9):1983–1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1517-6
Giraldo A, Penuela G, Torres-Palma R, Pino N, Palominos R, Mansilla H (2010) Degradation of the antibiotic oxolinic acid by photocatalysis with TiO2 in suspension. Water Res 44:5158–5167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.011
Gould JP, Richards JT, Miles MG (1984) The kinetics and primary products of uracil chlorination. Water Res 18:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(84)90070-8
Grey IE, Li C, MacRae DM, Bursill LA (1996) Boron incorporation into rutile. Phase equilibria and structure considerations. J Solid State Chem 127:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1996.0380
Hu Y, Cao Y, Wang P, Li D, Chen W, He Y, Fu X, Shao Y, Zheng Y (2012) A new perspective for effect of Bi on the photocatalytic activity of Bi-doped TiO2. Appl Catal B Environ 125:294–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.040
Jiang X, Su L, Yu P, Guo X, Tang H, Xu X, Zheng L, Li H, Xu J (2013) Broadband photoluminescence of Bi2O3–GeO2 binary systems: glass, glass-ceramics and crystals. Laser Phys 23(10):105812. https://doi.org/10.1088/1054-660X/23/10/105812
Kim YI, Atherton SJ, Brigham ES, Mallouk TE (1993) Sensitized layered metal oxide semiconductor particles for photochemical hydrogen evolution from nonsacrificial electron donors. J Phys Chem B 97:11802–11810. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100147a038
Koltsakidou Α, Antonopoulou M, Sykiotou M, Εvgenidou Ε, Konstantinou I, Lambropoulou DA (2017) Photo-fenton and fenton-like processes for the treatment of the antineoplastic drug 5-fluorouracil under simulated solar radiation. Environ Sci Pollut R 24(5):4791–4800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8138-3
Kovalova L, Siegrist H, von Gunten U, Eugster J, Hagenbuch M, Wittmer A, Moser R, McArdell CS (2013) Elimination of micropollutants during post-treatment of hospital wastewater with powdered activated carbon, ozone, and UV. Environ Sci Technol 47:7899–7908. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400708w
Li H, Liu J, Qian J, Li Q, Yang J (2014a) Preparation of Bi-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their visible light photocatalytic performance. Chin J Catal 35:1578–1589. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60124-8
Li Y-F, Zhang M, Guo D-L, He F-X, Li Y-Z, Wang A-J (2014b) Facile solvothermal synthesis of BiOCl/ZnO heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Nanomater 2014:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/347061
Lin AY-C, Lin HH-H (2014) Photocatalytic oxidation of 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide via UV/TiO2 in an aqueous environment. Water Res 48:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.011
Lin AY-C, Wang X-H, Lee W-N (2013) Phototransformation determines the fate of 5 fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide in natural surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 47:4104–4411. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304976q
Lutterbeck CA, Wilde ML, Baginska E, Leder C, Machado ÊL, Kümmerer K (2015) Degradation of 5-FU by means of advanced (photo)oxidation processes: UV/H2O2, UV/Fe2+/H2O2, and UV/TiO2—comparison of transformation products, ready biodegradability and toxicity. Sci Total Environ 527–528:232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.111
Murcia-López S, Hidalgo MC, Navío JA (2011) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of Bi-doped TiO2 photocatalysts under simulated solar irradiation. Appl Catal A Gen 404(1–2):59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.07.008
Nasirian M, Lin YP, Bustillo-Lecompte CF, Mehrvar M (2018) Enhancement of photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide using non-metal doping methods under visible light: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15(9):2009–2032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1618-2
Ofiarska A, Pieczyńska A, Fiszka Borzyszkowska A, Stepnowski P, Siedlecka EM (2016) Pt–TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of the cytostatic drugs ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide under artificial sunlight. Chem Eng J 285:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.109
Ren M, Drosos M, Frimmel FH (2018) inhibitory effect of NOM in photocatalysis process: explanation and resolution. Chem Eng J 334:968–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.099
Su K, Ai Z, Zhang L (2012) Efficient visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of pentachlorophenol with Bi2O3/TiO2 − xBx. J Phys Chem C 116(32):17118–17123. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp305432g
Subramonian W, Wu TY, Chai S-P (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of industrial pulp and paper mill effluent using synthesized magnetic Fe2O3–TiO2: treatment efficiency and characterizations of reused photocatalyst. J Environ Manag 187:298–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.024
Tan C, Zhu G, Hojamberdiev M, Xu C, Liang J, Luo P, Liu Y (2013) Room temperature synthesis and photocatalytic activity of magnetically recoverable Fe3O4/BiOCl nanocomposite photocatalysts. J Clust Sci 24:1115–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-013-0602-3
Teh CY, Wu TY, Juan JC (2017) An application of ultrasound technology in synthesis of titania-based photocatalyst for degrading pollutant. Chem Eng J 317:586–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.001
Zaleska A, Grabowska E, Sobczak JW, Gazda M, Hupka J (2009) Photocatalytic activity of boron-modified TiO2 under visible light: the effect of boron content, calcination temperature and TiO2 matrix. Appl Catal B Environ 89:469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.01.005
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education under the grant DS 530-8626-D596-18-1F, BMN 538-8626-B369-17, BMN 538-8375-B402-17 and BMN 538-8626-B409-17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiszka Borzyszkowska, A., Pieczyńska, A., Ofiarska, A. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of 5-fluorouracil in an aqueous environment via Bi–B co-doped TiO2 under artificial sunlight. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 2163–2176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02604-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02604-z